Abstract
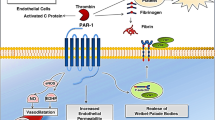
Certain serine proteases from the circulation (e.g., coagulation factors), inflammatory cells (e.g., mast-cell tryptase, neutrophil proteinase 3), and from many other cell types (e.g., trypsins) can specifically signal to cells by cleaving protease-activated receptors (PARs), a family of four G protein-coupled receptors. Proteases cleave PARs at specific sites within the extracellular amino-terminus to expose amino-terminal tethered ligand domains that bind to and activate the cleaved receptors. The proteases that activate PARs are often generated and released during injury and inflammation, and activated PARs orchestrate tissue responses to injury, including hemostasis, inflammation, pain, and repair. This review concerns protease and PAR signaling in the nervous system. Neurons of the central and peripheral nervous systems express all four PARs. Proteases that may derive from the circulation, inflammatory cells, or neural tissues can cleave PARs on neurons and thereby activate diverse signaling pathways that control survival, morphology, release of neurotransmitters, and activity of ion channels. In this manner proteases and PARs regulate neurodegeneration, neurogenic inflammation, and pain transmission. Thus, PARs may participate in disease states and PAR antagonists or agonists may be useful therapies for certain disorders.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akiyama H., Ikeda K., Kondo H., and McGeer P. L. (1992) Thrombin accumulation in brains of patients with Alzheimer’s disease. Neurosci. Lett. 146, 152–154.
Amadesi S., Nie J., Vergnolle N., et al. (2004) Protease-activated receptor 2 sensitizes the capsaicin receptor transient receptor potential vanilloid receptor 1 to induce hyperalgesia. J. Neurosci. 24, 4300–4312.
Aragay A. M., Collins L. R., Post G. R., et al. (1995) G12 requirement for thrombin-stimulated gene expression and DNA synthesis in 1321N1 astrocytoma cells. J. Biol. Chem. 270, 20,073–20,077.
Asfaha S., Brussee V., Chapman K., Zochodne D. W., and Vergnolle N. (2002) Proteinase-activated receptor-1 agonists attenuate nociception in response to noxious stimuli. Br. J. Pharmacol. 135, 1101–1106.
Baffy G., Yang L., Raj S., Manning D. R., and Williamson J. R. (1994) G protein coupling to the thrombin receptor in Chinese hamster lung fibroblasts. J. Biol. Chem. 269, 8483–8487.
Barbara G., Stanghellini V., De Giorgio R., et al. (2004) Activated mast cells in proximity to colonic nerves correlate with abdominal pain in irritable bowel syndrome. Gastroenterology 126, 693–702.
Barrios V. E., Jarosinski M. A., and Wright C. D. (2003) Proteinase-activated receptor-2 mediates hyper-responsiveness in isolated guinea pig bronchi. Biochem. Pharmacol. 66, 519–525.
Beecher K. L., Andersen T. T., Fenton J. W. N., and Festoff B. W. (1994) Thrombin receptor peptides induce shape change in neonatal murine astrocytes in culture. J. Neurosci. Res. 37, 108–115.
Benka M. L., Lee M., Wang G. R., et al. (1995) The thrombin receptor in human platelets is coupled to a GTP binding protein of the G alpha q family. FEBS Lett. 363, 49–52.
Bohm S. K., Khitin L. M., Grady E. F., Aponte G., Payan D. G., and Bunnett N. W. (1996a) Mechanisms of desensitization and resensitization of proteinase-activated receptor-2. J. Biol. Chem. 271, 22,003–22,016.
Bohm S. K., Kong W., Bromme D., et al. (1996b) Molecular cloning, expression and potential functions of the human proteinase-activated receptor-2. Biochem. J. 314, 1009–1016.
Buresi M. C., Buret A. G., Hollenberg M. D., and MacNaughton W. K. (2002) Activation of proteinase-activated receptor 1 stimulates epithelial chloride secretion through a unique MAP kinase-and cyclooxygenase-dependent pathway. FASEB J. 16, 1515–1525.
Bustos D., Negri G., De Paula J. A., et al. (1998) Colonic proteinases: increased activity in patients with ulcerative colitis. Medicina (B Aires) 58, 262–264.
Camerer E., Huang W., and Coughlin S. R. (2000) Tissue factor- and factor X-dependent activation of protease-activated receptor 2 by factor VIIa. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 97, 5255–5260.
Caterina M. J., Schumacher M. A., Tominaga M., Rosen T. A., Levine J. D., and Julius D. (1997) The capsaicin receptor: a heat-activated ion channel in the pain pathway. Nature 389, 816–824.
Cavanaugh K. P., Gurwitz D., Cunningham D. D., and Bradshaw R. A. (1990) Reciprocal modulation of astrocyte stellation by thrombin and protease nexin-1. J. Neurochem. 54, 1735–1743.
Cenac N., Coelho A. M., Nguyen C., et al. (2002) Induction of intestinal inflammation in mouse by activation of proteinase-activated receptor-2. Am. J. Pathol. 161, 1903–1915.
Cenac N., Garcia-Villar R., Ferrier L., et al. (2003) Proteinase-activated receptor-2-induced colonic inflammation in mice: possible involvement of afferent neurons, nitric oxide, and paracellular permeability. J. Immunol. 170, 4296–4300.
Cheng T., Liu D., Griffin J. H., et al. (2003) Activated protein C blocks p53-mediated apoptosis in ischemic human brain endothelium and is neuroprotective. Nat. Med. 9, 338–342.
Choi S. H., Joe E. H., Kim S. U., and Jin B. K. (2003a) Thrombin-induced microglial activation produces degeneration of nigral dopaminergic neurons in vivo. J. Neurosci. 23, 5877–5886.
Choi S. H., Lee da Y., Ryu J. K., Kim J., Joe E. H., and Jin B. K. (2003b) Thrombin induces nigral dopaminergic neurodegeneration in vivo by altering expression of death-related proteins. Neurobiol. Dis. 14, 181–193.
Chuang H. H., Prescott E. D., Kong H., et al. (2001) Bradykinin and nerve growth factor release the capsaicin receptor from PtdIns(4,5)P2-mediated inhibition. Nature 411, 957–962.
Coelho A. M., Vergnolle N., Guiard B., Fioramonti J., and Bueno L. (2002) Proteinases and proteinase-activated receptor 2: a possible role to promote visceral hyperalgesia in rats. Gastroenterology 122, 1035–1047.
Compton S. J., Renaux B., Wijesuriya S. J., and Hollenberg M. D. (2001) Glycosylation and the activation of proteinase-activated receptor 2 (PAR(2)) by human mast cell tryptase. Br. J. Pharmacol. 134, 705–718.
Compton S. J., Sandhu S., Wijesuriya S. J., and Hollenberg M. D. (2002) Glycosylation of human proteinase-activated receptor-2 (hPAR2): role in cell surface expression and signalling. Biochem. J. 368, 495–505.
Corvera C. U., Dery O., and McConalogue K. (1997) Mast cell tryptase regulates rat colonic myocytes through proteinase-activated receptor 2. J. Clin. Invest. 100, 1383–1393.
Corvera C. U., Dery O., McConalogue K., et al. (1999) Thrombin and mast cell tryptase regulate guineapig myenteric neurons through proteinase-activated receptors-1 and -2. J. Physiol. 517, 741–756.
Cottrell G. S., Amadesi S., Grady E. F., and Bunnett N. W. (2004) Trypsin IV, a novel agonist of protease-activated receptors 2 and 4. J. Biol. Chem. 279, 13,532–13,539.
Coughlin S. R. (2001) Protease-activated receptors in vascular biology. Thromb. Haemost. 86, 298–307.
Cuffe J. E., Bertog M., Velazquez-Rocha S., Dery O., Bunnett N., and Korbmacher C. (2002) Basolateral PAR-2 receptors mediate KCl secretion and inhibition of Na+ absorption in the mouse distal colon. J. Physiol. 539, 209–222.
D’Andrea M. R., Derian C. K., Leturcq D., et al. (1998) Characterization of protease-activated receptor-2 immunoreactivity in normal human tissues. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 46, 157–164.
Dai Y., Moriyama T., Higashi T., et al. (2004) Proteinase-activated receptor 2-mediated potentiation of transientreceptor potential vanilloid subfamily 1 activity reveals a mechanism for proteinase-induced inflammatory pain. J. Neurosci. 24, 4293–4299.
de Garavilla L., Vergnolle N., Young S. H., et al. (2001) Agonists of proteinase-activated receptor 1 induce plasma extravasation by a neurogenic mechanism. Br. J. Pharmacol. 133, 975–987.
DeFea K. A., Zalevsky J., Thoma M. S., Dery O., Mullins R. D., and Bunnett N. W. (2000) beta-arrestin-dependent endocytosis of proteinase-activated receptor 2 is required for intracellular targeting of activated ERK1/2. J. Cell Biol. 148, 1267–1281.
Dery O., Corvera C. U., Steinhoff M., and Bunnett N. W. (1998) Proteinase-activated receptors: novel mechanisms of signaling by serine proteases. Am. J. Physiol. 274, C1429-C1452.
Dery O., Thoma M. S., Wong H., Grady E. F., and Bunnett N. W. (1999) Trafficking of proteinase-activated receptor-2 and β-arrestin-1 tagged with green fluorescent protein. beta-Arrestin-dependent endocytosis of a proteinase receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 274, 18,524–18,535.
Dihanich M., Kaser M., Reinhard E., Cunningham D., and Monard D. (1991) Prothrombin mRNA is expressed by cells of the nervous system. Neuron 6, 575–581.
Ding-Pfennigdorff D., Averbeck B., and Michaelis M. (2004) Stimulation of PAR-2 excites and sensitizes rat cutaneous C-nociceptors to heat. Neuroreport 15, 2071–2075.
Donovan F. M. and Cunningham D. D. (1998) Signaling pathways involved in thrombin-induced cell protection. J. Biol. Chem. 273, 12,746–12,752.
Donovan F. M., Pike C. J., Cotman C. W., and Cunningham D. D. (1997) Thrombin induces apoptosis in cultured neurons and astrocytes via a pathway requiring tyrosine kinase and RhoA activities. J. Neurosci. 17, 5316–5326.
Festoff B. W., Smirnova I. V., Ma J., and Citron B. A. (1996) Thrombin, its receptor and protease nexin I, its potent serpin, in the nervous system. Semin. Thromb. Hemost. 22, 267–271.
Gao C., Liu S., Hu H. Z., et al. (2002) Serine proteases excite myenteric neurons through protease-activated receptors in guinea pig small intestine. Gastroenterology 123, 1554–1564.
Gill J. S., Pitts K., Rusnak F. M., Owen W. G., and Windebank A. J. (1998) Thrombin induced inhibition of neurite outgrowth from dorsal root ganglion neurons. Brain Res. 797, 321–327.
Gingrich M. B., Junge C. E., Lyuboslavsky P., and Traynelis S. F. (2000) Potentiation of NMDA receptor function by the serine protease thrombin. J. Neurosci. 20, 4582–4595.
Green B. T., Bunnett N. W., Kulkarni-Narla A., Steinhoff M., and Brown D. R. (2000) Intestinal type 2 proteinase-activated receptors: expression in opioid-sensitive secretomotor neural circuits that mediate epithelial ion transport. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 295, 410–416.
Gurwitz D. and Cunningham D. D. (1988) Thrombin modulates and reverses neuroblastoma neurite outgrowth. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 85, 3440–3444.
Hoogerwerf W. A., Shenoy M., Winston J. H., Xiao S. Y., He Z., and Pasricha P. J. (2004) Trypsin mediates nociception via the proteinase-activated receptor 2: A potentially novel role in pancreatic pain. Gastroenterology 127, 883–891.
Hoogerwerf W. A., Zou L., Shenoy M., et al. (2001) The proteinase-activated receptor 2 is involved in nociception. J. Neurosci. 21, 9036–9042.
Hoxie J. A., Ahuja M., Belmonte E., Pizarro S., Parton R., and Brass L. F. (1993) Internalization and recycling of activated thrombin receptors. J. Biol. Chem. 268, 13,756–13,763.
Hu H. J., Bhave G., and Gereau R. W. T. (2002) Prostaglandin and protein kinase A-dependent modulation of vanilloid receptor function by metabotropic glutamate receptor 5: potential mechanism for thermal hyperalgesia. J. Neurosci. 22, 7444–7452.
Hung D. T., Vu T. H., Nelken N. A., and Coughlin S. R. (1992a) Thrombin-induced events in non-platelet cells are mediated by the unique proteolytic mechanism established for the cloned platelet thrombin receptor. J. Cell Biol. 116, 827–832.
Hung D. T., Wong Y. H., Vu T. K., and Coughlin S. R. (1992b) The cloned platelet thrombin receptor couples to at least two distinct effectors to stimulate phosphoinositide hydrolysis and inhibit adenylyl cyclase. J. Biol. Chem. 267, 20,831–20,834.
Iaccarino G., Rockman H. A., Shotwell K. F., Tomhave E. D., and Koch W. J. (1998) Myocardial overexpression of GRK3 in transgenic mice: evidence for in vivo selectivity of GRKs. Am. J. Physiol. 275, H1298-H1306.
Ishihara H., Connolly A. J., Zeng D., et al. (1997) Protease-activated receptor 3 is a second thrombin receptor in humans. Nature 386, 502–506.
Ishii K., Chen J., Ishii M., et al. (1994) Inhibition of thrombin receptor signaling by a G protein coupled receptor kinase. Functional specificity among G protein coupled receptor kinases. J. Biol. Chem. 269, 1125–1130.
Jacob C., Cottrell G. S., Gehringer D., Schmidlin F., Grady E. F., and Bunnett N. W. (2005) c-Cbl Mediates Ubiquitination, Degradation, and Down-regulation of Human Protease-activated Receptor 2. J. Biol. Chem. 280, 16,076–16,087.
Jalink K., van Corven E. J., Hengeveld T., Morii N., Narumiya S., and Moolenaar W. H. (1994) Inhibition of lysophosphatidate- and thrombin-induced neurite retraction and neuronal cell rounding by ADP ribosylation of the small GTP-binding protein Rho. J. Cell Biol. 126, 801–810.
Julius D. and Basbaum A. I. (2001) Molecular mechanisms of nociception. Nature 413, 203–210.
Junge C. E., Lee C. J., Hubbard K. B., et al. (2004) Protease-activated receptor-1 in human brain: localization and functional expression in astrocytes. Exp. Neurol. 188, 94–103.
Kahn M. L., Zheng Y. W., Huang W., et al. (1998) A dual thrombin receptor system for platelet activation. Nature 394, 690–694.
Kaufmann R., Patt S., Zieger M., et al. (2000) The two-receptor system PAR-1/PAR-4 mediates alpha-thrombin-induced [Ca(2+)](i) mobilization in human astrocytoma cells. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 126, 91–94.
Kawabata A., Itoh H., Kawao N., et al. (2004) Activation of trigeminal nociceptive neurons by parotid PAR-2 activation in rats. Neuroreport 15, 1617–1621.
Kawabata A., Kawao N., Kuroda R., Itoh H., and Nishikawa H. (2002a) Specific expression of spinal Fos after PAR-2 stimulation in mast cell-depleted rats. Neuroreport 13, 511–514.
Kawabata A., Kawao N., Kuroda R., Tanaka A., Itoh H., and Nishikawa H. (2001a) Peripheral PAR-2 triggers thermal hyperalgesia and nociceptive responses in rats. Neuroreport 12, 715–719.
Kawabata A., Kawao N., Kuroda R., Tanaka A., and Shimada C. (2002b) The PAR-1-activating peptide attenuates carrageenan-induced hyperalgesia in rats. Peptides 23, 1181–1183.
Kawabata A., Kinoshita M., Kuroda R., and Kakehi K. (2002c) Capsazepine partially inhibits neurally mediated gastric mucus secretion following activation of protease-activated receptor 2. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 29, 360–361.
Kawabata A., Kinoshita M., Nishikawa H., et al. (2001b) The protease-activated receptor-2 agonist induces gastric mucus secretion and mucosal cytoprotection. J. Clin. Invest. 107, 1443–1450.
Kawabata A., Kuroda R., Nishida M., et al. (2002d) Protease-activated receptor-2 (PAR-2) in the pancreas and parotid gland: immunolocalization and involvement of nitric oxide in the evoked amylase secretion. Life Sci. 71, 2435–2446.
Kawao N., Ikeda H., Kitano T., et al. (2004) Modulation of capsaicin-evoked visceral pain and referred hyperalgesia by protease-activated receptors 1 and 2. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 94, 277–285.
Kiseleva E. V., Storozhevykh T. P., Pinelis V. G., Gluza E., and Strukova S. M. (2004) Role of thrombin in activation of neurons in rat hippocampus. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 137, 453–456.
Klages B., Brandt U., Simon M. I., Schultz G., and Offermanns S. (1999) Activation of G12/G13 results in shape change and Rho/Rho-kinase-mediated myosin light chain phosphorylation in mouse platelets. J. Cell Biol. 144, 745–754.
Kong W., McConalogue K., Khitin L. M., et al. (1997) Luminal trypsin may regulate enterocytes through proteinase-activated receptor 2. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 94, 8884–8889.
Linden D. R., Manning B. P., Bunnett N. W., and Mawe G. M. (2001) Agonists of proteinase-activated receptor 2 excite guinea pigileal myenteric neurons. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 431, 311–314.
Lourbakos A., Chinni C., Thompson P., et al. (1998) Cleavage and activation of proteinase-activated receptor-2 on human neutrophils by gingipain-R from Porphyromonas gingivalis. FEBS Lett. 435, 45–48.
Lourbakos A., Potempa J., Travis J., et al. (2001) Arginine-specific protease from porphyromonas gingivalis activates protease-activated receptors on human oral epithelial cells and induces interleukin-6 secretion. Infect. Immun. 69, 5121–5130.
Macfarlane S. R., Seatter M. J., Kanke T., Hunter G. D., and Plevin R. (2001) Proteinase-activated receptors. Pharmacol. Rev. 53, 245–282.
Miller H. R. and Pemberton A. D. (2002) Tissue-specific expression of mast cell granule serine proteinases and their role in inflammation in the lung and gut. Immunology 105, 375–390.
Minn A., Schubert M., Neiss W. F., and Muller-Hill B. (1998) Enhanced GFAP expression in astrocytes of transgenic mice expressing the human brain-specific trypsinogen IV. Glia 22, 338–347.
Mirza H., Schmidt V. A., Derian C. K., Jesty J., and Bahou W. F. (1997) Mitogenic responses mediated through the proteinase-activated receptor-2 are induced by expressed forms of mast cell alpha-or beta-tryptases. Blood 90, 3914–3922.
Mohapatra D. P. and Nau C. (2003) Desensitization of capsaicin-activated currents in the vanilloid receptor TRPV1 is decreased by the cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 278, 50,080–50,090.
Molino M., Barnathan E. S., Numerof R., et al. (1997) Interactions of mast cell tryptase with thrombin receptors and PAR-2. J. Biol. Chem. 272, 4043–4049.
Moller T., Hanisch U. K., and Ransom B. R. (2000) Thrombin-induced activation of cultured rodent microglia. J. Neurochem. 75, 1539–1547.
Mule F., Baffi M. C., Capparelli A., and Pizzuti R. (2003) Involvement of nitric oxide and tachykinins in the effects induced by protease-activated receptors in rat colon longitudinal muscle. Br. J. Pharmacol. 139, 598–604.
Mule F., Pizzuti R., Capparelli A., and Vergnolle N. (2004) Evidence for the presence of functional protease activated receptor 4 (PAR4) in the rat colon. Gut 53, 229–234.
Nakanishi-Matsui M., Zheng Y. W., Sulciner D. J., Weiss E. J., Ludeman M. J., and Coughlin S. R. (2000) PAR3 is a cofactor for PAR4 activation by thrombin. Nature 404, 609–613.
Niclou S. P., Suidan H. S., Pavlik A., Vejsada R., and Monard D. (1998) Changes in the expression of protease-activated receptor 1 and protease nexin-1 mRNA during rat nervous system development and after nerve lesion. Eur. J. Neurosci. 10, 1590–1607.
O’Brien P. J., Prevost N., Molino M., et al. (2000) Thrombin responses in human endothelial cells. Contributions from receptors other than PAR1 include the transactivation of PAR2 by thrombin-cleaved PAR1. J. Biol. Chem. 275, 13,502–13,509.
Offermanns S. (2001) In vivo functions of heterotrimeric G proteins: studies in Gα-deficient mice. Oncogene 20, 1635–1642.
Offermanns S., Laugwitz K. L., Spicher K., and Schultz G. (1994) G proteins of the G12 family are activated via thromboxane A2 and thrombin receptors in human platelets. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 91, 504–508.
Offermanns S., Mancino V., Revel J. P., and Simon M. I. (1997a) Vascular system defects and impaired cell chemokinesis as a result of Gα13 deficiency. Science 275, 533–536.
Offermanns S., Toombs C. F., Hu Y. H., and Simon M. I. (1997b) Defective platelet activation in G alpha(q)-deficient mice. Nature 389, 183–186.
Ossovskaya V. S. and Bunnett N. W. (2004) Protease-activated receptors: contribution to physiology and disease. Physiol. Rev. 84, 579–621.
Paing M. M., Stutts A. B., Kohout T. A., Lefkowitz R. J., and Trejo J. (2002) β-Arrestins regulate protease-activated receptor-1 desensitization but not internalization or down-regulation. J. Biol. Chem. 277, 1292–1300.
Pindon A., Berry M., and Hantai D. (2000) Thrombomodulin as a new marker of lesion-induced astrogliosis: involvement of thrombin through the G protein-coupled protease-activated receptor-1. J. Neurosci. 20, 2543–2550.
Prenzel N., Zwick E., Daub H., et al. (1999) EGF receptor transactivation by G protein-coupled receptors requires metalloproteinase cleavage of proHB-EGF. Nature 402, 884–888.
Raithel M., Winterkamp S., Pacurar A., Ulrich P., Hochberger J., and Hahn E. G. (2001) Release of mast cell tryptase from human colorectal mucosa in inflammatory bowel disease. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 36, 174–179.
Rathee P. K., Distler C., Obreja O., et al. (2002) PKA/AKAP/VR-1 module: a common link of Gs-mediated signaling to thermal hyperalgesia. J. Neurosci. 22, 4740–4745.
Reed D. E., Barajas-Lopez C., Cottrell G., et al. (2003) Mast cell tryptase and proteinase-activated receptor 2 induce hyperexcitability of guinea-pig submucosal neurons. J. Physiol. 547, 531–542.
Riewald M., Petrovan R. J., Donner A., Mueller B. M., and Ruf W. (2002) Activation of endothelial cell protease activated receptor 1 by the protein C pathway. Science 296, 1880–1882.
Riewald M. and Ruf W. (2001) Mechanistic coupling of protease signaling and initiation of coagulation by tissue factor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 98, 7742–7747.
Roosterman D., Schmidlin F., and Bunnett N. W. (2003) Rab5a and rab11a mediate agonist-induced trafficking of protease-activated receptor 2. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 284, C1319-C1329.
Ryu J., Pyo H., Jou I., and Joe E. (2000) Thrombin induces NO release from cultured rat microglia via protein kinase C, mitogen-activated protein kinase, and NF-kappa B. J. Biol. Chem. 275, 29,955–29,959.
Sambrano G. R., Huang W., Faruqi T., Mahrus S., Craik C., and Coughlin S. R. (2000) Cathepsin G activates protease-activated receptor-4 in human platelets. J. Biol. Chem. 275, 6819–6823.
Santos J., Bayarri C., Saperas E., et al. (1999) Characterisation of immune mediator release during the immediate response to segmental mucosal challenge in the jejunum of patients with food allergy. Gut 45, 553–558.
Santulli R. J., Derian C. K., Darrow A. L., et al. (1995) Evidence for the presence of a protease-activated receptor distinct from the thrombin receptor in human keratinocytes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 92, 9151–9155.
Sawada K., Nishibori M., Nakaya N., Wang Z., and Saeki K. (2000) Purification and characterization of a trypsin-like serine proteinase from rat brain slices that degrades laminin and type IV collagen and stimulates protease-activated receptor-2. J. Neurochem. 74, 1731–1738.
Scudamore C. L., Thornton E. M., McMillan L., Newlands G. F., and Miller H. R. (1995) Release of the mucosal mast cell granule chymase, rat mast cell protease-II, during anaphylaxis is associated with the rapid development of paracellular permeability to macromolecules in rat jejunum. J. Exp. Med. 182, 1871–1881.
Shu X. and Mendell L. M. (1999) Nerve growth factor acutely sensitizes the response of adult rat sensory neurons to capsaicin. Neurosci. Lett. 274, 159–162.
Smirnova I. V., Citron B. A., Arnold P. M., and Festoff B. W. (2001) Neuroprotective signal transduction in model motor neurons exposed to thrombin: G protein modulation effects on neurite outgrowth, Ca(2+) mobilization, and apoptosis. J. Neurobiol. 48, 87–100.
Smirnova I. V., Zhang S. X., Citron B. A., Arnold P. M., and Festoff B. W. (1998) Thrombin is an extracellular signal that activates intracellular death protease pathways inducing apoptosis in model motor neurons. J. Neurobiol. 36, 64–80.
Smith-Swintosky V. L., Cheo-Isaacs C. T., D’Andrea M. R., Santulli R. J., Darrow A. L., and Andrade-Gordon P. (1997) Protease-activated receptor-2 (PAR-2) is present in the rat hippocampus and is associated with neurodegeneration. J. Neurochem. 69, 1890–1896.
Smith-Swintosky V. L., Zimmer S., Fenton J. W., II, and Mattson M. P. (1995a) Opposing actions of thrombin and protease nexin-1 on amyloid β-peptide toxicity and on accumulation of peroxides and calcium in hippocampal neurons. J. Neurochem. 65, 1415–1418.
Smith-Swintosky V. L., Zimmer S., Fenton J. W., II, and Mattson M. P. (1995b) Protease nexin-1 and thrombin modulate neuronal Ca2+ homeostasis and sensitivity to glucose deprivation-induced injury. J. Neurosci. 15, 5840–5850.
Southan C. (2001) A genomic perspective on human proteases. FEBS Lett. 498, 214–218.
Stead R. H., Tomioka M., Quinonez G., Simon G. T., Felten S. Y., and Bienenstock J. (1987) Intestinal mucosal mast cells in normal and nematodeinfected rat intestines are in intimate contact with peptidergic nerves. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 84, 2975–2979.
Steinhoff M., Vergnolle N., Young S. H., et al. (2000) Agonists of proteinase-activated receptor 2 induce inflammation by a neurogenic mechanism. Nat. Med. 6, 151–158.
Striggow F., Riek M., Breder J., Henrich-Noack P., Reymann K. G., and Reiser G. (2000) The protease thrombin is an endogenous mediator of hippocampal neuroprotection against ischemia at low concentrations but causes degeneration at high concentrations. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 97, 2264–2269.
Suidan H. S., Bouvier J., Schaerer E., Stone S. R., Monard D., and Tschopp J. (1994) Granzyme A released upon stimulation of cytotoxic T lymphocytes activates the thrombin receptor on neuronal cells and astrocytes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 91, 8112–8116.
Sun G., Stacey M. A., Schmidt M., Mori L., and Mattoli S. (2001) Interaction of mite allergens der p3 and der p9 with protease-activated receptor-2 expressed by lung epithelial cells. J. Immunol. 167, 1014–1021.
Suo Z., Wu M., Citron B. A., Gao C., and Festoff B. W. (2003) Persistent protease-activated receptor 4 signaling mediates thrombin-induced microglial activation. J. Biol. Chem. 33, 31,177–31,183.
Tiruppathi C., Yan W., Sandoval R., et al. (2000) G protein-coupled receptor kinase-5 regulates thrombin-activated signaling in endothelial cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 97, 7440–7445.
Tominaga M., Wada M., and Masu M. (2001) Potentiation of capsaicin receptor activity by metabotropic ATP receptors as a possible mechanism for ATP-evoked pain and hyperalgesia. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 98, 6951–6956.
Trejo J., Altschuler Y., Fu H. W., Mostov K. E., and Coughlin S. R. (2000) Protease-activated receptor-1 down-regulation: a mutant HeLa cell line suggests novel requirements for PAR1 phosphorylation and recruitment to clathrin-coated pits. J. Biol. Chem. 275, 31,255–31,265.
Trevisani M., Smart D., Gunthorpe M. J., et al. (2002) Ethanol elicits and potentiates nociceptor responses via the vanilloid receptor-1. Nat. Neurosci. 5, 546–551.
Turgeon V. L., Lloyd E. D., Wang S., Festoff B. W., and Houenou L. J. (1998) Thrombin perturbs neurite outgrowth and induces apoptotic cell death in enriched chick spinal motoneuron cultures through caspase activation. J. Neurosci. 18, 6882–6891.
Ubl J. J. and Reiser G. (1997a) Activity of protein kinase C is necessary for sustained thrombin-induced [Ca2+]i oscillations in rat glioma cells. Pflugers Arch. 433, 312–320.
Ubl J. J. and Reiser G. (1997b) Characteristics of thrombin-induced calcium signals in rat astrocytes. Glia 21, 361–369.
Ubl J. J., Vohringer C., and Reiser G. (1998) Co-existence of two types of [Ca2+]i-inducing protease-activated receptors (PAR-1 and PAR-2) in rat astrocytes and C6 glioma cells. Neuroscience 86, 597–609.
Uehara A., Muramoto K., Takada H., and Sugawara S. (2003) Neutrophil serine proteinases activate human nonepithelial cells to produce inflammatory cytokines through protease-activated receptor 2. J. Immunol. 170, 5690–5696.
Vaughan P. J., Pike C. J., Cotman C. W., and Cunningham D. D. (1995) Thrombin receptor activation protects neurons and astrocytes from cell death produced by environmental insults. J. Neurosci. 15, 5389–5401.
Vaughan P. J., Su J., Cotman C. W., and Cunningham D. D. (1994) Protease nexin-1, a potent thrombin inhibitor, is reduced around cerebral blood vessels in Alzheimer’s disease. Brain Res. 668, 160–170.
Vellani V., Mapplebeck S., Moriondo A., Davis J. B., and McNaughton P. A. (2001) Protein kinase C activation potentiates gating of the vanilloid receptor VR1 by capsaicin, protons, heat and anandamide. J. Physiol. 534, 813–825.
Vergnolle N. (2004) Modulation of visceral pain and inflammation by protease-activated receptors. Br. J. Pharmacol. 141, 1264–1274.
Vergnolle N., Bunnett N. W., Sharkey K. A., et al. (2001a) Proteinase-activated receptor-2 and hyperalgesia: a novel pain pathway. Nat. Med. 7, 821–826.
Vergnolle N., Ferazzini M., D’Andrea M. R., Buddenkotte J., and Steinhoff M. (2003) Proteinase-activated receptors: novel signals for peripheral nerves. Trends Neurosci. 26, 496–500.
Vergnolle N., Macnaughton W. K., Al-Ani B., Saifeddine M., Wallace J. L., and Hollenberg M. D. (1998) Proteinase-activated receptor 2 (PAR2)-activating peptides: identification of a receptor distinct from PAR2 that regulates intestinal transport. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 95, 7766–7771.
Vergnolle N., Wallace J. L., Bunnett N. W., and Hollenberg M. D. (2001b) Protease-activated receptors in inflammation, neuronal signaling and pain. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 22, 146–152.
Vouret-Craviari V., Boquet P., Pouyssegur J., and Van Obberghen-Schilling E. (1998) Regulation of the actin cytoskeleton by thrombin in human endothelial cells: role of Rho proteins in endothelial barrier function. Mol. Biol. Cell 9, 2639–2653.
Vu T. K., Wheaton V. I., Hung D. T., Charo I., and Coughlin S. R. (1991) Domains specifying thrombin-receptor interaction. Nature 353, 674–677.
Wang H., Ubl J. J., and Reiser G. (2002a) Four subtypes of protease-activated receptors, co-expressed in rat astrocytes, evoke different physiological signaling. Glia 37, 53–63.
Wang H., Ubl J. J., Stricker R., and Reiser G. (2002b) Thrombin (PAR-1)-induced proliferation in astrocytes via MAPK involves multiple signaling pathways. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 283, C1351-C1364.
Wang Y., Zhou Y., Szabo K., Haft C. R., and Trejo J. (2002c) Down-regulation of protease-activated receptor-1 is regulated by sorting nexin 1. Mol. Biol. Cell 13, 1965–1976.
Weinstein J. R., Gold S. J., Cunningham D. D., and Gall C. M. (1995) Cellular localization of thrombin receptor mRNA in rat brain: expression by mesencephalic dopaminergic neurons and codistribution with prothrombin mRNA. J. Neurosci. 15, 2906–2919.
Widmann C., Gibson S., Jarpe M. B., and Johnson G. L. (1999) Mitogen-activated protein kinase: conservation of a three-kinase module from yeast to human. Physiol. Rev. 79, 143–180.
Wiegand U., Corbach S., Minn A., Kang J., and Muller-Hill B. (1993) Cloning of the cDNA encoding human brain trypsinogen and characterization of its product. Gene 136, 167–175.
Winitz S., Gupta S. K., Qian N. X., Heasley L. E., Nemenoff R. A., and Johnson G. L. (1994) Expression of a mutant Gi2 α-subunit inhibits ATP and thrombin stimulation of cytoplasmic phospholipase A2-mediated arachidonic acid release independent of Ca2+ and mitogen-activated protein kinase regulation. J. Biol. Chem. 269, 1889–1895.
Xu W. F., Andersen H., Whitmore T. E., et al. (1998) Cloning and characterization of human protease-activated receptor 4. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 95, 6642–6646.
Yang P. C., Berin M. C., Yu L., and Perdue M. H. (2001) Mucosal pathophysiology and inflammatory changes in the late phase of the intestinal allergic reaction in the rat. Am. J. Pathol. 158, 681–690.
Zhao A. and Shea-Donohue T. (2003) PAR-2 agonists induce contraction of murine small intestine through neurokinin receptors. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 285, G696-G703.
Zygmunt P. M., Petersson J., Andersson D. A., et al. (1999) Vanilloid receptors on sensory nerves mediate the vasodilator action of anandamide. Nature 400, 452–457.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Saito, T., Bunnett, N.W. Protease-activated receptors. Neuromol Med 7, 79–99 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1385/NMM:7:1-2:079
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1385/NMM:7:1-2:079