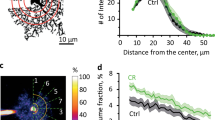
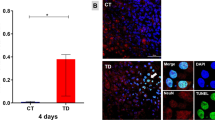
Abstract
Responses to neuronal degeneration are complex, involving activation of microglia, astrocytes, and synaptic remodeling. It has also been suggested that neuronal injury stimulates neurogenesis, the production of new neurons from neural stem cells. Because dietary restriction (DR) can increase hippocampal neurogenesis and promotes the survival of neurons following injury, we determined the effects of DR on the responses of neural stem cells, microglia, and astrocytes in the hippocampus to seizure-induced hippocampal damage. Mice on ad libitum or DR diets were given an intrahippocampal injection of kainate, administered the DNA precursor bromodeoxyuridine (BrdU) during a 5-d period, and euthanized 1 d or 3 wk later. Although kainate greatly increased the numbers of BrdU-labeled cells, it did not enhance neurogenesis and damaged neurons were not replaced. Instead, most BrdU-labeled cells were either proliferating microglia or neural progenitor cells that subsequently died. Microgliosis was transient and was strongly correlated with the amount of damage to CA3 neurons, whereas astrocytosis was delayed and not correlated with neuronal loss. Surprisingly, neurogenesis was not increased in response to seizure-induced damage, and although DR increased basal neurogenesis, it did not promote neurogenesis following brain injury. DR significantly decreased seizure-induced microgliosis, but did not affect astrocytosis. Our findings show that DR suppresses injury-induced microgliosis suggesting a contribution of a reduced microglial response to the neuroprotective effects of DR.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andersson P. B., Perry V. H., and Gordon S. (1991) The CNS acute inflammatory response to excitotoxic neuronal cell death. Immunol. Lett. 30, 177–181.
Anson R. M., Guo Z., de Cabo R., et al. (2003) Intermittent fasting dissociates beneficial effects of dietary restriction on glucose metabolism and neuronal resistance to injury from calorie intake. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 100, 6216–6220.
Bengzon J., Kokaia Z., Elmer E., Nanobashvili A., Kokaia M., and Lindvall O. (1997) Apoptosis and proliferation of dentate gyrus neurons after single and intermittent limbic seizures. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 94, 10432–10437.
Benraiss A., Chmielnicki E., Lerner K., Roh D., and Goldman S. A. (2001) Adenoviral brain-derived neurotrophic factor induces both neostriatal and olfactory neuronal recruitment from endogenous progenitor cells in the adult forebrain. J. Neurosci. 21, 6718–6731.
Bruce A. J., Boling W., Kindy M. S., et al. (1996) Altered neuronal and microglial responses to excitotoxic and ischemic brain injury in mice lacking TNF receptors. Nat. Med. 2, 788–794.
Bruce-Keller A. J., Umberger G., McFall R., and Mattson M. P. (1999) Food restriction reduces brain damage and improves behavioral outcome following excitotoxic and metabolic insults. Ann. Neurol. 45, 8–15.
Cameron H. A. and McKay R. D. (2001) Adult neurogenesis produces a large pool of new granule cells in the dentate gyrus. J. Comp. Neurol. 435, 406–417.
Carro E., Nunez A., Busiguina S., and Torres-Aleman I. (2000) Circulating insulin-like growth factor I mediates effects of exercise on the brain. J. Neurosci. 20, 2926–2933.
Cheng A., Wang S., Cai J., Rao M. S., and Mattson M. P. (2003) Nitric oxide acts in a positive feedback loop with BDNF to regulate neural progenitor cell proliferation and differentiation in the mammalian brain. Dev. Biol. 258, 319–333.
Covolan L., Ribeiro L. T., Longo B. M., and Mello L. E. (2000) Cell damage and neurogenesis in the dentate granule cell layer of adult rats after pilocarpine- or kainate-induced status epilepticus. Hippocampus 10, 169–180.
Duan W. and Mattson M. P. (1999) Dietary restriction and 2-deoxyglucose administration improve behavioral outcome and reduce degeneration of dopaminergic neurons in models of Parkinson’s disease. J. Neurosci. Res. 57, 195–206.
Duan W., Guo Z., and Mattson M. P. (2001a) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor mediates an excitoprotective effect of dietary restriction in mice. J. Neurochem. 76, 619–626.
Duan W., Lee J., Guo Z., and Mattson M. P. (2001b) Dietary restriction stimulates BDNF production in the brain and thereby protects neurons against excitotoxic injury. J. Mol. Neurosci. 16, 1–12.
Duan W., Guo Z., Jiang H., Ware M., Li X. J., and Mattson M. P. (2003) Dietary restriction normalizes glucose metabolism and BDNF levels, slows disease progression, and increases survival in huntingtin mutantmice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 100, 2911–2916.
Ekdahl C. T., Mohapel P., Elmer E., and Lindvall O. (2001) Caspase inhibitors increase short-term survival of progenitor-cell progeny in the adult rat dentate gyrus following status epilepticus. Eur. J. Neurosci. 14, 937–945.
Feng R., Rampon C., Tang Y. P. et al. (2001) Deficient neurogenesis in forebrain-specific presenilin-1 knockout mice is associated with reduced clearance of hippocampal memory traces. Neuron 32, 911–926.
Gebicke-Haerter P. J. (2001) Microglia in neurodegeneration: molecular aspects. Microsc. Res. Tech. 54, 47–58.
Goodrick C. L., Ingram D. K., Reynolds M. A., Freeman J. R., and Cider N. L. (1983) Effects of intermittent feeding upon growth, activity, and lifespan in rats allowed voluntary exercise. Exp. Aging Res. 9, 203–209.
Gould E. and Tanapat P. (1997) Lesion-induced proliferation of neuronal progenitors in the dentate gyrus of the adult rat. Neuroscience 80, 427–436.
Grassi Zucconi G., Semprevivo M., Laurenzi M. A., and Giuditta A. (2002) Sleep impairment by diethyldithiocarbamate in rat. Protective effects of pre-conditioning and antioxidants. Brain Res. 939, 87–94.
Gray W. P. and Sundstrom L. E. (1998) Kainic acid increases the proliferation of granule cell progenitors in the dentate gyrus of the adult rat. Brain Res. 790, 52–59.
Gundersen H. J. and Jensen E. B. (1987) The efficiency of systematic sampling in stereology and its prediction. J. Microsc. 147, 229–263.
Guo Z., Ersoz A., Butterfield D.A., and Mattson M. P. (2000) Beneficial effects of dietary restriction on cerebral cortical synaptic terminals: preservation of glucose and glutamate transport and mitochondrial function after exposure to amyloid beta-peptide, iron, and 3-nitropropionic acid. J. Neurochem. 75, 314–320.
Haughey N. J., Liu D., Nath A., Borchard A. C., and Mattson M. P. (2002a) Disruption of neurogenesis in the subventricular zone of adult mice, and in human cortical neuronal precursor cells in culture, by amyloid beta-peptide: implications for the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease. Neuromolecular Med. 1, 125–135.
Haughey N. J., Nath A., Chan S. L., Borchard A. C., Rao M. S., and Mattson M. P. (2002b) Disruption of neurogenesis by amyloid beta-peptide, and perturbed neural progenitor cell homeostasis, in models of Alzheimer’s disease. J. Neurochem. 83, 1509–1524.
Haydon P. G. (2001) GLIA: listening and talking to the synapse. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2, 185–193.
Hays S. J. (1998) Therapeutic approaches to the treatment of neuroinflammatory diseases. Curr. Pharm. Des. 4, 335–348.
Jensen M. B., Finsen B., and Zimmer J. (1997) Morphological and immunophenotypic microglial changes in the denervated fascia dentata of adult rats: correlation with blood-brain barrier damage and astroglial reactions. Exp. Neurol. 143, 103–116.
Jiang W., Gu W., Brannstrom T., Rosqvist R., and Wester P. (2001) Cortical neurogenesis in adult rats after transient middle cerebral artery occlusion. Stroke 32, 1201–1207.
Jin K., Minami M., Lan J. Q., et al. (2001) Neurogenesis in dentate subgranular zone and rostral subventricular zone after focal cerebral ischemia in the rat. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 98, 4710–4715.
Kempermann G., Kuhn H. G., and Gage F. H. (1997) More hippocampal neurons in adult mice living in an enriched environment. Nature 386, 493–495.
Kuhn H. G. and Svendsen C. N. (1999) Origins, functions, and potential of adult neural stem cells. Bioessays 21, 625–630.
Lee J., Duan W., Long J. M., Ingram D. K., and Mattson M. P. (2000) Dietary restriction increases the number of newly generated neural cells, and induces BDNF expression, in the dentate gyrus of rats. J. Mol. Neurosci. 15, 99–108.
Lee J., Seroogy K. B., and Mattson M. P. (2002a) Dietary restriction enhances neurotrophin expression and neurogenesis in the hippocampus of adult mice. J. Neurochem. 80, 539–547.
Lee J., Duan W. and Mattson M. P. (2002b) Evidence that brain-derived neurotrophic factor is required for basal neurogenesis and mediates, in part, the enhancement of neurogenesis by dietary restriction in the hippocampus of adult mice. J. Neurochem. 82, 1367–1375.
Lee J., Chan S. L., and Mattson M. P. (2002c) Adverse effect of a presenilin-1 mutation in microglia results in enhanced nitric oxide and inflammatory cytokine responses to immune challenge in the brain. Neuromolecular Med. 2, 29–45.
Long J. M., Kalehua A. N., Muth N. J., et al. (1998) Stereological estimation of total microglia number in mouse hippocampus. J. Neurosci. Methods 84, 101–108.
Mattson M. P., Chan S. L., and Duan W. (2002) Modification of brain aging and neurodegenerative disorders by genes, diet, and behavior. Physiol. Rev. 82, 637–672.
Morgan T. E., Nichols N. R., Pasinetti G. M., and Finch C. E. (1993) TGF-beta 1 mRNA increases in macrophage/microglial cells of the hippocampus in response to deafferentation and kainic acid-induced neurodegeneration. Exp. Neurol. 120, 291–301.
Nilsson M., Perfilieva E., Johansson U., Orwar O., and Eriksson P. S. (1999) Enriched environment increases neurogenesis in the adult rat dentate gyrus and improves spatial memory. J. Neurobiol. 39, 569–578.
Parent J. M., Yu T. W., Leibowitz R. T., et al. (1997) Dentate granule cell neurogenesis is increased by seizures and contributes to aberrant network reorganization in the adult rat hippocampus. J. Neurosci. 17, 3727–3738.
Paxinos G. and Franklin K. B. J. (1997) The mouse brain in stereotaxic coordinates. New York: Academic Press, p. 132.
Peterson D. A. (2002) Stem cells in brain plasticity and repair. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2, 34–42.
Rao M. S. and Mattson M. P. (2001) Stem cells and aging: expanding the possibilities. Mech. Ageing Dev. 122, 713–734.
Rossi F. and Cattaneo E. (2002) Opinion: neural stem cell therapy for neurological diseases: dreams and reality. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 3, 401–409.
Sankar R., Shin D., Liu H., Katsumori H., and Wasterlain C. G. (2000) Granule cell neurogenesis after status epilepticus in the immature rat brain. Epilepsia 41, S53-S56.
Scharfman H. E., Goodman J. H., and Sollas A. L. (2000) Granule-like neurons at the hilar/CA3 border after status epilepticus and their synchrony with area CA3 pyramidal cells: functional implications of seizure-induced neurogenesis. J. Neurosci. 20, 6144–6158.
Schauwecker P. E. (2000) Seizure-induced neuronal death is associated with induction of c-Jun N-terminal kinase and is dependent on genetic background. Brain Res. 884, 116–128.
Scott B. W., Wang S., Burnham W. M., De Boni U., and Wojtowicz J. M (1998) Kindling-induced neurogenesis in the dentate gyrus of the rat. Neurosci. Lett. 248, 73–76.
Scott B. W., Wojtowicz J. M., and Burnham W. M. (2000) Neurogenesis in the dentate gyrus of the rat following electroconvulsive shock seizures. Exp. Neurol. 165, 231–236.
Shors T. J., Miesegaes G., Beylin A., Zhao M., Rydel T., and Gould, E. (2001) Neurogenesis in the adult is involved in the formation of trace memories. Nature 410, 372–376.
Song H., Stevens C. F., and Gage F. H. (2002a) Astroglia induce neurogenesis from adult neural stem cells. Nature 417, 39–44.
Ullian E. M., Sapperstein S. K., Christopherson K. S., and Barres B. A. (2001) Control of synapse number by glia. Science 291, 657–661.
van Praag H., Kempermann G., and Gage, F. H. (1999) Running increases cell proliferation and neurogenesis in the adult mouse dentate gyrus. Nat. Neurosci. 2, 266–270.
Vezzani A., Conti M., De Luigi A., et al. (1999) Interleukin-1beta immunoreactivity and microglia are enhanced in the rat hippocampus by focal kainate application: functional evidence for enhancement of electrographic seizures. J. Neurosci. 19, 5054–5065.
West M. J. (1993) New stereological methods for counting neurons. Neurobiol. Aging 14, 275–285.
Yoshimura S., Takagi Y., Harada J., et al. (2001) FGF-2 regulation of neurogenesis in adult hippocampus after brain injury. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 98, 5874–5679.
Yu B. P., Masoro E. J., and McMahan C. A. (1985) Nutritional influences on aging of Fischer 344 rats: I. Physical, metabolic, and longevity characteristics. J. Gerontol. 40, 657–670.
Yu Z. F. and Mattson M. P. (1999) Dietary restriction and 2-deoxyglucose administration reduce focal ischemic brain damage and improve behavioral outcome: evidence for a preconditioning mechanism. J. Neurosci. Res. 57, 830–839.
Zhu H., Guo Q., and Mattson M. P. (1999) Dietary restriction protects hippocampal neurons against the death- promoting action of a presenilin-1 mutation. Brain Res. 842, 224–229.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, J., Auyeung, W.W. & Mattson, M.P. Interactive effects of excitotoxic injury and dietary restriction on microgliosis and neurogenesis in the hippocampus of adult mice. Neuromol Med 4, 179–195 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1385/NMM:4:3:179
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1385/NMM:4:3:179