Abstract
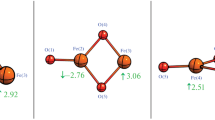
The ground state properties of γ-Fe4X (X = B, C, N, and O) were studied by means of the density functional theory. The calculations were performed using the linearized augmented plane wave method as implemented in the Wien2k code. From the equilibrium cohesive energy point of view, all the compounds are ferromagnetic and the stability increases in the following sequence: γ-Fe4O, γ-Fe4N, γ-Fe4B, γ-Fe4C. The electron density suggests that the chemical bonding in γ-Fe4X (X = B, C, N, and O) is a mixture of covalent and ionic character that vary in intensity with the X atom. The magnetic moments and hyperfine interactions are clearly and differently affected by the nature of the X atom. The results indicated that there is not a linear relation between the 2 p electron number of the X atom and the magnetic properties of the compounds.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
K.H. Jack: The iron-nitrogen system: The preparation and the crystal structures of nitrogen-austenite (Γ) and nitrogen-martensite (α´). Proc. R. Soc. London, Ser. A 208, 216–224 (1951).
T.K. Kim and M. Takahashi: New magnetic material having ultrahigh magnetic moment. Appl. Phys. Lett. 20, 492–494 (1972).
J.M.D. Coey and P.A.I. Smith: Magnetic nitrides. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 200, 405–424 (1999).
L. Rissanen, M. Neubauer, K.P. Lieb, and P. Schaaf: The new cubic iron-nitride phase FeN prepared by reactive magnetron sputtering. J. Alloys Compd. 274, 74–82 (1998).
K.H. Jack: The iron-nitrogen system: The crystal structure of ε-phase iron nitrides. Acta Cryst. 5, 404–411 (1952).
G.W. Wiener and J.A. Berger: Structure and magnetic properties of some transition metalnitrides. J. Met. 7, 360–365 (1955).
B.C. Frazer: Magnetic structure of Fe4N. Phys. Rev. 112, 751–754 (1958).
G. Shirane, W.J. Takei, and S.L. Ruby: Mössbauer study of hyperfine fields and isomer shifts in Fe4N. Phys. Rev. 126, 49–52 (1962).
S. Suzuki, H. Sakumoto, J. Minegishi, and Y. Omote: Coercivity and unit particle size of metal pigment. IEEE Trans. Magn. 17, 3017–3019 (1981).
K. Tagawa, E. Kita, and A. Tasaki: Synthesis of fine Fe4N powder and its magnetic characteristics. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 21, 1596–1598 (1982).
S. Matar, P. Mohn, G. Demazeau, and B. Siberchicot: The calculated electronic and magnetic structures of Fe4N and Mn4N. J. Phys. 49, 1761–1768 (1988).
A. Sakuma: Self-consistent calculations for the electronic structure of iron nitrides Fe3N, Fe4N and Fe16N2. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 102, 127–134 (1991).
C.A. Kuhnen, R.S. de Figueredo, V. Drago, and E.Z. da Silva: Mössbauer studies and electronic structure of γ´-Fe4N. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 111, 95–104 (1992).
R. Coehoorn, G.H.O. Daalderop, and H.J.F. Jansen: Full-potential calculations of the magnetization of Fe16N2 and Fe4N. Phys. Rev. B 48, 3830–3834 (1993).
S. Ishida and K. Kitawatase: Electronic structure and magnetic properties of iron nitrides. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 104–107, 1933–1934 (1992).
C. Paduani and J.C. Krause: Local magnetic properties and electronic structure of γ´-Fe4N. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 138, 109–114 (1994).
J.G.M. Armitage, R.G. Graham, J.S. Lord, P.C. Riedi, S.F. Matar, and G. Demazeau: Pressure dependence of magnetic properties of Fe4N and Mn4N. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 104–107, 1935–1936 (1992).
Y. Kong, R. Zhou, and L. Fashen: A linear muffin-tin orbital calculation of the volume dependence of local electronic and magnetic properties of γ′-Fe4N. J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 8, 3829–3834 (1996).
M. Sifkovits, H. Smolinski, S. Hellwig, and W. Weber: Interplay of chemical bonding and magnetism in Fe4N, Fe3N and ζ-Fe2N. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 204, 191–198 (1999).
Y. Kong, R. Zhou, and F. Li: Spin-polarized linear muffin-tin orbitals calculation of the interstitial-atom effect in gamma-Fe4Z (Z= H, C, N). Phys. Rev. B 54, 5460 (1996).
A.V. dos Santos, M.I. da Costa, and C.A. Kuhnen: Electronic structure and magnetic properties of Fe4C. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 166, 223–230 (1997).
J.C. Krause, C. Paduani, and M.I. da Costa: Cluster calculations of the electronic structure of Fe4C. Hyperfine Interact. 108, 465–475 (1997).
N. Ishimatsu, H. Maruyama, N. Kawamura, M. Suzuki, Y. Ohishi, M. Ito, S. Nasu, T. Kawakami, and O. Shimomura: Pressure-induced magnetic transition in Fe4N probed by Fe K-edge XMCD measurement. J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 72, 2372–2376 (2003).
M. Ogura and H. Akai: Magnetic properties and electric field gradients of Fe4N and Fe4C. Hyperfine Interact. 158, 19–23 (2004).
R.S. de Figueiredo and J. Foct: Mössbauer study of superstructures induced by mechanical alloying in nanocrystalline (MexFe1-x)4N nitrides. In Proceedings of ICAME-95, Vol. 50 (Italian Physical Society: Rimini, Italy, 1996); p. 509.
R.S. de Figueiredo, C.A. Kuhnen, and A.V. dos Santos: Crystallographic, magnetic and electronic struture of iron-silver and iron-gold perovskite nitrides. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 173, 141–154 (1997).
C.A. Kuhnen, R.S. de Figueiredo, and A.V. dos Santos: Mössbauer spectroscopy, crystallographic, magnetic and electronic structure of ZnFe3N and InFe3N. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 219, 58–68 (2000).
R.S. de Figueiredo, J. Foct, A.V. dos Santos, and C.A. Kuhnen: Crystallographic and electronic structure of CuxFe4−xN. J. Alloys Compd. 315, 42–50 (2001).
J. Foct, R.S. de Figueiredo, O. Richard, and J.P. Mormiroli: Mechanical Alloying of Interstitial Solid Solutions and Compounds. Mater. Sci. Forum 225–227, 409–416 (1996).
A.V. dos Santos and C.A. Kuhnen: Electronic structure and magnetic properties of CoFe3N, CrFe3N and TiFe3N. J. Alloys Compd. 321, 60–66 (2001).
S. Matar, P. Mohn, and J. Kübler: Magnetovolume effects in PtFe3N. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 104–107, 1927–1928 (1992).
X.G. Ma, J.J. Jiang, P. Liang, J. Wang, Q. Ma, and Q.K. Zhang: Structural stability and magnetismo of γ′-Fe4N and CoFe3N compounds. J. Alloys Compd. 480, 475–480 (2009).
A.V. Gil Rebaza, J. Desimoni, and E.L. Peltzer y Blancá: Study on the oscillatory behaviour of the lattice parameter in ternary iron–nitrogen compounds. Phys. B 407, 3240–3243 (2012).
K. Hocine, M. Rabah, D. Rached, S. Djili, and H. Baltache: Ab initio study of electronic structure and magnetic properties of MFe3N (M = Ru and Os). Comput. Mater. Sci. 65, 6–12 (2012).
Y. Zhang, Z. Wang, and J. Cao: Predicting magnetostriction of MFe3N (M = Fe, Mn, Ir, Os, Pd, Rh) from ab initio calculations. Comput. Mater. Sci. 92, 464–467 (2014).
D. Music and J.M. Schneider: Elastic properties of MFe3N (M = Ni, Pd, Pt) studied by ab initio calculations. Appl. Phys. Lett. 88, 031914 (2006).
E. Zhao, H. Xiang, J. Meng, and Z. Wu: First-principles investigation on the elastic, magnetic and electronic properties of MFe3N (M = Fe, Ru, Os). Chem. Phys. Lett. 449, 96–100 (2007).
M.F. Yan, Y.Q. Wu, and R.L. Liu: Plasticity and initio characterizations on Fe4N produced on the surface of nanocrystallized 18Ni-maraging steel plasma nitrided at lower temperature. Appl. Surf. Sci. 255, 8902–8906 (2009).
A.N. Timoshevskii and S.O. Yablonovskii: Ab-initio modeling of the short range order in Fe-N and Fe-C autenitic alloys. Funct. Mater. 18, 517–522 (2011).
Z.Q. Lv, Y. Gao, S.H. Sun, M.G. Qv, Z.H. Wang, Z.P. Shi, and W.T. Fu: Electronic, magnetic and elastic properties of γ-Fe4X (X = B/C/N) from density functional theory calculations. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 333, 39–45 (2013).
J.P. Perdew, K. Burke, and M. Ernzerhof: Generalized gradient approximation made simple. Phys. Rev. B 77, 3865–3868 (1996).
J.A. White and D.M. Bird: Implementation of gradient-corrected exchange-correlation potentials in Car-Parrinello total-energy calculations. Phys. Rev. B 50, 4954–4957 (1994).
P. Blaha, K. Schwarz, and J. Luitz: Computer code WIEN97, Universitat Wien, Austria, 1997.
E.L. Peltzer y Blanca, J. Desimoni, and N.E. Christensen: Electronic structure of FCC-FenX (X=C, N; n=4, 8) alloys. Phys. B 354, 341–344 (2004).
W.K. Choo and R. Kaplow: Mössbauer measurements on the aging of iron-carbon martensite. Acta Metall. 21, 725–732 (1973).
N. De Cristofaro and R. Kaplow: Interstitial atom configurations in stable and metastable Fe-N and Fe-C solid solutions. Metall. Trans. A 8, 35–44 (1977).
R.E. Watson and A.J. Freeman: Origin of effective fields in magnetic materials. Phys. Rev. 123, 2027–2047 (1961).
A.N. Timoshevskii, V.A. Timoshevskii, and B.Z. Yanchitsky: The influence of carbon and nitrogen on the electronic structure and hyperfine interactions in face-centred-cubic iron-based alloys. J. Phys.: Condens. Matter 13, 1051–1061 (2001).
J. Haglund, A. Fernández Guillermet, G. Grimvall, and M. Korling: Theory of bonding in transition-metal carbides and nitrides. Phys. Rev. B 48, 11685–11691 (1993).
K.J. Duff: Calibration of the isomer shift for 57Fe. Phys. Rev. B 9, 66–72 (1974).
C.L Yang, M.M Abd-Elmeguid, H. Micklitz, G. Michels, J.W Otto, Y. Kong, D.S. Xue, and F.S. Li: Pressure effects on the electronic properties and the magnetic ground state of γ′-Fe4N. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 151, L19–L23 (1995).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
dos Santos, A.V., Samudio Pérez, C.A. Ab initio investigation of the substitution effects of 2 p elements on the electronic structure of γ-Fe4X (X = B, C, N, and O) in the ground state. Journal of Materials Research 31, 202–212 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2015.394
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2015.394