Abstract
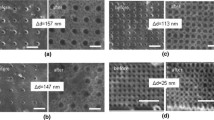
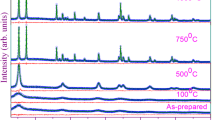
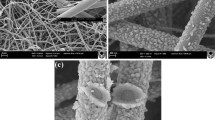
Titania nanotube arrays were synthesized electrochemically by anodization of titanium foils, and the synthesized titania nanotubes were then implanted with indium ions. The effect of In-ions implantation on crystallization and phase transformation of titania was investigated using in-situ high-temperature X-ray diffraction and synchrotron radiation diffraction from room temperature to 1000 °C. Diffraction results show that crystalline anatase first appeared at 400 °C in both the non-implanted and the In-implanted materials. The temperature at which crystalline rutile temperature appeared was 600 °C for non-implanted materials and 700 °C for In-implanted materials, and the indium implantation inhibited the anatase-to-rutile transformation. Although In3+ is expected to increase oxygen vacancy concentration and then the rate of titania transformation, the observations are consistent with implanted In-ions occupying the Ti sublattice substitutionally and then inhibiting the transformation. The relatively difficult anatase-to-rutile transformation in the In-implanted material appears to result from the relatively large In3+ radius (0.080 nm). The In3+ partly replaces the Ti4+ (0.061 nm), which provides a greater structural rigidity and prevents relaxation in the Ti bonding environment.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
H. Li, L. Cao, W. Liu, G. Su, and B. Dong: Synthesis and investigation of TiO2 nanotube arrays prepared by anodization and their photocatalytic activity. Ceram. Int. 38, 5791 (2012).
D.V. Bavykin, A.N. Kulak, V.V. Shvalagin, N.S. Andryushna, and O.L. Stroyuk: Photocatalytic properties of rutile nanoparticles obtained via low temperature route from titanate nanotubes. J. Photochem. Photobiol., A 218, 231 (2011).
O.K. Varghese, D. Gong, M. Paulose, C.A. Grimes, and E.C. Dickey: Crystallization and high-temperature structural stability of titanium oxide nanotube arrays. J. Mater. Res. 18, 156 (2003).
M. Inagakia, N. Kondoa, R. Nonakaa, E. Itob, M. Toyodac, K. Sogabec, and T. Tsumura: Structure and photoactivity of titania derived from nanotubes and nanofibers. J. Hazard. Mater. 161, 1514 (2009).
M. Senna, N. Myers, A. Aimable, V. Laporte, C. Pulgarin, O. Baghriche, and P. Bowen: Modification of titania nanoparticles for photocatalytic antibacterial activity via a colloidal route with glycine and subsequent annealing. J. Mater. Res. 28, 354 (2013).
J.M. Macak, H. Tsuchiya, A. Ghicov, K. Yasuda, R. Hahn, S. Bauer, and P. Schmuki: TiO2 nanotubes: Self-organized electrochemical formation, properties and applications. Curr. Opin. Solid State Mater. Sci. 11, 3 (2007).
H. Xiong, M.D. Slater, M. Balasubramanian, C.S. Johnson, and T. Rajh: Amorphous TiO2 nanotube anode for rechargeable sodium ion batteries. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2, 2560 (2011).
D. Yanga, H. Parka, S. Choa, H. Kima, and W. Choi: TiO2-nanotube-based dye-sensitized solar cells fabricated by an efficient anodic oxidation for high surface area. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 69, 1272 (2008).
D. Hanaor and C. Sorrell: Review of the anatase to rutile phase transformation. J. Mater. Sci. 46, 855 (2011).
S. Chuangchote, J. Jitputti, T. Sagawa, and S. Yoshikawa: Photocatalytic activity for hydrogen evolution of electrospun TiO2 nanofibers. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 1, 1140 (2009).
D. Kim, N. Enomoto, Z. Nakagawa, and K. Kawamura: Molecular dynamic simulation in titanium dioxide polymorphs: Rutile, brookite, and anatase. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 79, 1095 (1996).
G. Liu, L. Wang, H.G. Yang, H.M. Cheng, and G.Q.M. Lu: Titania-based photocatalysts-crystal growth, doping and heterostructuring. J. Mater. Chem. 20, 831 (2010).
H. Albetran, H. Haroosh, Y. Dong, V.M. Prida, B.H. O’Connor, and I.M. Low: Phase transformations and crystallization kinetics in electrospun TiO2 nanofibers in air and argon atmospheres. Appl. Phys. A 116, 161 (2014).
H. Albetran, H. Haroosh, Y. Dong, B.H. O’Connor, and I.M. Low: Effect of atmosphere on crystallisation kinetics and phase relations in electrospun TiO2 nanofibres. Ceram. Trans. 246, 125 (2013).
A. Ghicov, H. Tsuchiya, J.M. Macak, and P. Schmuki: Annealing effects on the photoresponse of TiO2 nanotubes. Phys. Status Solidi A 203, 28 (2006).
Z. Liu, X. Yan, W. Chu, and D. Li: Effects of impurities containing phosphorus on the surface properties and catalytic activity of TiO2 nanotube arrays. Appl. Surf. Sci. 257, 1295 (2010).
R.P. Antony, T. Mathews, P.K. Ajikumar, D.N. Krishna, S. Dash, and A.K. Tyagi: Electrochemically synthesized visible light absorbing vertically aligned N-doped TiO2 nanotube array films. Mater. Res. Bull. 47, 4491 (2012).
Y. Iida and S. Ozaki: Grain growth and phase transformation of titanium oxide during calcination. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 44, 120 (1961).
R.D. Shannon and J.A. Pask: Kinetics of the anatase-rutile transformation. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 48, 391 (1965).
H. Li, W. Zhang, and W. Pan: Enhanced photocatalytic activity of electrospun TiO2 nanofibers with optimal anatase/rutile ratio. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 94, 3184 (2011).
J. Lee, T. Ha, M. Hong, and H. Park: The effect of porosity on the CO sensing properties of TiO2 xerogel thin films. Thin Solid Films 529, 98 (2013).
Z. Zainal and C.Y. Lee: Properties and photoelectrocatalytic behaviour of sol-gel derived TiO2 thin films. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 37, 19 (2006).
D. Monti, A. Ponrouch, M. Estruga, M.R. Palacin, J.A. Ayllon, and A. Roig: Microwaves as a synthetic route for preparing electrochemically active TiO2 nanoparticles. J. Mater. Res. 28, 340 (2013).
C. Arunchandran, S. Ramya, R.P. George, and U.K. Mudali: Corrosion inhibitor storage and release property of TiO2 nanotube powder synthesized by rapid breakdown anodization method. Mater. Res. Bull. 48, 635 (2012).
N. Baram, D. Starosvetsky, J. Starosvetsky, M. Epshtein, R. Armon, and Y. Ein-Eli: Enhanced photo-efficiency of immobilized TiO2 catalyst via intense anodic bias. Electrochem. Commun. 9, 1684 (2007).
K.P. Beh, F.K. Yam, S.S. Tneh, and Z. Hassan: Fabrication of titanium dioxide nanofibers via anodic oxidation. Appl. Surf. Sci. 257, 4706 (2011).
J. Liao, S. Lin, N. Pan, D. Li, S. Li, and J. Li: Free-standing open-ended TiO2 nanotube membranes and their promising through-hole applications. Chem. Eng. J. 211–212, 343 (2012).
R. Sanchez-Tovar, K. Lee, J. Garcia-Anton, and P. Schmuki: Formation of anodic TiO2 nanotube or nanosponge morphology determined by the electrolyte hydrodynamic conditions. Electrochem. Commun. 26, 1 (2012).
D.V. Bavykin, A.N. Kulak, and F.C. Walsh: Control over the hierarchical structure of titanate nanotube agglomerates. Langmuir 27, 5644 (2011).
D.V. Bavykin, A.A. Lapkin, P.K. Plucinski, J.M. Friedrich, and F.C. Walsh: Reversible storage of molecular hydrogen by sorption into multilayered TiO2 nanotubes. J. Phys. Chem. B 109, 19422 (2005).
A.W. Tan, B. Pingguan-Murphy, R. Ahmad, and S.A. Akbar: Review of titania nanotubes: Fabrication and cellular response. Ceram. Int. 38, 4421 (2012).
I.M. Low, H. Albetran, V.M. Prida, V. Vega, P. Manurung, and M. Ionescu: A comparative study on crystallization behavior, phase stability, and binding energy in pure and Cr-doped TiO2 nanotubes. J. Mater. Res. 28, 304 (2013).
H. Albetran, B.H. O’Connor, and I.M. Low: Effect of vanadium ion implantation on the crystallization kinetics and phase transformation of electrospun TiO2 nanofibers. Appl. Phys. A 120, 623 (2015).
K. Okada, N. Yamamoto, Y. Kameshima, A. Yasumori, and K.J.D. MacKenzie: Effect of silica additive on the anatase-to-rutile phase transition. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 84, 1591 (2001).
E.H. Kisi: Rietveld analysis of powder diffraction patterns. Mater. Forum 18, 135 (1994).
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This research was supported by the funding from the Australian Institute of Nuclear Science and Engineering (AINGRA-11134), and the Australian Synchrotron (PD-3611). The authors would like to thank Prof. V.M. Prida from Department of Physics, University of Oviedo for XRD collection. Dr M. Ionescu of ANSTO assisted with work on ion-implantation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Albetran, H., Low, I.M. Effect of indium ion implantation on crystallization kinetics and phase transformation of anodized titania nanotubes using in-situ high-temperature radiation diffraction. Journal of Materials Research 31, 1588–1595 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2016.83
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2016.83