Abstract
We have developed a Monte Carlo (simulation) model to describe glass dissolution. This model uses similar parameters to those used in the Grambow model, which has been the main glass dissolution model during the last decade. While the Grambow model is macroscopic, ours is microscopic. This assures that the value of our parameters is time independent and allows changes in the gel structure (not just concentrations) to be described.
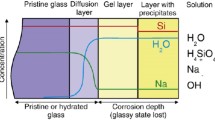
We relate our parameters to those of the Grambow model and test whether the basic assumptions of the Grambow model are consistent with our simulation results. In these simulations, as the solution evolves towards silica saturation, the silica concentration in solution can become higher than the (final) silica saturation concentration. A possible explanation for this behavior, which is observed experimentally as well, is that the silica saturation concentration is not constant as a function of time. Initially, the silica saturation concentration is the glass saturation concentration. The glass saturation concentration is higher than the final silica saturation concentration, which corresponds to saturation of the gel. In the Grambow model, the initial dissolution rate (at the gel/water interface) and the diffusion coefficient of silica in the gel are not constant either. The existence of a final dissolution rate depends on the silica content of the glass and on the protection provided by the gel layer. In the simulations, a protective gel is mainly formed by the adsorption (precipitation) of dissolved silica particles from the solution in contact with the gel. This makes us expect that (1) the gel would be non protective for dynamic tests (with a low silica content in solution) and (2) the gel would be very protective in static tests with high surface to volume ratios.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
P. Aagaard and H. Helgeson., Am. J. of Science 282, p. 237 (1982).
B. Grambow, Nuclear waste glass dissolution. mechanism, model and application, (Report to the JSS-project 87-02, phase IV, 1987).
T. Advocat, J. L. Couchan, J. L. Crovisier, C. Guy, V. Daux, C. Jégou, S. Gin and E. Vernaz in Scientific Basis for Nuclear Waste Management XXI, edited by I. Mc Kinley, C. McCombie (Mat. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. 506, 1998) pp. 63–70.
W. Kuhn and L. Bunnell, Results of testing the Grambow rate law for use in HWVP glass durability correlations, (Report PNNL-1 1070 UC-810, Richland, Washington, USA, 1996).
C. Jdgou, S. Gin, E. Vernaz and F. Larché in Proc. of XVIII Int. Congr. on Glass, edited by. M. Choudhary., N. Huff and C. Drummond (Am. Ceram. Soc., San Francisco, USA, 1998).
S. Gin, C. Jégou, E. Vernaz, and F. Larché in Proc. of XVIII Int. Congr. on Glass, edited by. M. Choudhary, N. Huff and C. Drummond (Am. Ceram. Soc., San Francisco, USA, 1998).
A. Lasaga in Kinetics of geochemical processes, edited by A. Lasaga and R. Kirkpatrick (Rev. Mineralogy 8, 1981), p. 1.
T. Böhm and J. Chudek, Fundamentals of Glass Science and Technology (Glafo, Växjö, Sweden, 1997), p. 476.
M. Aertsens and P. Van Iseghem in Scientific Basis for Nuclear Waste Management XX, edited by W. Murphy and D. Knecht (Mat. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. 412, 1996) pp. 271–277.
M. Aertsens in Glass, scientifc research for high performance containment (CEA/Vairh6, Summer Session Proc., 1998), p. 343.
M. Aertsens in Proc. of XVIII Int. Congr. on Glass, edited by. M. Choudhary, N. Huff, and C. Drummond (Am. Ceram. Soc., San Francisco, USA, 1998).
P. Dove and C. Crerar, Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 54, p. 955 (1990).
E. Vernaz and J. Dussossoy, Applied Geochem., Suppl. Issue no 1, p. 13 (1992).
C. Jantzen, in Corrosion of Glass, Ceramics and Ceramic Conductors-Principles, edited by D. Clark and B. Zoitos. (Noyes Publications, Park Ridge, New Jersey, 1992), p. 153.
F. Delage, F. Larche and E. Vernaz in Scientific Basis for Nuclear Waste Management XVI, edited by C. Interrante and R. Mc Pabalan (Mat. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. 294, 1993) pp. 171–176.
A. Lodding and P. Van Iseghem in Scientific Basis for Nuclear Waste Management XX, edited by W. Murphy and D. Knech (Mat. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. 412, 1996) pp. 229–238.
B. Bunker, D. Tallant, T. Headley, G. Turner and R. Kirkpatrick, Phys. Chem. Glasses 29, p. 106 (1988).
E. Vernaz, B. Grambow, W. Lutze, K. Lemmens, and P. Van Iseghem in Proc. Fourth Conf, European Comm. on management and disposal of radioactive waste, edited by T. McMenamin (EUR 17543 EN, 1996), pp. 239–253.
S. Xing, A. Buechele and I. Pegg in Scientific Basis for Nuclear Waste Management XVII, edited by A. Barkatt and R. Van Konynenbur, (Mat. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. 333, 1994) pp. 541–548.
G. Perera, R. Doremus and W. Lanford., J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 74, p. 1269 (1991).
O. Deruelle, P. Barboux, O. Spalla, S. Ricol, J. Lambard and E. Vernaz. in Glass, scientific research for high performance containment (CEA/Valrhô, Summer Session Proc., 1998), p. 435.
A. Helebrant, Silikaty 41 (4), p. 147 (1997).
T. Lee and D. Clark, Adv. Ceram. 20, p. 505 (1986).
L. Chick and L. Pederson, in Scientific Basis for Nuclear Waste Management VII, edited by G. Mc Vay (Mat. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc. 26, 1984) pp. 635–642.
Y. Xiao and A. Lasaga, Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 60, p. 2283 (1996).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aertsens, M. Testing the Grambow Glass Dissolution Model by Comparing it With Monte Carlo Simulation Results. MRS Online Proceedings Library 556, 409 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1557/PROC-556-409
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/PROC-556-409