Abstract
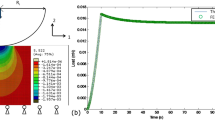
Spherical and conical nanoindentation experiments were performed for the same polymer specimens to compare Young’s moduli measured from the elastic loading and unloading curves, and bending experiments. Finite-element simulation was employed to ensure pure elastic deformation during spherical nanoindentation. The moduli measured from the elastic loading curves using Hertz’s contact law are very close to the bending moduli, because both measurements were conducted under the same elastic deformation. However, the moduli measured from the elastic unloading curves are up to 60% higher than the bending moduli owing to plastic deformation close to the sharp conical indenter tip.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
P. Wang and L.R. Xu: Dynamic interfacial debonding initiation induced by an incident crack. Int. J. Solids Struct. 43, 6535 (2006).
X. Wei and J.W. Kysar: Experimental validation of multiscale modeling of indentation of suspended circular graphene membranes. Int. J. Solids Struct. 49, 3201 (2012).
L.R. Xu, L. Li, C.M. Lukehart, and H. Kuai: Mechanical property characterization nanofiber-reinforced composite adhesives. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 7, 2546 (2007).
B. Anasori and M.W. Barsoum: reversible dislocation motion and micro-cracking in plastically anisotropic solids under cyclic spherical nanoin-dentation. MRS Communications, available on CJO September 2013. doi:10.1557/mrc.2013.39.
G.M. Odegard, T.S. Gate, and H.M. Herring: Characterization of visco-elastic properties of polymeric materials through nanoindentation. Exp. Mech. 45, 130 (2005).
Y.C. Lu, D.C. Jones, G.P. Tandon, S. Putthanarat, and G.A. Schoeppner: High temperature nanoindentation of PMR-15 polyimide. Exp. Mech. 50, 491 (2010).
M.I. Oyen and R.F. Cook: Load-displacement behavior during sharp indentation of viscous elastic-plastic materials. J. Mater. Res. 18, 139 (2002).
A. Delafrague and F.J. Ulm: Explicit approximations of the indentation modulus of elastically orthotropic solids for conical indenters. Int. J. Solids Struct. 41, 7351 (2004).
W. Li and T. Siegmund: A numerical study of indentation delamination of weakly bonded ductile films on elastic substrates. Acta Mater. 52, 2989 (2004).
Y.F. Gao and G.M. Pharr: Multidimensional contact moduli of elastically anisotropic solids. Scr. Mater. 57, 13 (2007).
G. Cao, X. Chen, Z.H. Xu and X.D. Li: Measuring mechanical properties of micro- and nano-fibers embedded in an elastic substrate: theoretical framework and experiment. Composites 6 41, 33 (2010).
Y.T. Cheng and C.M. Cheng: Relationships between initial unloading slope, contact depth, and mechanical properties for conical indentation in linear viscoelastic solids. J. Mater. Res. 20, 1046 (2005).
B.R. Donohue, A. Ambrus, and S.R. Kalidindi: Critical evaluation of the indentation data analyses methods for the extraction of isotropic uniaxial mechanical properties using finite element models. Acta Mater. 60, 3943 (2012).
C. Feng, J.M. Tannenbaum, B.S. King, and M.A. Alvin: A load-based multiple-partial unloading micro-indentation technique for mechanical property evaluation. Exp. Mech. 50, 737 (2009).
D. Ghosh, G. Subhash, T.S. Sudarshan, R. Radhakrishnan,and X-L. Gao: Dynamic indentation response of fine-grained boron carbide. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 90, 1850 (2007).
W.W. Gerberich, W.Y. Kramer, D. Bahr, A. Stronjy, E. Lilleodden, and J. Nelson: Elastic loading and elastoplastic unloading from nanometer level indentations for modulus determinations. J. Mater. Res. 13, 421 (1997).
A-Y. Jee and M. Lee: Comparative analysis on the nanoindentation of polymers using atomic force microscopy. Polym. Test. 20, 95 (2009).
K.K. Jha, N. Suksawang, D. Lahiri, and A. Agarwal: Evaluating initial unloading stiffness from elastic work-of-indentation measured in a nanoindentation experiment. J. Mater. Res. 28, 789 (2013).
C.T. McKee, J.A. Last, P. Russell, and C.J. Murphy: Indentation versus tensile measurements of Young’s modulus for soft biological tissues. Tissue Eng. 617, 155 (2011).
T. Nakamura and Y. Gu: Identification of elastic-plastic anisotropic parameters using instrumented indentation and inverse analysis. Mech. Mater. 39, 340 (2007).
W.C. Oliver and G.M. Pharr: An improved technique for determining hardness and elastic modulus using load and displacement sensing indentation experiments. J. Mater. Res. 7, 1564 (1992).
B.P. Rittel and G. Ravichandran: An analysis of nanoindentation in linearly elastic solids. Int. J. Solids Struct. 45, 6018 (2008).
D. Tranchida, S. Piccarolo, J. Loos, and A. Alexeev: Accurately evaluating Young’s modulus of polymers through nanoindentations: a phenomenological correction factor to the Oliver and Pharr procedure. Appl. Phys. Lett. 89, 171905 (2006).
C.Y. Zhang, Y.W. Zhang, K.Y. Zeng,and L. Shen: Nanoindentation of polymers with sharp indenters. J. Mater. Res. 20, 1597 (2005).
Z. Zhou and H. Lu: On the measurements of viscoelastic functions of a sphere by nanoindentation. Mech. Time-Depend. Mater. 14, 1 (2010).
E.R. Olivas, J.G. Swadener, and Y-L. Shen: Nanoindentation measurement of surface residual stresses in particle-reinforced metal matrix composites. Scr. Mater. 54, 263 (2006).
A.C. Fischer-Cripps: Nanoindentation, 2nd ed. (Springer Publisher, New South Wales, Australia, 2011), p. 163.
Y.F. Wu, H.Y. Yu,and W.Q. Chen: Mechanics of indentation for piezoelectric thin films on elastic substrate. Int. J. Solids Struct. 49, 95 (2012).
A. Krishnan and L.R. Xu: Experimental studies on the interaction among cracks, notches and interfaces of bonded polymers. Int. J. Solids Struct. 50, 1583 (2014).
R. Martinez and L.R. Xu: Approximate measurements of the though-thickness Young’s moduli of fibrous composite laminates using nanoindentation. Submitted for publication (2014).
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the support from the Office of Naval Research (Polymer Composites Program) and the National Science Foundation (Surface Engineering and Materials Design Program). Valuable discussion with Professor Yu-Lin Sheng is appreciated.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Supplementary materials
Supplementary materials
For supplementary material for this article, please visit http://dx.doi.org/10.1557/mrc.2014.19
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Martinez, R., Xu, L.R. Comparison of the Young’s moduli of polymers measured from nanoindentation and bending experiments. MRS Communications 4, 89–93 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1557/mrc.2014.19
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/mrc.2014.19