Abstract
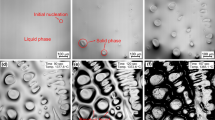
Formation and evolution details of a two-phase coupled microstructure in AISI 304 stainless steel are studied by quenching method during directional solidification. Results show that the coupled growth microstructure, which is composed of thin lath-like ferrite (δ) and austenite (γ), crystallizes first in the form of colony from the melt. As solidification develops, the retained liquid transforms into austenite gradually. On cooling, solid-state transformation from ferrite to austenite results in the disappearance of part thinner ferrites and the final two-phase coupled microstructure is formed after the solid-state transformation. The formation mechanism of the two-phase coupled microstructure is analyzed based on the nucleation and constitutional undercooling criterion (NCU) before steady-state growth of each phase is reached.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
J.A. Brooks and A.W. Thompson: Microstructural development and solidification cracking susceptibility of austenitic stainless steel welds. Int. Mater. Rev. 36, 16 (1991).
U. Siegel, H.J. Spies, and H.J. Eckstein: Effect of solidification conditions on the solidification sequence of austenitic chromiumnickel stainless steels. Steel Res. 57, 25 (1986).
A. Hunter and M. Ferry: Phase formation during solidification of AISI 304 austenitic stainless steel. Scr. Mater. 46, 253 (2002).
K. Rajasekhar, C.S. Harendranath, R. Raman, and S.D. Kulkarni: Microstructural evolution during solidification of austenitic stainless steel weld metals: A color metallographic and electron microprobe analysis study. Mater. Charact. 38, 53 (1997).
R.N. Wright, J.C. Bae, T.F. Kelly, J.E. Flinn, and G.E. Korth: The microstructure and phase relationships in rapidly solidified type 304 stainless steel powders. Metall. Trans. A 31, 2399 (1988).
J.A. Brooks, J.C. Williams, and A.W. Thompson: STEM analysis of primary austenite solidified stainless steel welds. Metall. Trans. A 14, 23 (1983).
N. Suutala, T. Takalo, and T. Moisio: The relationship between solidification and microstructure in austenitic and austeniticferritic stainless steel welds. Metall. Trans. A 10, 512 (1979).
J.C. Lippold and W.F. Savage: Solidification of austenitic stainless steel weldments. Part 2: The effect of alloy composition on ferrite morphology. Welding J. 59, 48s (1980).
S.A. David: Ferrite morphology and variations in ferrite content in austenitic stainless steel welds. Welding J. 60, 63s (1981).
J.A. Brooks, J.C. Williams, and A.W. Thompson: Microstructural origin of the skeletal ferrite morphology of austenitic stainless steel welds. Metall. Trans. A 14, 1271 (1983).
H. Fredriksson: Solute segregation and microstructure of directionally solidified austenitic stainless steel. Metall. Trans. 3, 2989 (1972).
J.C. Ma, Y.S. Yang, W.H. Tong, Y. Fang, Y. Yu, and Z.Q. Hu: Microstructural evolution in AISI 304 stainless steel during directional solidification and subsequent solid-state transformation. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 444, 64 (2007).
D. Baldissin, M. Baricco, and L. Battezzati: Microstructures in rapidly solidified AISI 304 interpreted according to phase selection theory. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 449–451, 999 (2007).
N.H. Pryds and X. Huang: The effect of cooling rate on the microstructures formed during solidification of ferritic steel. Metall. Trans. A 31, 3155 (2000).
A.D. Schino, M.G. Mecozzi, M. Barteri, and J.M. Kenny: Solidification mode and residual ferrite in low-Ni austenitic stainless steels. J. Mater. Sci. 35, 375 (2000).
Th. Schubert, W. Löser, S. Schinnerling, and I. Bächer: Alternative phase formation in thin strip casting of stainless steels. Mater. Sci. Technol. 11, 181 (1995).
J.W. Fu, Y.S. Yang, J.J. Guo, and W.H. Tong: Effect of cooling rate on solidification microstructures in AISI 304 stainless steel. Mater. Sci. Technol. 24, 941 (2008).
N. D’Souza, M. Lekstrom, and H.B. Dong: An analysis of measurement of solute segregation in Ni-base superalloys using x-ray spectroscopy. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 490, 258 (2008).
P.L. Ferrandini, C.T. Rios, A.T. Dutra, M.A. Jaime, P.R. Mei, and R. Caram: Solute segregation and microstructure of directionally solidified austenitic stainless steel. Mater. Sci. Eng., A 435–436, 139 (2006).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fu, J.W., Yang, Y.S., Guo, J.J. et al. Formation of two-phase coupled microstructure in AISI 304 stainless steel during directional solidification. Journal of Materials Research 24, 2385–2390 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2009.0282
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/jmr.2009.0282