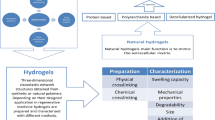
Abstract
Bioengineered hydrogels enable systematic variation of mechanical and biochemical properties, resulting in the identification of optimal in vitro three-dimensional culture conditions for individual cell types. As the scientific community attempts to mimic and study more complex biologic processes, hydrogel design has become multi-faceted. To mimic organ and tissue heterogeneity in terms of spatial arrangement and temporal changes, hydrogels with spatiotemporal control over mechanical and biochemical properties are needed. In this prospective article, we present studies that focus on the development of hydrogels with dynamic mechanical and biochemical properties, highlighting the discoveries made using these scaffolds.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. Nowak, U. Freudenberg, M.V. Tsurkan, C. Werner, and K.R. Levental: Modular GAG-matrices to promote mammary epithelial morphogenesis in vitro. Biomaterials 112, 20 (2017).
A. Ranga, M. Girgin, A. Meinhardt, D. Eberle, M. Caiazzo, E.M. Tanaka, and M.P. Lutolf: Neural tube morphogenesis in synthetic 3D microenvironments. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 113, E6831 (2016).
E. Moeendarbary, I.P. Weber, G.K. Sheridan, D.E. Koser, S. Soleman, B. Haenzi, E.J. Bradbury, J. Fawcett, and K. Franze: The soft mechanical signature of glial scars in the central nervous system. Nat. Commun. 8, 14787 (2017).
T. Mammoto, A. Mammoto, and D.E. Ingber: Mechanobiology and developmental control. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 29, 27 (2013).
C.-P. Heisenberg and Y. Bellaïche: Forces in tissue morphogenesis and patterning. Cell 153, 948 (2013).
N. Bouchonville, M. Meyer, C. Gaude, E. Gay, D. Ratel, A. Nicolas, C.A. Reinhart-King, S.S. Margulies, M. Dembo, D. Boettiger, D.A. Hammer, V.M. Weaver, Y. Shi, and S.P. Robinson: AFM mapping of the elastic properties of brain tissue reveals kPa μm−1 gradients of rigidity. Soft Mat. 12, 6232 (2016).
S. Budday, G. Sommer, C. Birkl, C. Langkammer, J. Haybaeck, J. Kohnert, M. Bauer, F. Paulsen, P. Steinmann, E. Kuhl, and G.A. Holzapfel: Mechanical characterization of human brain tissue. Acta Biomater. 48, 319 (2017).
J.Y. Rho, R.B. Ashman, and C.H. Turner: Young’s modulus of trabecular and cortical bone material: Ultrasonic and microtensile measurements. J. Biomech. 26, 111 (1993).
E. Hoenig, U. Leicht, T. Winkler, G. Mielke, K. Beck, F. Peters, A.F. Schilling, and M.M. Morlock: Mechanical properties of native and tissue-engineered cartilage depend on carrier permeability: a bioreactor study. Tissue Eng. A 19, 1534 (2013).
L.E. Bilston: Brain Tissue Mechanical Properties in Biological and Medical Physics, Biomedical Engineering (Springer, New York, USA, 2011, vol. 69).
A.J. Engler, S. Sen, H.L. Sweeney, and D.E. Discher: Matrix elasticity directs stem cell lineage specification. Cell 126, 677 (2006).
B. Trappmann, J.E. Gautrot, J.T. Connelly, D.G.T. Strange, Y. Li, M.L. Oyen, M.A. Cohen Stuart, H. Boehm, B. Li, V. Vogel, J.P. Spatz, F.M. Watt, and W.T.S. Huck: Extracellular-matrix tethering regulates stem-cell fate. Nat. Mater. 11, 642 (2012).
J.H. Wen, L.G. Vincent, A. Fuhrmann, Y.S. Choi, K.C. Hribar, H. Taylor-Weiner, S. Chen, and A.J. Engler: Interplay of matrix stiffness and protein tethering in stem cell differentiation. Nat. Mater. 13, 979 (2014).
N.D. Leipzig and M.S. Shoichet: The effect of substrate stiffness on adult neural stem cell behavior. Biomaterials 30, 6867 (2009).
J. You, S.-A. Park, D.-S. Shin, D. Patel, V.K. Raghunathan, M. Kim, C.J. Murphy, G. Tae, and A. Revzin: Characterizing the effects of heparin gel stiffness on function of primary hepatocytes. Tissue Eng. A 19, 2655 (2013).
N. Mittal, F. Tasnim, C. Yue, Y. Qu, D. Phan, Y. Choudhury, M.-H. Tan, and H. Yu: Substrate stiffness modulates the maturation of human pluripotent stem-cell-derived hepatocytes. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2, 1649 (2016).
A. Nava, E. Mazza, M. Furrer, P. Villiger, and W.H. Reinhart: In vivo mechanical characterization of human liver. Med. Image Anal. 12, 203 (2008).
L. Huwart, F. Peeters, R. Sinkus, L. Annet, N. Salameh, L.C. ter Beek, Y. Horsmans, and B.E. Van Beers: Liver fibrosis: non-invasive assessment with MR elastography. NMR Biomed.. 19, 173 (2006).
D. Hanjaya-Putra, J. Yee, D. Ceci, R. Truitt, D. Yee, and S. Gerecht: Vascular endothelial growth factor and substrate mechanics regulate in vitro tubulogenesis of endothelial progenitor cells. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 14, 2436 (2010).
S.R. Caliari, S.L. Vega, M. Kwon, E.M. Soulas, and J.A. Burdick: Dimensionality and spreading influence MSC YAP/TAZ signaling in hydrogel environments. Biomaterials 103, 314 (2016).
S. Khetan, M. Guvendiren, W.R. Legant, D.M. Cohen, C.S. Chen, and J.A. Burdick: Degradation-mediated cellular traction directs stem cell fate in covalently crosslinked three-dimensional hydrogels. Nat. Mater. 12, 458 (2013).
N. Huebsch, P.R. Arany, A.S. Mao, D. Shvartsman, O.A. Ali, S.A. Bencherif, J. Rivera-feliciano, and D.J. Mooney: Harnessing traction-mediated manipulation of the cell/matrix interface to control stem-cell fate. Nat. Mater. 9, 518 (2010).
N. Gjorevski, N. Sachs, A. Manfrin, S. Giger, M.E. Bragina, P. Ordóñez-Morán, H. Clevers, and M.P. Lutolf: Designer matrices for intestinal stem cell and organoid culture. Nat. Publ. Gr. 539, 560 (2016).
S.R. Caliari, M. Perepelyuk, E.M. Soulas, G.Y. Lee, R.G. Wells, and J.A. Burdick: Gradually softening hydrogels for modeling hepatic stellate cell behavior during fibrosis regression. Integr. Biol. 8, 720 (2016).
N. Boehnke, C. Cam, E. Bat, T. Segura, and H.D. Maynard: Imine hydrogels with tunable degradability for tissue engineering. Biomacromolecules 16, 2101 (2015).
P.M. Kharkar, A.M. Kloxin, and K.L. Kiick: Dually degradable click hydrogels for controlled degradation and protein release. J. Mater. Chem. B, Mater. Biol. Med. 2, 5511 (2014).
J.L. Young and A.J. Engler: Hydrogels with time-dependent material properties enhance cardiomyocyte differentiation in vitro. Biomaterials 32, 1002 (2011).
C. Yang, M.W. Tibbitt, L. Basta, and K.S. Anseth: Mechanical memory and dosing influence stem cell fate. Nat. Mater. 13, 645 (2014).
M. Guvendiren and J.A. Burdick: Stiffening hydrogels to probe short- and long-term cellular responses to dynamic mechanics. Nat. Commun. 3, 792 (2012).
R.S. Stowers, S.C. Allen, and L.J. Suggs: Dynamic phototuning of 3D hydrogel stiffness. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 112, 1953 (2015).
A.A. Abdeen, J. Lee, N.A. Bharadwaj, R.H. Ewoldt, and K.A. Kilian: Temporal modulation of stem cell activity using magnetoactive hydrogels. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 5, 2536 (2016).
U. Ubaidillah, J. Sutrisno, A. Purwanto, and S.A. Mazlan: Recent progress on magnetorheological solids: materials, fabrication, testing, and applications. Adv. Eng. Mater. 17, 563 (2015).
T. Mitsumata, S. Ohori, A. Honda, and M. Kawai: Magnetism and viscoelasticity of magnetic elastomers with wide range modulation of dynamic modulus. Soft Matter 9, 904 (2013).
M. Mayer, R. Rabindranath, J. Boerner, E. Hoerner, A. Bentz, J. Salgado, H. Han, H. Boese, J. Probst, M. Shamonin, G.J. Monkman, and G. Schlunck: Ultra-soft PDMS-based magnetoactive elastomers as dynamic cell culture substrata. PLoS ONE 8, e76196 (2013).
Y. Lei and D.V. Schaffer: A fully defined and scalable 3D culture system for human stem cell expansion and differentiation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 110, E5039 (2013).
Q. Li, H. Lin, O. Wang, X. Qiu, S. Kidambi, L.P. Deleyrolle, B.A. Reynolds, and Y. Lei: Scalable production of glioblastoma tumor-initiating cells in 3 dimension thermoreversible hydrogels. Sci. Rep. 6, 31915 (2016).
M.O. Cho, Z. Li, H.-E. Shim, I.-S. Cho, M. Nurunnabi, H. Park, K.Y. Lee, S.-H. Moon, K.-S. Kim, S.-W. Kang, and K.M. Huh: Bioinspired tuning of glycol chitosan for 3D cell culture. NPG Asia Mater. 8, e309 (2016).
H. Wolfenson, G. Meacci, S. Liu, M.R. Stachowiak, T. Iskratsch, S. Ghassemi, P. Roca-Cusachs, B. O’Shaughnessy, J. Hone, and M.P. Sheetz: Tropomyosin controls sarcomere-like contractions for rigidity sensing and suppressing growth on soft matrices. Nat. Cell Biol. 18, 33 (2015).
G. Meacci, H. Wolfenson, S. Liu, M.R. Stachowiak, T. Iskratsch, A. Mathur, S. Ghassemi, N. Gauthier, E. Tabdanov, J. Lohner, A. Gondarenko, A.C. Chander, P. Roca-Cusachs, B. O’Shaughnessy, J. Hone, and M.P. Sheetz: α-Actinin links extracellular matrix rigidity-sensing contractile units with periodic cell-edge retractions. Mol. Biol. Cell 27, 3471 (2016).
M. Whang and J. Kim: Synthetic hydrogels with stiffness gradients for durotaxis study and tissue engineering scaffolds. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 13, 126 (2016).
X. Tingting, L. Wanqian, and Y. Li: A review of gradient stiffness hydrogels used in tissue engineering and regenerative medicine. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 105, 1799 (2017).
J.R. Tse and A.J. Engler: Stiffness gradients mimicking in vivo tissue variation regulate mesenchymal stem cell fate. PLoS ONE 6, e15978 (2011).
C. Yang, F.W. DelRio, H. Ma, A.R. Killaars, L.P. Basta, K.A. Kyburz, and K.S. Anseth: Spatially patterned matrix elasticity directs stem cell fate. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 113, E4439 (2016).
M.P. Lutolf, J.L. Lauer-Fields, H.G. Schmoekel, A.T. Metters, F.E. Weber, G.B. Fields, and J.A. Hubbell: Synthetic matrix metalloproteinase-sensitive hydrogels for the conduction of tissue regeneration: engineering cell-invasion characteristics. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 100, 5413 (2003).
S.A. Fisher, P.N. Anandakumaran, S.C. Owen, and M.S. Shoichet: Tuning the microenvironment: click-crosslinked hyaluronic acid-based hydrogels provide a platform for studying breast cancer cell invasion. Adv. Funct. Mater. 25, 7163 (2015).
K.M. Schultz, K.A. Kyburz, and K.S. Anseth: Measuring dynamic cell–material interactions and remodeling during 3D human mesenchymal stem cell migration in hydrogels. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 112, E3757 (2015).
X. Tong and F. Yang: Sliding hydrogels with mobile molecular ligands and crosslinks as 3D stem cell niche. Adv. Mater. 28, 7257 (2016).
Z. Liu and L. Bilston: On the viscoelastic character of liver tissue: experiments and modelling of the linear behaviour. Biorheology 37, 191 (2000).
M. Geerligs, G.W.M. Peters, P.A.J. Ackermans, C.W.J. Oomens, and F.P.T. Baaijens: Linear viscoelastic behavior of subcutaneous adipose tissue. Biorheology 45, 677 (2008).
S.J. McDonald, P.C. Dooley, A.C. McDonald, J.A. Schuijers, A.R. Ward, and B.L. Grills: Early fracture callus displays smooth muscle-like viscoelastic properties ex vivo: implications for fracture healing. J. Orthop. Res. 27, 1508 (2009).
O. Chaudhuri, L. Gu, M. Darnell, D. Klumpers, S.A. Bencherif, J.C. Weaver, N. Huebsch, and D.J. Mooney: Substrate stress relaxation regulates cell spreading. Nat. Commun. 6, 6365 (2015).
O. Chaudhuri, L. Gu, D. Klumpers, M. Darnell, S.A. Bencherif, J.C. Weaver, N. Huebsch, H.-P. Lee, E. Lippens, G.N. Duda, and D.J. Mooney: Hydrogels with tunable stress relaxation regulate stem cell fate and activity. Nat. Mater. 15, 326 (2015).
J. Tao, H. Wang, Q. Lin, H. Shen, and L.S. Li: Quantum-dot-based light-emitting diodes with improved brightness and stability by using sulfuric acid-treated PEDOT:PSS as efficient hole injection layer. IEEE Trans. Nanotechnol. 14, 57 (2015).
J.A. Burdick and G.D. Prestwich: Hyaluronic acid hydrogels for biomedical applications. Adv. Mater. 23, H41 (2011).
S.A. Fisher, R.Y. Tam, and M.S. Shoichet: Tissue mimetics: engineered hydrogel matrices provide biomimetic environments for cell growth. Tissue Eng. A 20, 895 (2014).
T. Nie, R.E. Akins, and K.L. Kiick: Production of heparin-containing hydrogels for modulating cell responses. Acta Biomater.. 5, 865 (2009).
H.H. Nguyen, B. Payré, J. Fitremann, N. Lauth-De Viguerie, and J.D. Marty: Thermoresponsive properties of PNIPAM-based hydrogels: effect of molecular architecture and embedded gold nanoparticles. Langmuir 31, 4761 (2015).
K. Chwalek, M.V. Tsurkan, U. Freudenberg, and C. Werner: Glycosaminoglycan-based hydrogels to modulate heterocellular communication in in vitro angiogenesis models. Sci. Rep. 4, 4414 (2014).
M.H. Hettiaratchi, C. Chou, N. Servies, J.M. Smeekens, A. Cheng, C. Esancy, R. Wu, T.C. McDevitt, R.E. Guldberg, and L. Krishnan: Competitive protein binding influences heparin-based modulation of spatial growth factor delivery for bone regeneration. Tissue Eng. A 23, 683 (2017).
M.H. Hettiaratchi, T. Miller, J.S. Temenoff, R.E. Guldberg, and T.C. McDevitt: Heparin microparticle effects on presentation and bioactivity of bone morphogenetic protein-2. Biomaterials 35, 7228 (2014).
J.M. Chalovich and E. Eisenberg: Heparin mimicking polymer promotes myogenic differentiation of muscle progenitor cells. Biophys. Chem. 257, 2432 (2005).
K.L. Christman, V. Vázquez-Dorbatt, E. Schopf, C.M. Kolodziej, R.C. Li, R.M. Broyer, Y. Chen, and H.D. Maynard: Nanoscale growth factor patterns by immobilization on a heparin-mimicking polymer. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 130, 16585 (2008).
L. Lin, R.E. Marchant, J. Zhu, and K. Kottke-Marchant: Extracellular matrix-mimetic poly(ethylene glycol) hydrogels engineered to regulate smooth muscle cell proliferation in 3-D. Acta Biomater. 10, 5106 (2014).
Y.F. Tian, H. Ahn, R.S. Schneider, S.N. Yang, L. Roman-Gonzalez, A.M. Melnick, L. Cerchietti, and A. Singh: Integrin-specific hydrogels as adaptable tumor organoids for malignant B and T cells. Biomaterials 73, 110 (2015).
S.T. Gould and K.S. Anseth: Role of cell-matrix interactions on VIC phenotype and tissue deposition in 3D PEG hydrogels. J. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 10, E443 (2016).
N.O. Enemchukwu, R. Cruz-Acuna, T. Bongiorno, C.T. Johnson, J.R. Garcia, T. Sulchek, and A.J. Garcia: Synthetic matrices reveal contributions of ECM biophysical and biochemical properties to epithelial morphogenesis. J. Cell Biol. 212, 113 (2016).
T.T. Lee, J.R. García, J.I. Paez, A. Singh, E.A. Phelps, S. Weis, Z. Shafiq, A. Shekaran, A. Del Campo, and A.J. García: Light-triggered in vivo activation of adhesive peptides regulates cell adhesion, inflammation and vascularization of biomaterials. Nat. Mater. 14, 352 (2015).
A.M. Kloxin, A.M. Kasko, C.N. Salinas, and K.S. Anseth: Photodegradable hydrogels for dynamic tuning of physical and chemical properties. Science 324, 59 (2009).
C.A. DeForest and D.A. Tirrell: A photoreversible protein-patterning approach for guiding stem cell fate in three-dimensional gels. Nat. Mater. 14, 523 (2015).
C.A. Goubko, S. Majumdar, A. Basak, and X. Cao: Hydrogel cell patterning incorporating photocaged RGDS peptides. Biomed. Microdevices 12, 555 (2010).
Y. Luo and M.S. Shoichet: Light-activated immobilization of biomolecules to agarose hydrogels for controlled cellular response. Biomacromolecules 5, 2315 (2004).
S.V. Wegner, O.I. Sentürk, and J.P. Spatz: Photocleavable linker for the patterning of bioactive molecules. Sci. Rep. 5, 18309 (2015).
M.V. Tsurkan, R. Wetzel, H.R. Pérez-Hernández, K. Chwalek, A. Kozlova, U. Freudenberg, G. Kempermann, Y. Zhang, A.F. Lasagni, and C. Werner: Photopatterning of multifunctional hydrogels to direct adult neural precursor cells. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 4, 516 (2015).
K.A. Mosiewicz, L. Kolb, A.J. van der Vlies, M.M. Martino, P.S. Lienemann, J.A. Hubbell, M. Ehrbar, and M.P. Lutolf: In situ cell manipulation through enzymatic hydrogel photopatterning. Nat. Mater. 12, 1072 (2013).
S.C. Owen, S.A. Fisher, R.Y. Tam, C.M. Nimmo, and M.S. Shoichet: Hyaluronic acid click hydrogels emulate the extracellular matrix. Langmuir 29, 7393 (2013).
B. Gao, T. Konno, and K. Ishihara: Building cell-containing multilayered phospholipid polymer hydrogels for controlling the diffusion of a bioactive reagent. RSC Adv. 5, 44408 (2015).
J.H. Wosnick and M.S. Shoichet: Three-dimensional chemical patterning of transparent hydrogels. Chem. Mater. 20, 55 (2008).
R.G. Wylie, S. Ahsan, Y. Aizawa, K.L. Maxwell, C.M. Morshead, and M.S. Shoichet: Spatially controlled simultaneous patterning of multiple growth factors in three-dimensional hydrogels. Nat. Mater. 10, 799 (2011).
Y. Aizawa, R. Wylie, and M. Shoichet: Endothelial cell guidance in 3D patterned scaffolds. Adv. Mater. 22, 4831 (2010).
M.M. Mahmoodi, S.A. Fisher, R.Y. Tam, P.C. Goff, R.B. Anderson, J.E. Wissinger, D.A. Blank, M.S. Shoichet, M.D. Distefano: 6-Bromo-7-hydroxy-3-methylcoumarin (mBhc) is an efficient multi-photon labile protecting group for thiol caging and three-dimensional chemical patterning. Org. Biomol. Chem. 14, 8289 (2016).
G.R. Souza, J.R. Molina, R.M. Raphael, M.G. Ozawa, D.J. Stark, C.S. Levin, L.F. Bronk, J.S. Ananta, J. Mandelin, M.-M. Georgescu, J.A. Bankson, J.G. Gelovani, T.C. Killian, W. Arap, and R. Pasqualini: Three-dimensional tissue culture based on magnetic cell levitation. Nat. Nanotechnol. 5, 291 (2010).
A.M. Bratt-Leal, K.L. Kepple, R.L. Carpenedo, M.T. Cooke, and T.C. McDevitt: Magnetic manipulation and spatial patterning of multi-cellular stem cell aggregates. Integr. Biol. 3, 1224 (2011).
K.M. Mabry, M.E. Schroeder, S.Z. Payne, and K.S. Anseth: Three-dimensional high-throughput cell encapsulation platform to study changes in cell-matrix interactions. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 8, 21914 (2016).
H.F. Chan, Y. Zhang, Y.-P. Ho, Y.-L. Chiu, Y. Jung, and K.W. Leong: Rapid formation of multicellular spheroids in double-emulsion droplets with controllable microenvironment. Sci. Rep. 3, 3462 (2013).
Acknowledgments
We are grateful for funding from the Canadian Institutes of Health Research (Foundation grant to M.S.S.), the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council (Discovery grant to M.S.S.), the QEII-GSST graduate student scholarship (to L.C.B.) and the Canada First Research Excellence Fund, Medicine by Design (to M.S.S.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bahlmann, L.C., Fokina, A. & Shoichet, M.S. Dynamic bioengineered hydrogels as scaffolds for advanced stem cell and organoid culture. MRS Communications 7, 472–486 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1557/mrc.2017.72
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/mrc.2017.72