Abstract
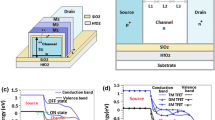
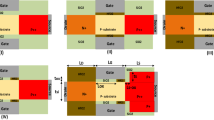
The gate tunneling current in ultrathin gate dielectric NMOSFETs with positive gate bias is due to the tunneling of electrons from the conduction and valence bands of the substrate. Valence-band electrons tunnel from the substrate of NMOS devices when the valence-band edge in the substrate rises above the conduction-band edge in the substrate. This paper reports experimental trends in the contribution of valence-band electrons tunneling to the gate current of NMOSFETs with gate oxides composed of pure SiO2. The large gate tunneling current can be reduced by replacing the conventional SiO2 gate dielectric with alternative dielectrics with larger dielectric constants. This paper reports the effect of replacing SiO2 with alternative dielectrics on the contribution of valence-band electron tunneling to the gate current. Simulations are carried out for composite SiO2/Ta2O5 gate dielectric structures.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. Modeli, Appl. Surf. Sci., 30, 298 (1987).
B. Eitan and A. Kolodny, Appl. Phys. Lett., 43, 106 (1983).
B. Majkusiak, IEEE Trans. on Electron Devices, 37, 1087 (1990).
C. Chang, et al., J. Appl. Phys., 57, 302 (1985).
C. Chang, et al., p. 194, IEDM, 1983.
C. Bowen, et al., p. 869, IEDM, 1997.
A. Shanware, et al., submitted to IEEE Electron Device Letters.
Q. Lu, et al., IEEE Electron Device Lett., 19, 341 (1998).
D. Park, et al., IEEE Electron Device Lett., 19, 441 (1998).
I. Kizilyalli, et al., IEEE Electron Device Lett., 19, 423 (1998).
P. K. Roy, et al., Appl. Phys. Lett., 72, 2835 (1998).
E. Vogel, et al., IEEE Trans. on Electron Devices, 45, 1350 (1998).
J. R. Hauser and K. Ahmed, p. 235, International Conference on Characterization and Metrology for ULSI Technology - 1998, Edited by D. G. Seiler, A. C. Diebold, W. M. Bullis, T. J. Shaffner, R. McDonald, and E. J. Walters, American Institute of Physics, 1998.
S. Zaima, et al., J. Electrochem. Soc., 137, 853 (1990).
J. Simmons, J. Appl. Phys., 34, 1793 (1963).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shanware, A., Massoud, H.Z., Vogel, E. et al. Comparison of Valence-Band Tunneling in Pure SiO2, Composite SiO2 /Ta2O5, and Pure Ta2O5, in Mosfets with 1.0 nm-Thick SiO2-Equivalent Gate Dielectrics. MRS Online Proceedings Library 567, 515–520 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1557/PROC-567-515
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/PROC-567-515