Abstract
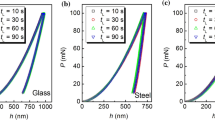
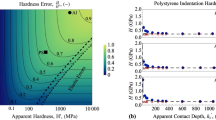
In the relationship between unloading contact stiffness, elastic modulus, and contact area, which is the fundamental basic equation for nanoindentation analysis, a multiplicative correction factor is generally needed. Sometimes this correction factor is called γ to take into account the elastic radial inward displacements, and sometimes it is called β to correct for the fact that the indenter shape is not a perfect cone. In reality, these two effects simultaneously coexist and thus it is proposed that this correction factor is α γ βγ. From nanoindentation data measured on three materials of different elastic moduli with a sharp Berkovich indenter and a worn one, the tip of which was blunt, it is demonstrated that the correction factor α does not have a constant value for a given material and indenter type but depends on the indenter tip rounding and also on the deformation of the indenter during indentation. It seems that α increases with the tip radius and also with the elastic modulus of the measured materials.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
W.C. Oliver and G.M. Pharr: An improved technique for determining hardness and elastic modulus using load and displacement sensing indentation experiments. J. Mater. Res. 7, 564 (1992).
M. Martin, and M. Troyon: Fundamental relations used in nano-indentation: Critical examination based on experimental measurements. J. Mater. Res. 17, 2227 (2002).
G.M. Pharr, W.C. Oliver, and F.R. Brotzen: On the generality of the relationship among contact stiffness, contact area, and elastic modulus during indentation. J. Mater. Res. 7, 613 (1992).
R.B. King: Elastic analysis of some punch problems for a layered medium. Int. J. Solids Structures 23, 1657 (1987).
J.C. Hay, A. Bolshakov, and G.M. Pharr: A critical examination of the fundamental relations used in the analysis of nanoindenta-tion data. J. Mater. Res. 14, 2296 (1999).
Y-T. Cheng and C-M. Cheng: Further analysis of indentation loading curves: Effects of tip rounding on mechanical property measurements. J. Mater. Res. 13, 1059 (1998).
M. Troyon, and M. Martin: A critical examination of the P-h relationship in nanoindentation. Appl. Phys. Lett. 83, 863 (2003).
J. Gong, H. Miao, and Z. Peng: On the contact area for nanoindentation tests with Berkovich indenter: Case study on soda-lime glass. Mater. Lett. 58, 1349 (2004).
C.W. Shih, M. Yang, and J.C.M. Li: Effect of tip radius on nanoindentation. J. Mater. Res. 6, 2623 (1991).
Y.Y. Lim and M.M. Chaudhri: Experimental investigations of the normal loading of elastic spherical and conical indenters on to elastic flats. Philos. Mag. 83, 3427 (2003).
M.M. Chaudhri: A note on a common mistake in the analysis of nanoindentation data. J. Mater. Res. 16, 336 (2001).
A. Bolshakov and G.M. Pharr: Influences of pile-up on the measurement of mechanical properties by load and depth-sensing indentation techniques. J. Mater. Res. 13, 1049 (1998).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Troyon, M., Huang, L. Correction factor for contact area in nanoindentation measurements. Journal of Materials Research 20, 610–617 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1557/JMR.2005.0099
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1557/JMR.2005.0099