Abstract
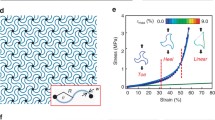
In this paper, we describe unique thermally responsive polymer system based on nanotube-elastomers dispersed with core-shell expanding microspheres (phase-change material). Upon thermal or infrared stimuli, liquid hydrocarbon cores encapsulated within the microspheres vaporize, expanding the surrounding shells and stretching the matrix. Microsphere transformation resulted in visible dimensional changes associated with macroscopic volume increase (>500%), reduction in density (>80%), and increase in elastic modulus (>675%). Additionally, electrically conductive nanotubes allowed for expansion dependent electrical responses. We present our new findings on expansion dependent superhydrophobicity in these materials and present some outlook and comparison of our stimuli responsive polymers with other material systems for future origami based applications.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. V. Ahir and E. M. Terentjev, Nat Mater 4 (6), 491–495 (2005).
E. Hawkes, B. An, N. M. Benbernou, H. Tanaka, S. Kim, E. D. Demaine, D. Rus and R. J. Wood, P Natl Acad Sci USA 107 (28), 12441–12445 (2010).
S. Felton, M. Tolley, E. Demaine, D. Rus and R. Wood, Science 345 (6197), 644–646 (2014).
E. Smela, O. Inganas and I. Lundstrom, Science 268 (5218), 1735–1738 (1995).
E. W. H. Jager, O. Inganas and I. Lundstrom, Science 288 (5475), 2335–2338 (2000).
E. W. H. Jager, E. Smela and O. Inganas, Science 290 (5496), 1540–1545 (2000).
J. H. So, A. S. Tayi, F. Guder and G. M. Whitesides, Adv Funct Mater 24 (45), 7197–7204 (2014).
M. Yoshida and J. Lahann, Acs Nano 2 (6), 1101–1107 (2008).
M. P. Thompson, M. P. Chien, T. H. Ku, A. M. Rush and N. C. Gianneschi, Nano Lett 10 (7), 2690–2693 (2010).
P. Y. Chen, J. McKittrick and M. A. Meyers, Prog Mater Sci 57 (8), 1492–1704 (2012).
J. Loomis, P. Xu and B. Panchapakesan, Nanotechnology 24 (18) (2013).
L. R. G. Treloar, The Physics of Rubber Elasticity. (Oxford University Press, Oxford, 2005).
J. Fritzsche and M. Kluppel, Journal of Physics: Condensed Matter 23 (3), 035104 (035111 pp.) (2011).
H. J. Ensikat, P. Ditsche-Kuru, C. Neinhuis and W. Barthlott, Beilstein J Nanotech 2, 152–161 (2011).
W. D. Zhang, L. Shen, I. Y. Phang and T. Liu, Macromolecules 37 (2), 256-259 (2004).
C. D. Onal, R. J. Wood and D. Rus, 2011 Ieee International Conference on Robotics and Automation (Icra) (2011).
T. S. Kelby, M. Wang and W. T. S. Huck, Adv Funct Mater 21 (4), 652–657 (2011).
T. S. Kelby and W. T. S. Huck, Macromolecules 43 (12), 5382–5386 (2010).
S. M. Felton, M. T. Tolley, B. Shin, C. D. Onal, E. D. Demaine, D. Rus and R. J. Wood, Soft Matter 9 (32), 7688–7694 (2013).
T. G. Leong, C. L. Randall, B. R. Benson, N. Bassik, G. M. Stern and D. H. Gracias, P Natl Acad Sci USA 106 (3), 703–708 (2009).
V. Luchnikov, O. Sydorenko and M. Stamm, Adv Mater 17 (9), 1177-+ (2005).
J. J. Guan, H. Y. He, D. J. Hansford and L. J. Lee, J Phys Chem B 109 (49), 23134–23137 (2005).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Panchapakesan, B., Onal, C. & Loomis, J. Programmable Skins based on Core-Shell Microsphere/Nanotube/Polymer Composites. MRS Online Proceedings Library 1800, 10 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1557/opl.2015.781
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/opl.2015.781