Abstract
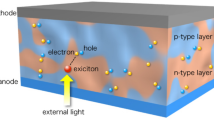
Carbon nanotubes (CNTs) are one-dimensional nanostructures with unique properties. This article discusses why CNTs provide an ideal basis for a future carbonbased nanoelectronic technology, focusing specifically on single-carbon-nanotube fieldeffect transistors (CNT-FETs). Results of transport experiments and theoretical modeling will be used to address such issues as the nature of the switching mechanism, the role of the metal contacts, the role of the environment, the FET scaling properties, and the use of these findings to produce high-performance p-type, n-type, and ambipolar CNT-FETs and simple intra-nanotube circuits. CNTs are also direct-gap nanostructures that show promise in the field of optoelectronics. This article briefly reviews their optical behavior and presents results that show that ambipolar CNT-FETs can be used to produce electrically controlled light sources based on radiative electron–hole recombination. The reverse process—that is, the generation of photocurrents by the irradiation of single CNT-FETs—and photoconductivity spectra of individual CNTs are also demonstrated.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
S.M. Sze, Physics of Semiconducting Devices (Wiley, New York, 1981).
M.S. Dresselhaus, G. Dresselhaus, and R. Saito, Phys. Rev. B 45 (1992) p. 6234.
J.W. Mintmire, B.I. Dunlap, and C.T. White, Phys. Rev. Lett. 68 (1992) p. 631.
M.S. Dresselhaus, G. Dresselhaus, and Ph. Avouris, eds., Carbon Nanotubes: Synthesis, Structure, Properties and Applications (Springer-Verlag, Berlin, 2001).
Y. Imry and R. Landauer, Rev. Mod. Phys. 71 1999) p. S306.
S. Datta, Electronic Transport in Mesoscopic Systems (Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK, 1995).
P.L. McEuen, M. Bockrath, D.H. Cobden, Y.-G. Yoon, and S.G. Louie, Phys. Rev. Lett. 83 (1999) p. 5098.
L. Wenjie, M. Bockrath, D. Bozovic, J.H. Hafner, M. Tinkman, and P. Hongkum, Nature 411 (2001) p. 665.
J. Kong, E. Yenilmez, T.W. Tombler, W. Kim, H. Dai, R.B. Laughlin, L. Liu, C.S. Jayanthi, and S.Y. Wu, Phys. Rev. Lett. 87 106801 (2001).
J. Appenzeller, R. Martel, Ph. Avouris, H. Stahl, and B. Lengeler, Appl. Phys. Lett. 78 (2001) p. 3313.
D. Mann, A. Javey, J. Kong, Q. Wang, and H. Dai, Nano Lett. 3 (2003) p. 1541.
J.-Y. Park, S. Rosenblatt, Y. Yaish, V. Sazonova, H. Ustunel, S. Braig, T.A. Arias, D.W. Brouwer, and P.L. McEuen, “Electron-Phonon Scattering in Metallic Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes,” arXiv.org e-print archive, cond-mat/0309641_(accessed March 2004).
A.Z. Yao, C.L. Kane, and C. Dekker, Phys. Rev. Lett. 61 (2000) p. 2941.
A. Javey, J. Guo, M. Paulson, Q. Wang, D. Mann, M. Lundstrom, and H. Dai, “High-Field, Quasi-Ballistic Transport in Short Carbon Nanotubes,” arXiv.org e-print archive, cond-mat/0309242 (accessed March 2004).
P.G. Collins, M. Hersam, M. Arnold, R. Martel, and Ph. Avouris, Phys. Rev. Lett. 86 (2001) p. 3128.
P.G. Collins, M.S. Arnold, and Ph. Avouris, Science 292 (2001) p. 706.
S. Wind, J. Appenzeller, and Ph. Avouris, Phys. Rev. Lett. 91 058301 (2003).
Y. Yaish, J.-Y. Park, S. Rosenblatt, V. Sazonova, M. Brink, and P.L. McEuen, “Electrical Nanoprobing of Semiconducting Carbon Nanotubes Using an Atomic Force Microscope,” arXiv.org e-print archive, cond-mat/0305108 (accessed March 2004).
A. Javey, J. Guo, Q. Wang, M. Lundstrom, and H. Dai, Nature 424 (2003) p. 654.
Ph. Avouris, J. Appenzeller, R. Martel, and S.J. Wind, Proc. IEEE 91 (2003) p. 1772.
S. Tans, S. Verschueren, and C. Dekker, Nature 393 (1998) p. 49.
R. Martel, T. Schmidt, H.R. Shea, T. Hertel, and Ph. Avouris, Appl. Phys. Lett. 73 (1998) p. 2447.
H.T. Soh, C.F. Quate, A.F. Morpurgo, C. Marcus, J. Kong, and H. Dai, App. Phys. Lett. 75 (1999) p. 627.
R. Martel, H.-S.P. Wong, K. Chan, and Ph. Avouris, in Proc. IEDM 2001 (Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers, Piscataway, NJ, 2001) p. 159.
P.L. McEuen, M.S. Fuhrer, and H. Park, IEEE Trans. Nanotechnol. 1 (2002) p. 78 and references therein.
S.J. Wind, J. Appenzeller, R. Martel, and Ph. Avouris, Appl. Phys. Lett. 80 (2002) p. 3817.
A. Javey, H. Kim, M. Brink, Q. Wang, A. Ural, J. Guo, P. McIntyre, P. McEuen, M. Lundstrom, and H. Dai, Nat. Mater. 1 (2002) p. 241.
J. Appenzeller, J. Knoch, V. Derycke, R. Martel, S. Wind, and Ph. Avouris, Phys. Rev. Lett. 89 126801 (2002).
A. Javey, J. Guo, Q. Wang, M. Lundstrom, and H.J. Dai, Nature 424 (2003) p. 654.
M. Radosavljevic, J. Appenzeller, and Ph. Avouris, Appl. Phys. Lett. 84 (2004) p. 3693.
Y.-C. Tseng, P. Xuan, A. Javey, R. Malloy, Q. Wang, J. Bokor, and H. Dai, Nano Lett. 2004) in press.
A. Rochefort, M. Di Ventro and Ph. Avouris, Appl. Phys. Lett. 78 (2001) p. 2521.
T. Durkop, S.A. Getty, E. Cobas, and M.S. Fuhrer, Nano Lett. 4 (2004) p. 35.
R. Martel, V. Derycke, C. Lavoie, J. Appenzeller, K. Chen, J. Tersoff, and Ph. Avouris, Phys. Rev. Lett. 87 256805 (2001).
J. Appenzeller, M. Radosavljevic, J. Knoch, and Ph. Avouris, Phys. Rev. Lett. 92 648301 (2004).
Ph. Avouris, I.-W. Lyo, and Y. Hasegawa, J. Vac. Sci. Technol., A 11 (1993) p. 1725.
F. Leonard and J. Tersoff, Phys. Rev. Lett. 84 (2000) p. 4693.
M. Freitag, M. Radosavljevic, Y. Zhou, A.T. Johnson, and W.F. Smith, Appl. Phys. Lett. 79 (2001) p. 3326.
S. Heinze, J. Tersoff, R. Martel, V. Derycke, J. Appenzeller, and Ph. Avouris, Phys. Rev. Lett. 89 106801 (2002).
S.J. Wind, J. Appenzeller, and Ph. Avouris, Phys. Rev. Lett. 91 058301 (2003).
N.D. Lang and Ph. Avouris, Phys. Rev. Lett. 84 (2000) p. 358; Phys. Rev. B 64 125323 (2001).
P. Nikolaev, M.J. Bronikowski, R.K. Bradley, F. Rohmund, D.T. Colbert, K.A. Smith, and R.E. Smalley, Chem. Phys. Lett. 313 (1999) p. 91.
A. Thess, R. Lee, P. Nikolaev, H. Dai, P. Petit, J. Robert, X. Chunhui, L. Young Hee, K. Seong Gon, A.G. Rinzler, D.T. Colbert, G.E. Scuseria, D. Tomanek, J.E. Fischer, and R.E. Smalley, Science 273 (1996) p. 483.
M. Radosavljevic, S. Heinze, J. Tersoff, and Ph. Avouris, Appl. Phys. Lett. 83 (2003) p. 2435.
S. Heinze, J. Tersoff, and Ph. Avouris, Appl. Phys. Lett. 83 (2003) p. 5038.
Y.-M. Lin, J. Appenzeller, and Ph. Avouris, Nano Lett. 4 (2004) p. 947.
P.G. Collins, K. Bradley, M. Ishigami, and A. Zettl, Science 287 (2000) p. 1801.
S.-H. Jhi, S.G. Louie, and M.L. Cohen, Phys. Rev. Lett. 85 (2000) p. 1710.
V. Derycke, R. Martel, J. Appenzeller, and Ph. Avouris, Appl. Phys. Lett. 80 (2002) p. 2773.
X. Cui, M. Freitag, R. Martel, L. Brus, and Ph. Avouris, Nano Lett. 3 (2003) p. 783.
S. Heinze, M. Radosavljevic, J. Tersoff, and Ph. Avouris, Phys. Rev. B 68 235418 (2003).
V. Derycke, R. Martel, J. Appenzeller, and Ph. Avouris, Nano Lett. 1 (2001) p. 453.
A. Bachtold, P. Hadley, T. Nakanishi, and C. Dekker, Science 294 (2001) p. 1317.
A. Javey, Q. Wang, A. Urai, Y. Li, and H. Dai, Nano Lett. 2 (2002) p. 929.
D.J. Frank and J. Appenzeller, IEEE Electron Device Lett. 25 (2004) p. 34.
M. Ishida, S. Mizuno, T. Yoshihino, Y. Saito, and A. Nakamura, J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 68 (1999) p. 3131
R. Saito and H. Kataura, in Carbon Nanotubes: Synthesis, Structure, Properties and Applications, edited by M.S. Dresselhaus, G. Dresselhaus, and Ph. Avouris (Springer-Verlag, Berlin, 2001) p. 213.
M.J. O’Connell, S.M. Bachilo, C.B. Huffman, V.C. Moore, M.S. Strano, E.H. Haroz, K.L. Rialon, P.J. Boul, W.H. Noon, C. Kittrell, J. Ma, R.H. Hauge, R.E. Smalley, and R.B. Weisman, Science 297 (2002) p. 2361.
S.M. Bachilo, M.S. Strano, C. Kittrell, R.H. Hauge, R.E. Smalley, and R.B. Weisman, Science 298 (2002) p. 2361.
A. Hagen and T. Hertel, Nano Lett. 3 (2003) p. 383.
J. Lefebvre, Y. Homma, and P. Finnie, Phys. Rev. Lett. 90 217401 (2003).
T. Ando, J. Phys. Soc. Jpn 66 (1996) p. 1066.
T.G. Pedersen, Phys. Rev. B 67 073401 (2003).
C.L. Kane and E.J. Mele, Phys. Rev. Lett. 90 207401 (2003).
C.D. Spataru, S. Ismail-Beigi, L.X. Benedict, and S.G. Louie, Phys. Rev. Lett. 92 077402 (2004).
V. Perebeinos, J. Tersoff, and Ph. Avouris, “Scaling of Excitons in Carbon Nanotubes,” arXiv e-print archive, cond-mat/0402091 (accessed March 2004); Phys. Rev. Lett. 2004) in press.
A. Fujuwara, Y. Matsuoka, H. Suematsu, N. Ogata, et al. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys., Part 1 40 2001) p. L1229.
Y. Yamada, N. Naka, N. Nagasawa, Z.M. Li, and Z.K. Tang, Physica B 323 (2002) p. 239.
Y. Zhang and S. Iijima, Phys. Rev. Lett. 82 (1999) p. 3472.
M. Freitag, Y. Martin, J.A. Misewich, R. Martel, and Ph. Avouris, Nano Lett. 3 (2003) p. 1067.
J.A. Misewich, R. Martel, Ph. Avouris, J.C. Tsang, S. Heinze, and J. Tersoff, Science 300 (2003) p. 783.
M. Freitag, J. Chen, A. Stein, T. Tsang, J. Misewich, R. Martel, and Ph. Avouris, Nano Lett. 2004) in press.
M. Freitag, J. Chen, J. Tsang, Q. Fu, J. Liu, and Ph. Avouris, Phys. Rev. Lett. 2004) submitted for publication.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Avouris, P. Carbon Nanotube Electronics and Optoelectronics. MRS Bulletin 29, 403–410 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1557/mrs2004.123
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/mrs2004.123