Abstract
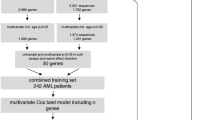
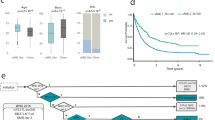
Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is characterized by clonal growth of immature leukemic blasts and develops either de novo or secondarily to anticancer treatment or to other hematologic disorders. Given that the current classification of AML, which is based on blast karyotype and morphology, is not sufficiently robust to predict the prognosis of each affected individual, new stratification schemes that are of better prognostic value are needed. Global profiling of gene expression in AML blasts has the potential both to identify a small number of genes whose expression is associated with clinical outcome and to provide insight into the molecular pathogenesis of this condition. Emerging genomics tools, especially DNA microarray analysis, have been applied in attempts to isolate new molecular markers for the differential diagnosis of AML and to identify genes that contribute to leukemogenesis. Progress in bioinformatics has also yielded means with which to classify patients according to clinical parameters such as long-term prognosis. The application of such analysis to large sets of gene expression data has begun to provide the basis for a new AML classification that is more powerful with regard to prediction of prognosis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
The Genome International Sequencing Consortium. Initial sequencing and analysis of the human genome. Nature. 2001;409: 860-921.
The C. elegans Sequencing Consortium. Genome sequence of the nematode C. elegans: a platform for investigating biology. Science. 1998;282:2012-2018.
Cheung VG, Morley M, Aguilar F, Massimi A, Kucherlapati R, Childs G. Making and reading microarrays. Nat Genet. 1999;21:15–19.
Khan J, Bittner ML, Saal LH, et al. cDNA microarrays detect activation of a myogenic transcription program by the PAX3-FKHR fusion gene. Proc NatlAcad Sci USA. 1999;96:13264–13269.
Heller RA, Schena M, Chai A, et al. Discovery and analysis of inflammatory disease-related genes using cDNA microarrays. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1997;94:2150–2155.
Dhanasekaran SM, Barrette TR, Ghosh D, et al. Delineation of prognostic biomarkers in prostate cancer. Nature. 2001;412:822–826.
Beer DG, Kardia SL, Huang CC, et al. Gene-expression profiles predict survival of patients with lung adenocarcinoma. Nat Med. 2002;8:816–824.
Jaffe ES, Harris NL, Vardman JW, eds. Tumours of Haematopoietic and Lymphoid Tissues. Lyon, France: IARC Press; 2001.
Grimwade D, Walker H, Oliver F, et al. The importance of diagnostic cytogenetics on outcome in AML: analysis of 1,612 patients entered into the MRC AML 10 trial: the Medical Research Council Adult and Children’s Leukaemia Working Parties. Blood. 1998; 92:2322–2333.
Byrd JC, Mrozek K, Dodge RK, et al. Pretreatment cytogenetic abnormalities are predictive of induction success, cumulative inci dence of relapse, and overall survival in adult patients with de novo acute myeloid leukemia: results from Cancer and Leukemia Group B (CALGB 8461). Blood. 2002;100:4325–4336.
Smith SM, Le Beau MM, Huo D, et al. Clinical-cytogenetic associations in 306 patients with therapy-related myelodysplasia and myeloid leukemia: the University of Chicago series. Blood. 2003; 102:43–52.
Bain BJ. The bone marrow aspirate of healthy subjects. Br J Haematol. 1996;94:206–209.
Schoch C, Kohlmann A, Schnittger S, et al. Acute myeloid leukemias with reciprocal rearrangements can be distinguished by specific gene expression profiles. Proc NatlAcad Sci U SA. 2002;99:10008–10013.
Yagi T, Morimoto A, Eguchi M, et al. Identification of a gene expression signature associated with pediatric AML prognosis. Blood. 2003;102:1849–1856.
Virtaneva K, Wright FA, Tanner SM, et al. Expression profiling reveals fundamental biological differences in acute myeloid leukemia with isolated trisomy 8 and normal cytogenetics. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001;98:1124–1129.
Miyazato A, Ueno S, Ohmine K, et al. Identification of myelodys- plastic syndrome-specific genes by DNA microarray analysis with purified hematopoietic stem cell fraction. Blood. 2001;98:422–427.
Hin AH, Miraglia S, Zanjani ED, et al. AC133, a novel marker for human hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells. Blood. 1997;90:5002–5012.
Oshima Y, Ueda M, Yamashita Y, et al. DNA microarray analysis of hematopoietic stem cell-like fractions from individuals with the M2 subtype of acute myeloid leukemia. Leukemia. 2003;17:1990–1997.
Lefkovits I, Kuhn L, Valiron O, Merle A, Kettman J. Toward an objective classification of cells in the immune system. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1988;85:3565–3569.
Fellenberg K, Hauser NC, Brors B, Neutzner A, Hoheisel JD, Vin-gron M. Correspondence analysis applied to microarray data. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2001;98:10781–10786.
Moore KA, Pytowski B, Witte L, Hicklin D, Lemischka IR. Hematopoietic activity of a stromal cell transmembrane protein containing epidermal growth factor-like repeat motifs. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1997;94:4011–4016.
Smas CM, Sul HS. Pref-1, a protein containing EGF-like repeats, inhibits adipocyte differentiation. Cell. 1993;73:725–734.
Hofmann WK, de Vos S, Komor M, Hoelzer D, Wachsman W, Koef-fler HP. Characterization of gene expression of CD34+ cells from normal and myelodysplastic bone marrow. Blood. 2002;100:3553–3560.
Pellagatti A, Esoof N, Watkins F, et al. Gene expression profiling in the myelodysplastic syndromes using cDNA microarray technology. Br J Haematol. 2004;125:576–583.
Brito-Babapulle F, Catovsky D, Galton DAG. Clinical and laboratory features of de novo acute myeloid leukemia with trilineage myelodysplasia. Br J Haematol. 1987;66:445–450.
Jinnai I, Tomonaga M, Kuriyama K, et al. Dysmegakaryocyto- poiesis in acute leukaemias: its predominance in myelomonocytic (M4) leukaemia and implication for poor response to chemotherapy. Br J Haematol. 1987;66:467–472.
Kuriyama K, Tomonaga M, Matsuo T, et al. Poor response to intensive chemotherapy in de novo acute myeloid leukaemia with trilineage myelodysplasia: Japan Adult Leukaemia Study Group (JALSG). Br J Haematol. 1994;86:767–773.
Tsutsumi C, Ueda M, Miyazaki Y, et al. DNA microarray analysis of dysplastic morphology associated with acute myeloid leukemia. Exp Hematol. 2004;32:828–835.
Bullinger L, Dohner K, Bair E, et al. Use of gene-expression profiling to identify prognostic subclasses in adult acute myeloid leukemia. N EnglJ Med. 2004;350:1605–1616.
Valk PJ, Verhaak RG, Beijen MA, et al. Prognostically useful gene- expression profiles in acute myeloid leukemia. N Engl J Med. 2004; 350:1617–1628.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Mano, H. Stratification of Acute Myeloid Leukemia Based on Gene Expression Profiles. Int J Hematol 80, 389–394 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1532/IJH97.04111
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1532/IJH97.04111