Abstract
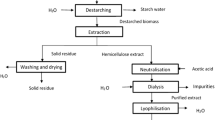
Arabinoxylans are polysaccharides constituted of a linear backbone of xylose in which arabinose substituents are attached, some ferulic acid esterifies arabinose. Arabinoxylan can form covalent gels by oxidative coupling of ferulic acid. Arabinoxylan gels could have potential applications for colon-specific biomolecules delivery due to their macroporous structure, and their aqueous environment and their dietary fiber nature. Lycopene has received increasing attention for its possible role in the prevention of colon cancer. It has been previously reported that arabinoxylan gels could be formed in presence of lycopene with no detriment on the lycopene antioxidant activity. The objective of this research was to investigate the in vitro degradation of arabinoxylan gels (AX gels) by two human colon bacterial species (Bacteroides ovatus and Bifidobacterium longum). Bacterial counts (CFU ml−1) and metabolic heat production (p) followed a similar pattern with a high response during the first 24 h at 37 °C. A regression model related CFU ml−1 and p (r2 = 0.98). These results show that AX gels could be carriers for lycopene delivery in colon due structure degradation by gut microbiota.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fincher G.B.; Stone B.A. Aust. J. Biol. Sci. 1974, 27, 117–132.
Izydorczyk M.S.; Biliaderis C.G. Carbohydr. Polym. 1995, 28, 33–48.
Figueroa-Espinoza M.C.; Rouau X. Cereal Chem. 1998, 75, 259–265.
Carvajal-Millan E.; Landillon V.; Morel M.H.; Rouau X.; Doublier J.L.; Micard V. Biomacromolecules 2005, 6, 309–317.
Van Laere K.M.J.; Hartemink R.; Bosveld M.; Schols H.A.; Voragen A.G.J. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2000, 48, 1644–1652.
Hopkins M.J.; Englyst H.N.; Macfarlane S.; Furrie E.; Macfarlane G.T.; McBain A.J. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2003, 69, 6354–6360.
Teeling H.; Cypionka H. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 1997, 48, 275–279.
Andlid T.; Blomberg L.; Gustafsson L.; Blomberg A. Syst. Appl. Microbiol. 1999, 22, 145–155.
Berridge N.J.; Cousins C.M.; Cliffe A.J. J. Dairy Res. 1974, 41, 203–215.
Gardea A.A.; Carvajal-Millan E.; Higuera-Ciapara I.; Figueroa C.; Molina-Corral J.; Rascon-Chu A.; Orozco A.; Inda A. Thermochimica Acta 2002, 394, 179–184.
Martensson O.; Oste R.; Holst O. Food Res. Int. 2002, 35, 775–784.
SAS. 1992. Version 6.8, SAS Institute Inc.
Crittenden R.; Karppinen S.; Ojanen S.; Tenkanen M.; Fagerström R.; Mättö J.; Saarela M.; Mattila-Sandholm T.; Poutanen K. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2002, 82, 781–789.
Mirande C.; Mosoni P.; Béra-Maillet C.; Bernalier-Donadille A.; Forano E. App. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2010, 87, 2097–2105.
Vardakou M.; Nueno Palop C.; Christakopoulos P.; Faulds C.B.; Gasson M.A.; Narbad A. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2008, 123, 166–170.
Broekaert W.; Courtin C.M.; Verbeke K.; Van de Wiele T.; Verstraete W.; Delcour J.A. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2011, 51, 178–194.
Acknowledgments
The authors are pleased to acknowledge Valérie Micard (SupAgro, Montpellier, France) for collaboration in this project; Alma C. Campa-Mada and Karla G. Martínez-Robinson (CIAD, A.C.) for their technical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rascón-Chu, A., Martinez-López, A., Berlanga-Reyes, C. et al. Arabinoxylans Gels as Lycopene Carriers: in vitro Degradation by Colonic Bacteria. MRS Online Proceedings Library 1487, 26–32 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1557/opl.2012.1527
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/opl.2012.1527