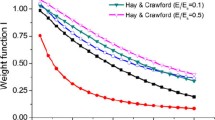
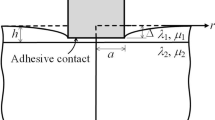
Abstract
Nanoindentation testing of compliant materials has recently attracted substantial attention. However, nanoindentation is not readily applicable to softer materials, as numerous challenges remain to be overcome. One key concern is the significant effect of adhesion between the indenter tip and the sample, leading to larger contact areas and higher contact stiffness for a given applied force relative to the Hertz model. Although the nano-Johnson–Kendall–Roberts (JKR) force curve method has demonstrated its capabilities to correct for errors due to adhesion, it has not been widely adopted, mainly because it works only with perfectly spherical tips. In this paper, we successfully extend the nano-JKR force curve method to include Berkovich and flat indenter tips by conducting numerical simulations in which the adhesive interactions are represented by an interaction potential and the surface deformations are coupled by using half-space Green’s functions discretized on the surface.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
ISO standard 14577: Metallic materials—Instrumented indentation test for hardness and materials parameter. Part 1, part 2 and part 3, 2003; part 4, 2007.
D.M. Ebenstein and L.A. Pruitt: Nanoindentation of biological materials. Nano Today 1, 26 (2006).
D.M. Ebenstein: Nanoindentation of soft tissues and other biological materials. In Handbook of Nanoindentation with Biological Applications, M.L. Oyen, ed. (Pan Stanford Publishing, Singapore, 2010); p. 350.
J.D. Kaufman, G.J. Miller, E.F. Morgan, and C.M. Klapperich: Time-dependent mechanical characterization of poly(2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate) hydrogels using nanoindentation and unconfined compression. J. Mater. Res. 23, 1472 (2008).
J.D. Kaufman and C.M. Klapperich: Surface detection errors cause overestimation of the modulus in nanoindentation on soft materials. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2, 312 (2009).
J. Deuschle, S. Enders, and E. Arzt: Surface detection in nanoindentation of soft polymers. J. Mater. Res. 22, 3107 (2007).
M.R. Van Landingham, J.S. Villarrubia, W.F. Guthrie, and G.F. Meyers: Nanoindentation of polymers: An overview. Macromol. Symp. 167, 15 (2001).
F. Carrillo, S. Gupta, M. Balooch, S.J. Marshall, G.W. Marshall, L. Pruitt, and C.M. Puttlitz: Nanoindentation of polydimethylsiloxane elastomers: Effect of crosslinking, work of adhesion, and fluid environment on elastic modulus. J. Mater. Res. 20, 2820 (2005).
D.M. Ebenstein and K.J. Wahl: A comparison of JKR-based methods to analyze quasi-static and dynamic indentation force curves. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 298, 652 (2006).
S. Gupta, F. Carrillo, C. Li, L. Pruitt, and C. Puttlitz: Adhesive forces significantly affect elastic modulus determination of soft polymeric materials in nanoindentation. Mater. Lett. 61, 448 (2007).
O. Franke, M. Goken, and A.M. Hodge: The nanoindentation of soft tissue: Current and developing approaches. JOM 60, 49 (2008).
B. Tang and A.H.W. Ngan: Nanoindentation measurement of mechanical properties of soft solid covered by a thin liquid film. Soft Matter 5, 169 (2007).
Y.F. Cao, D.H. Yang, and W. Soboyejoy: Nanoindentation method for determining the initial contact and adhesion characteristics of soft polydimethylsiloxane. J. Mater. Res. 20, 2004 (2005).
J.C. Grunlan, X. Xinyun, D. Rowenhorst, and W.W. Gerberich: Preparation and evaluation of tungsten tips relative to diamond for nanoindentation of soft materials. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 72, 2804 (2001).
J.K. Deuschle, G. Buerki, H.M. Deuschle, S. Enders, J. Michler, and E. Arzt: In situ indentation testing of elastomers. Acta Mater. 56, 4390 (2008).
Z. Wang, A.A. Volinsky, and N.D. Gallant: Nanoindentation study of polydimethylsiloxane elastic modulus using Berkovich and flat punch tips. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 132, 41384 (2015).
F. De Paoli and A.A. Volinsky: Obtaining full contact for measuring polydimethylsiloxane mechanical properties with flat punch nanoindentation. MethodsX 2, 374 (2015).
C.M. Buffinton, K.J. Tong, R.A. Blaho, E.M. Buffinton, and D.M. Ebenstein: Comparison of mechanical testing methods for biomaterials: Pipette aspiration, nanoindentation, and macroscale testing. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 51, 367 (2015).
K.J. Tong and D.M. Ebenstein: Comparison of spherical and flat tips for indentation of hydrogels. JOM 67, 713 (2015).
J.C. Kohn and D.M. Ebenstein: Eliminating adhesion errors in nanoindentation of compliant polymers and hydrogels. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 20, 316 (2013).
V.L. Ferguson, A.J. Bushby, and A. Boyde: Nanomechanical properties and mineral concentration in articular calcified cartilage and subchondral bone. J. Anat. 203, 191 (2003).
P.L. Leong and E.F. Morgan: Measurement of fracture callus material properties via nanoindentation. Acta Biomaterialia 4, 1569 (2008).
D.M. Ebenstein: Nano-JKR force curve method overcomes challenges of surface detection and adhesion for nanoindentation of a compliant polymer in air and water. J. Mater. Res. 28, 1026 (2011).
F. Alisafaei, C-S. Han, and S.H.R. Sanei: On the time and indentation depth dependence of hardness, dissipation and stiffness in poly-dimethylsiloxane. Polym. Test. 32, 1220 (2013).
C. Klapperich, L. Pruitt, and K. Komvopoulos: Nanomechanical properties of energetically treated polyethylene surfaces. J. Mater. Res. 17, 423 (2002).
K.L. Johnson: Contact Mechanics (Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 1985).
W.C. Oliver and G.M. Pharr: An improved technique for determining hardness and elastic modulus using load and displacement sensing indentation experiments. J. Mater. Res. 7, 1564 (1992).
F.M. Borodich and B.A. Galanov: Non-direct estimations of adhesive and elastic properties of materials by depth-sensing indentation. Proc. R. Soc., Ser. A 464, 2759 (2008).
E.S. Berkovich: Three-faced diamond pyramid for micro-hardness testing. Int. Diamond Rev. 11, 129 (1951).
I.A. Sneddon: The relation between load and penetration in the axisymmetric boussinesq problem for a punch of arbitrary profile. Int. J. Eng. Sci. 3, 47 (1965).
D. Tabor: Surface forces and surface interactions. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 58, 2 (1977).
E. Barthel: Adhesive elastic contacts: JKR and more. J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 41, 163001 (2008).
V.M. Muller, V.S. Yushchenko, and B.V. Derjaguin: On the influence of molecular forces on the deformation of an elastic sphere and its sticking to a rigid plane. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 77, 91 (1980).
J.A. Greenwood: Adhesion of elastic spheres. Proc. R. Soc. London, Ser. A 453, 1277 (1997).
B.A. Galanov: Development of analytical and numerical methods for study of models of materials. In Report for the Project 7.06.00/001-92, 7.06.00/015-92. (Institute for Problems in Materials Science, Kiev, Ukrainian, 1993).
F.M. Borodich: Hertz type contact problems for power-law shaped bodies. In Contact Problems: The Legacy of L.A. Galin, G.M.L. Gladwell, ed. (Springer, Dordrecht, Netherlands, 2008); p. 261.
F.M. Borodich: The Hertz-type and adhesive contact problems for depth-sensing indentation. Adv. Appl. Mech. 47, 225 (2014).
C. Jin, A. Jagota, and C-Y. Hui: An easy-to-implement numerical simulation method for adhesive contact problems involving asymmetric adhesive contact. J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 44, 405303 (2011).
A.E. Giannakopoulos, P-L. Larsson, and R. Vestregaard: Analysis of Vickers indentation. Int. J. Solids Struct. 31, 2670 (1994).
P-L. Larsson, A.E. Giannakopoulos, E. Soderlund, D.J. Rowcliffe, and R. Vestergaard: Analysis of Berkovich indentation. Int. J. Solids Struct. 33, 221 (1996).
T. Chudoba and N. Jennett: Higher accuracy analysis of instrumented indentation data obtained with pointed indenters. J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 41, 215407 (2008).
J.N. Israelachvili: Intermolecular and Surface Forces, 2nd ed. (Academic, San Diego, 1992).
C-Y. Hui, A. Jagota, S.J. Bennison, and J.D. Londono: Crack blunting and the strength of soft elastic solids. Proc. R. Soc. London, Ser. A 459, 1489 (2003).
T. Tang, C.Y. Hui, A. Jagota, and M.K. Chaudhury: Thermal fluctuations limit the adhesive strength of compliant solids. J. Adhes. 82, 671 (2006).
K.L. Johnson and J.A. Greenwood: An adhesion map for the contact of elastic spheres. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 192, 326 (1997).
L. Kogut and I. Etsion: Adhesion in elastic-plastic spherical microcontact. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 261, 372 (2003).
Y. Du, L. Chen, N.E. McGruer, G.G. Adams, and I. Etsion: A finite element model of loading and unloading of an asperity contact with adhesion and plasticity. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 312, 522 (2007).
Z. Song and K. Komvopoulos: Adhesion-induced instabilities in elastic and elastic–plastic contacts during single and repetitive normal loading. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 59, 884 (2011).
A. Jagota and C. Argento: An intersurface stress tensor. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 191, 326 (1997).
N. Yu and A. Polycarpou: Adhesive contact based on the Lennard–Jones potential: A correction to the value of the equilibrium distance as used in the potential. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 278, 428 (2004).
F.M. Borodich, B.A. Galanov, L.M. Keer, and M.M. Suarez-Alvarez: The JKR-type adhesive contact problems for transversely isotropic elastic solids. Mech. Mater. 75, 34 (2014).
M. Fafard and B. Massicotte: Geometrical interpretation of the arc-length method. Comput. Struct. 46, 603 (1993).
C. Jin, K. Khare, S. Vajpayee, S. Yang, A. Jagota, and C-Y. Hui: Adhesive contact between a rippled elastic surface and a rigid spherical indenter: From partial to full contact. Soft Matter 7, 10728 (2011).
F.M. Borodich, B.A. Galanov, and M.M. Suarez-Alvarez: The JKR-type adhesive contact problems for power-law shaped axisymmetric punches. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 68, 14 (2014).
R. Spolenak, S. Gorb, H. Gao, and E. Arzt: Effects of contact shape on biological attachments. Proc. R. Soc. London, Ser. A 461, 305 (2005).
K.W. McElhaney, J.J. Vlassak, and W.D. Nix: Determination of indenter tip geometry and indentation contact area for depth-sensing indentation experiments. J. Mater. Res. 13, 1300 (1998).
I.D. Johnston, D.K. McCluskey, C.K.L. Tan, and M.C. Tracey: Mechanical characterization of bulk Sylgard 184 for microfluidics and microengineering. J. Micromech. Microeng. 24, 035017 (2014).
A. Sharfeddin, A.A. Volinsky, G. Mohan, and N.D. Gallant: Comparison of the macroscale and microscale tests for measuring elastic properties of polydimethylsiloxane. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 132, 42680 (2015).
K.R. Shull: Contact mechanics and the adhesion of soft solids. Mater. Sci. Eng., R 36, 1 (2002).
Y.L. Yu, D. Sanchez, and N.S. Lu: Work of adhesion/separation between soft elastomers of different mixing ratios. J. Mater. Res. 30, 2702 (2015).
R.L. Smith and G.E. Sutherland: Some notes on the use of a diamond pyramid for hardness testing. Iron Steel Inst. 1, 285 (1925).
F. Knoop, C.G. Peters, and W.B. Emerson: A sensitive pyramidal-diamond tool for indentation measurements. J. Res. Natl. Bur. Stand. 23, 39 (1939).
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This work is supported by start-up funds provided by the Department of Mechanical Engineering at State University of New York at Binghamton. The nanoindenter used in this study was obtained through the support of the National Science Foundation (MRI-1040319). Conclusions and recommendations expressed in this paper are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect the views of the National Science Foundation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jin, C., Ebenstein, D.M. Nanoindentation of compliant materials using Berkovich tips and flat tips. Journal of Materials Research 32, 435–450 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2016.483
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2016.483