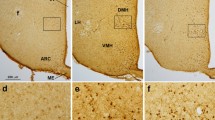
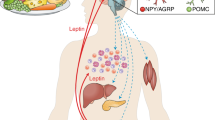
Abstract
It is well established that the adipocyte-derived hormone leptin is an important circulating satiety factor that regulates body weight and food intake via its actions on specific hypothalamic nuclei. However, there is growing evidence that leptin and its receptors are widely expressed throughout the brain, in regions not generally associated with energy homeostasis, such as cortex, cerebellum, brainstem, basal ganglia, and hippocampus. In this review the author discusses recent advances made in leptin neurobiology, with particular emphasis on the role of this endocrine peptide in normal and pathophysiological hippocampal function.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sinha M. K., Opentanova I., Ohannesian J. P., Kolacynski J. W., Hale L., Becker G. W., et al. (1996) Evidence of free and bound leptin in human circulation: studies in lean and obese subjects and during short-term fasting. J. Clin. Invest. 98, 1277–1282.
Maffei M. J., Halaas J., Ravussin E., Pratley R. E., Lee G. M., Zhang Y., et al. (1995) Leptin levels in human and rodent: measurement of plasma leptin and ob mRNA in obese and weight-reduced subjects. Nat. Med. 1, 1155–1161.
Frederich R. C., Hamann A., Anderson S., and Lollman B. (1995) Leptin levels reflect body lipid content in mice: evidence for diet-induced resistance to leptin action. Nat. Med. 1, 1311–1314.
Hamilton B. S., Paglia D., Kwan A. Y. W., and Dietel M. (1995) Increased obese mRNA expression in omental fat cells from massively obese humans. Nat. Med. 1, 953–956.
Elmquist J. K., Elias C. F., and Saper C. B. (1999) From lesions to leptin: hypothalamic control of food intake and body weight. Neuron 22, 221–232.
Schwartz M. W., Peskind E., Raskind M., Boyko E. J., and Porte D. (1996) Cerebrospinal fluid leptin concentrations: relationship to plasma leptin and to adiposity in humans. Nature Med. 2, 589–593.
Banks W. A., Kastin A. J., Huang W., Jaspan J. P., and Maness L. M. (1996) Leptin enters the brain by a saturable transport system independent of insulin. Peptides 17, 305–311.
Banks W. A., Clever C. M., and Farrell C. L. (2000) Partial saturation and regional variation in the blood-to-brain transport of leptin in normal weight mice. Am. J. Physiol. 278, E1158-E1165.
Morash B., Li A., Murphy P., Wilkinson M., and Ur E. (1999) Leptin gene expression in the brain and pituitary gland. Endocrinol. 140, 5995–5997.
Ur E., Wilkinson D. A., Morash B. A., and Wilkinson M. (2002) Leptin immunoreactivity is localised to neurons in the rat brain. Neuroendocrinol. 75, 264–272.
Tartaglia L. A., Dempski M., Weng X., et al. (1995) Identification and expression cloning of a leptin receptor, Ob-R. Cell 83, 1263–1271.
Lee G. H., Proenca R., Montez J. M., Carroll K., and Darvishzadeh J. G. (1996) Abnormal splicing of the leptin receptor in diabetic mice. Nature 379, 632–635.
Wang M.-Y., Zhou Y. T., Newgard C. B., and Unger R. H. (1998) A novel leptin receptor isoform in rat. FEBS Lett. 392, 87–90.
Chen H., Charlat O., Tartaglia L. A., et al. (1996) Evidence that the diabetes gene encodes the leptin receptor: identification of a mutation in the leptin receptor gene in db/db mice. Cell 84, 491–495.
Zhang Y., Proenca R., Maffei M., Barone M., Leopold L., and Friedman J. M. (1994) Positional cloning of the mouse obese gene and its human homologue. Nature 372, 425–432.
Pellymounter M. A., Culen M. J., Baker M. B., Hecht R., Winters D., Boone T., and Colins F. (1995) Effects of the obese gene product on body weight regulation in ob/ob mice. Science 269, 540–543.
Halaas J. L., Gajiwala K. S., Maffei M., et al. (1995) Weight reducing effects of the plasma protein encoded by the obese gene. Science 269, 543–546.
Campfield L. A., Smith F. J., Guisez Y., Devos R., and Burn P. (1995) Recombinant mouse OB protein: evidence for a peripheral signal linking adiposity and central neural networks. Science 269, 546–549.
Da Silva B. A., Bjorbaek C., Uotani S., and Flier J. S. (1998) Functional properties of leptin receptor isoforms containing the gln > pro extracellular domain mutation of the fatty rat. Endocrinol. 139, 3681–3690.
Clement K., Vaisse C., Lahlous N., Cabroll S., and Pelloux V. (1998) A mutation in the human leptin receptor gene causes obesity and pituitary dysfunction. Nature 392, 398–401.
Tartaglia L. A. (1997) The leptin receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 272, 6093–6096.
Kile B. T. and Alexander W. S. (2001) The suppressors of cytokine signaling (SOCS). Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 58, 1627–1635.
Ihle J. N. (1995) Cytokine receptor signaling. Nature 377, 591–594.
Myers M. G. and White M. F. (1996) Insulin signal transduction and the IRS proteins. Ann. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 36, 615–658.
Baumann H., Morella K. K., White D. W., et al. (1996) The full length leptin receptor has signaling capabilities of interleukin 6-type cytokine receptors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 93, 8374–8378.
Bjorbaek C., Uotani S., da Silva B., and Flier J. S. (1997) Divergent signaling capacities of the long and short isoforms of the leptin receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 272, 32,686–32,695.
Ghilardi N. and Skoda R. C. (1997) The leptin receptor activates janus tyrosine kinase 2 and signals for proliferation in a factor-dependent cell line. Mol. Endocrinol. 11, 393–399.
Kloek C., Haq A. K., Dunn S. L., Lavery H. J., Banks A. S., and Myers M. G. (2002) Regulation of JAK kinases by intracellular leptin receptor sequences. J. Biol. Chem. 277, 41,547–41,555.
Carpenter L. R., Farruggella T. J., Symes A., Karow M. L., Yancopoulos G. D., and Stahl N. (1998) Enhancing leptin response by preventing SH2-containing phosphatase 2 interaction with Ob receptor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 95, 6061–6066.
Li C. and Friedman J. M. (1999) Leptin receptor activation of SH2 domain-containing protein tyrosine phosphatase 2 modulates Ob receptor signal transduction. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 96, 9677–9682.
Morton N. M., Emilsson V., Liu Y. L., and Cawthorne M. A. (1999) Leptin action in intestinal cells. J. Biol. Chem. 273, 26,194–26,201.
Vaisse C., Halaas J. L., Horvath C. M., Darnell J. E., Stoffel M., and Friedman J. M. (1996) Leptin activation of STAT3 in the hypothalamus of wild type and ob/ob mice but not db/db mice. Nature Gen. 14, 95–97.
Hubschle T., Thom E., Watson A., Roth J., Klaus S., and Meyerhof W. (2001) Leptin-induced translocation of STAT3 immunoreactivity in hypothalamic nuclei involved in body weight regulation. J. Neurosci. 21, 2413–2424.
Bjorbaek C., Elmquist J. K., Frantz J. D., Shoelson S. E., and Flier J. S. (1998) Identification of SOCS-3 as a potential mediator of leptin resisitance. Mol. Cell. 1, 619–625.
Bates S. H., Stearns W. H., Dundon T. A., et al. (2003) STAT3 signalling is required for leptin regulation of energy balance but not reproduction. Nature 421, 856–859.
Bjorbaek C., El-Haschimi K., Frantz J. D., and Flier J. S. (1999) The role of SOCS3 in leptin signaling and resistance. J. Biol. Chem. 274, 30,059–30,065.
Bjorbaek C., Lavery H. J., Bates S. H., et al. (2000) SOCS3 mediates feedback inhibition of the leptin receptor via Tyr985. J. Biol. Chem. 275, 40,649–40,657.
Spanwick D., Smith M. A., Groppi V., Logan S. D., and Ashford M. L. J. (1997) Leptin inhibits hypothalamic neurons by activation of ATP-sensitive potassium channels. Nature 390, 521–525.
Keiffer T. J., Heller R. S., Leech C. A., Holz G. G., and Habener J. (1997) Leptin suppression of insulin secretion by activation of ATP-sensitive K+ channels in pancreatic beta cells. Diabetes 46, 1087–1093.
Harvey J., McKenna F., Herson P. S., Spanswick D., and Ashford M. L. J. (1997) Leptin activates ATP-sensitive potassium channels in the rat insulin-secreting cell line, CRI-GI. J. Physiol. 504, 527–535.
Janmey P. (1998) The cytoskeleton and cell signalling: component localisation and mechanical coupling. Physiol. Rev. 78, 763–781.
Harvey J., Hardy S. C., and Ashford M. L. J. (2000) Leptin activation of KATP channels in rat CRI-GI insulinoma cells involves disruption of the cytoskeleton. J. Physiol. 527, 95–107.
Zhao A. Z., Bornfeldt K. E., and Beavo J. A. (1998) Leptin inhibits insulin secretion by activation of phosphodiesterase 3B. J. Clin. Invest. 102, 869–873.
Zhao A. Z., Huan J. N., Gupta S., Pal R., and Sahu A. (2002) A phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase phosphodiesterase 3B-cyclic AMP pathway in hypothalamic action of leptin on feeding. Nat. Neurosci. 5, 727–728.
Tanabe K., Okuya S., Tanizawa Y., Matsutani A., and Oka Y. (1997) Leptin induces proliferation of pancreatic beta cell line, MIN6 through activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Comm. 241, 765–768.
Takahashi Y., Okimura Y., Mizuno I., et al. (1997) Leptin induces mitogen-activated protein kinase-dependent proliferation of C1H10T1/2 cells. J. Biol. Chem. 272, 12,897–12,900.
Banks A. S., Davies S. M., Bates S. H., and Myers M. G. (2000) Activation of downstream signals by the long form of the leptin receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 275, 14,653–14,672.
Machinal-Quelin F., Dieudonne M. N., Leneveu M. C., Pecquery R., and Giudicelli Y. (2002) Proadipogenic effect of leptin on rat preadipocytes in vitro: activation of MAPK and STAT3 signalling pathways. Am. J. Physiol. 282, C853–863.
Takekoshi K., Ishii K., Kawakami Y., Isobe K., Nanmoku T., and Nakai T. (2001) Ca2+ mobilisation, tyrosine hydroxylase activity and signalling mechanisms in cultured porcine adrenal medullary chromaffin cells: effects of leptin. Endocrinol. 142, 290–298.
Martin-Romero C. and Sanchez-Margalet V. (2001) Human leptin activates PI3K and MAPK pathways in human peripheral blood mononuclear cells: possible role of Sam68. Cell. Immunol. 212, 83–91.
Yamashita T., Murakami T., Otani S., Kuwajima M., and Shima K. (1998) Leptin receptor signal transduction: ObRa and ObRb of a fa type. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Comm. 246, 752–759.
Hileman S. M., Pieroz D. D., Masuzaki H., et al. (2002) Characterisation of short isoforms of the leptin receptor in rat cerebral microvessels and of brain uptake of leptin in mouse models of obesity. Endocrinol. 143, 775–783.
Cohen B., Novick D., and Rubinstein M. (1996) Modulation of insulin activities by leptin. Science 274, 1185–1188.
Szanto I. and Khan C. R. (2000) Selective interaction between leptin and insulin signaling pathways in a hepatic cell line. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 97, 2355–2360.
Harvey J. and Ashford M. L. J. (1998) Insulin occludes leptin activation of ATP-sensitive K+ channels in rat CRI-Gl insulin-secreting cells. J. Physiol. 511, 695–706.
Kellerer M., Lammers R., Fritsche A., et al. (2001) Insulin inhibits leptin receptor signaling in HEK293 cells at the level of JAk2: a potential mechanism for hyperinsulinaemia-associated leptin resistance. Diabetol. 44, 1125–1132.
Spanswick D., Smith M. A., Mirshamsi S., Routh V. H., and Ashford M. L. J. (2000) Insulin activates ATP-sensitive K+ channels in hypothalamic neurons of lean, but not obese rats. Nat. Neurosci. 3, 757–758.
Niswender K. D. and Schwartz M. W. (2003) Insulin and leptin revisited: adiposity signals with overlapping physiological and intracellular signalling capabilities. Front. Neuroendocrinol. 24, 1–10.
Carvalheira J. B., Siloto R. M., Ignacchitti I., et al. (2001) Insulin modulates leptin-induced STAT3 activation in rat hypothalamus. FEBS Lett. 500, 119–124.
Hakansson M.-L., Hulting A. L., and Meister B. (1996) Expression of leptin receptor mRNA in the hypothalamic arcuate nucleus-relationship with NPY neurons. Neuroreport 7, 3087–3092.
Hakansson M.-L., Brown H., Ghilardi N., Skoda R. C., and Meister B. J. (1998) Leptin receptor immunoreactivity in chemically-defined target neurons of the hypothalamus. J. Neurosci. 18, 559–572.
Elmquist J. K., Bjorbaek C., Ahima R. S., Flier J. S., and Saper C. B. (1998) Distributions of leptin receptor mRNA isoforms in the rat brain. J. Comp. Neurol. 395, 535–547.
Savioz A., Charnay Y., Huguenin C., Graviou C., Greggio B., and Bouras C. (1997) Expression of leptin receptor mRNA (long form slice variant) in the human cerebellum. Neuroreport 8, 3123–3126.
Burguera B., Counc M. E., Long J., et al. (2000) The long form of the leptin receptor (Ob-Rb) is widely expressed in the human brain. Neuroendocrinol. 71, 187–195.
Dawson R., Pellymounter M., Millard W., Liu S., and Eppler B. (1996) Attenuation of leptin-mediated effects by monosodium glutamate-induced arcuate nucleus damage. Am. J. Physiol. 273, E202-E206.
Baskin D. G., Seeley R. J., Kuijper J. L., et al. (1998) Increased expression of mRNA for the long form of the leptin receptor in the hypothalamus is associated with leptin hypersensitivity and fasting. Diabetes 47, 538–543.
Lin S., Storlien L. H., and Huang X. F. (2000) Leptin receptor, NPY, POMC mRNA expression in the diet-induced obese mouse brain. Brain Res. 875, 89–95.
Mercer J. G., Hoggard N., Williams L. M., Lawrence C. B., Hannah L. T., and Trayhurn P. (1996) Localisation of leptin receptor mRNA and the long form splice variant (Ob-Rb) in mouse hypothalamus and adjacent brain regions by in situ hybridization. FEBS Lett. 387, 113–166.
Baskin D. G., Schwartz M. W., Seeley R. J., et al. (1999) Leptin receptor long-form slice variant protein expression in neuron cell bodies of the brain and colocalisation with neuropeptide Y mRNA in the arcuate nucleus. J. Hist. Cytochem. 47, 353–362.
Haung X. F., Koutcherov I., Lin S., Wang H. Q., and Storlien L. (1996) Localisation of leptin receptor mRNA expression in mouse brain. Neuroreport 7, 2635–2638.
Lin S. and Huang X. F. (1997) Fasting increases leptin receptor mRNA expression in lean but not obese (ob/ob) mouse brain. Neuroreport 8, 3625–3629.
Bliss T. V. P. and Collingridge G. L. (1993) A synaptic model of memory: long-term potentiation in the hippocampus. Nature 361, 31–39.
Shepherd P. R., Withers D. W., and Siddle K. (1998) Phosphoinositide 3-kinase: the key switch mechanism in insulin signalling. Biochem. J. 333, 417–490.
Liu L., Brown J. C., Webster W. W., Morrisett R. A., and Monoghan D. T. (1995) Insulin potentiates N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor activity in Xenopus oocytes and rat hippocampus. Neurosci. Lett. 192, 5–8.
Chen C. and Leonard J. P. (1996) Protein tyrosine kinase-mediated potentiation of currents cloned from NMDA receptors. J. Neurochem. 67, 194–200.
Liao G. Y. and Leonard J. P. (1999) Insulin modulation of cloned mouse NMDA receptor currents in Xenopus oocytes. J. Neurochem. 73, 1510–1519.
Gispen W. H. and Biessels G. J. (2000) Cognition and synaptic plasticity in diabetes mellitus. TINS 23, 542–549.
Li X. L., Aou S., Oomura Y., Hori N., Fukunaga K., and Hori T. (2002) Impairment of long-term potentiation and spatial memory in leptin-receptor deficient rodents. Neurosci. 113, 607–615.
Lau L. F. and Huganir R. L. (1995) Differential tyrosine phosphorylation of N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor subunits. J. Biol. Chem. 270, 20,036–20,041.
Moon I. S., Apperson M. L., and Kennedy M. B. The major tyrosine phosphorylated protein in the postsynaptic density fraction is N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor subunit 2B. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 91, 3954–3958.
Salter M. W. (1998) Src, N-methyl-d-aspartate (NMDA) receptors and synaptic plasticity. Biochem. Pharmacol. 56, 789–798.
Herron C. E., Lester R. A., Coan E. J., and Collingridge G. L. (1986) Frequency-dependent involvement of NMDA receptors in the hippocampus: a novel synaptic mechanism. Nature 322, 265–268.
Spanswick D., Smith M. A., Groppi V., Logan S. D., and Ashford M. L. J. (1997) Leptin inhibits hypothalamic neurons by activation of ATP-sensitive potassium channels. Nature 390, 521–525.
Alger B. E., and Williamson A. A. (1988) A transient calcium-dependent potassium component of the epileptiform burst after-hyperpolarisation in rat hippocampus. J. Physiol. 399, 191–205.
Shao L. R., Halvorsrud R., Borg-Graham L., and Storm J. F. (1999) The role of BK-type Ca2+-dependent K+ channels in spike broadening during repetitive firing in rat hippocampal pyramidal cells. J. Physiol. 521, 135–146.
Kohling R., Vreugdenhil M., Bracci E., and Jefferys J. G. (2000) Ictal epileptiform activity is facilitated by hippocampal GABAA receptor-mediated oscillations. J. Neurosci. 20, 6820–6829.
Abele A. E., Scholz K. P., Scholz W. K., and Miller R. J. (1990) Excitotoxicity induced by enhanced neurotransmission in cultured hippocampal pyramidal neurons. Neuron 4, 413–419.
McLeod J. R., Shen M., Kim D. J., and Thayer S. A. (1998) Neurotoxicity mediated by aberrant patterns of synaptic activity between rat hippocampal neurons in culture. J. Neurophysiol. 80, 2688–2698.
Masuzaki H., Ogawa Y., Sagawa N., et al. (1997) Non-adipose production of leptin: leptin as a novel placenta-derived hormone in humans. Nat. Med. 3, 1029–1033.
Hoggard N., Hunter L., Duncan J. S., Williams L. M., Trayhurn P., and Mercer J. G. (1997) Leptin and leptin receptor mRNA and protein expression in the urine fetus and placenta. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 94, 11,073–11,078.
Akerman F., Lei Z. M., and Rao C. V. (2002) Human umbilical cord and fetal membranes co-express leptin and its receptor genes. Gynecol. Endocrinol. 16, 299–306.
Camand O., Turban S., Abitbol M., and Guerre-Millo M. (2002) Embryonic expression of the leptin receptor gene in mesoderm-derived tissues. C. R. Biol. 325, 77–87.
Sierra-Honigmann M. R., Nath A. K., Murakami C., et al. (1998) Biological actions of leptin as an angiogenic factor. Science 281, 1683–1686.
Park H. Y., Kwon H. M., Lim H. J., et al. (2001) Potential role of leptin in angiogenesis: leptin induces endothelial cell proliferation and expression of matrix matelloproteinases in vivo and in vitro. Exp. Mol. Med. 33, 95–102.
Goetze S., Bungenstock A., Czupalla C., et al. (2002) Leptin induced endothelial cell migration through Akt, which is inhibited by PPAR gamma ligands. Hypertension 40, 748–754.
Chen S. C., Kochan J. P., Campfield L. A., Burn P., and Smeyne R. J. (1999) Splice variants of the OB receptor gene are differentially expressed in brain and peripheral tissues of mice. J. Recept. Signal Trans. Res. 19, 245–266.
Chen S. C., Cunningham J. J., and Smeyne R. J. (2000) Expression of OB receptor splice variants during prenatal development of the mouse. J. Recept. Signal Trans. Res. 20, 87.
Matsuda J., Yokota I., Tsuruo Y., Murakami T., Ishimura K., Shima K., and Kuroda Y. (1999) Development changes in long form leptin receptor expression and localisation in rat brain. Endocrinol. 140, 5233–5238.
Udagawa J., Hatta T., Naora H., and Otani H. (2000) Expression of the long form of leptin receptor (Ob-Rb) mRNA in the brain of mouse embryos and newborn mice. Brain Res. 868, 251–258.
Ahima R. S., Bjorbaek C., Osei S., and Flier J. S. (1999) Regulation of neuronal and glial proteins by leptin: implications for brain development. Endocrinol. 140, 2755–2762.
Steppan C. M. and Swick A. G. (1999) A role for leptin in brain development. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Comm. 24, 600–602.
Sena A., Sarlieve L. L., and Rebel G. (1985) Brain myelin of genetically obese mice. J. Neurol. Sci. 68, 233–243.
Bereiter D. A. and Jeanrenaud B. (1980) Altered dendritic orientation of hypothalamic neurons from genetically obese (ob/ob) mice. Brain Res. 202, 201–206.
Bereiter D. A. and Jeanrenaud B. (1979) Altered anatomical organisation in the central nervous system of genetically obese (ob/ob) mouse. Brain Res. 165, 249–260.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Harvey, J. Leptin. Mol Neurobiol 28, 245–258 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1385/MN:28:3:245
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1385/MN:28:3:245