Abstract
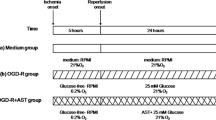
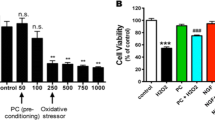
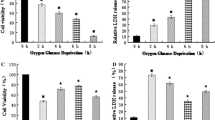
Neurotrophins such as nerve growth factor (NGF) are considered putative neuroprotective compounds in the central nervous system. To investigate the cellular and molecular neuroprotective mechanisms of NGF under ischemia, we used a unique oxygen and glucose deprivation (OGD) device. In this system we used pheochromocytoma PC12 cells to elucidate NGF neuroprotective effect. PC12 cells were exposed to OGD, followed by addition of glucose and oxygen (OGD reperfusion). Neuronal cell death induced in this model was measured by the release of lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), activation of caspase-3 and mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs), measured with specific anti-phospho-antibodies. Pretreatment of the cultures with 50 ng/mL NGF, 18 h prior to OGD insult, conferred 30% neuroprotection. However, treatment of the cultures with NGF concomitantly with the OGD insult did not result in neuroprotection. Time-course experiments showed marked activation of extracellular signal-regulated protein kinase, c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK), and p38 MAPK isoforms during the OGD phase but not during OGD reperfusion. Pretreatment of the cultures with 50 ng/mL NGF, 18 h prior to OGD insult, resulted in 50% attenuation of OGD-induced activation of JNK1, and 20% and 50% attenuation of OGD-induced activation of p38α and β, respectively. These findings support the notion that NGF confers neuroprotection from OGD insult, a phenomenon coincidentally related to differential inhibition of MAPK stress kinase isoforms, and provide the PC12 model as an in vitro OGD system to investigate molecular mechanisms of neurotoxicity and neuroprotection.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abu Raya S., Trembovler V., Shohami E., and Lazarovici P. (1993) A tissue culture ischemic device to study eicosanoid release by pheochromocytoma PC12 cultures. J. Neurosci. Methods 50, 197–203.
Alessandrini A., Namura S., Moskowitz M. A., and Bonventre J. V. (1999) MEK1 protein kinase inhibition protects against damage resulting from focal cerebral ischemia. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 96, 12866–12869.
Banasiak K. J., Xia Y., and Haddad G. G. (2000) Mechanisms underlying hypoxia-induced neuronal apoptosis. Prog. Neurobiol. 62, 215–249.
Barone F. C., Irving E. A., Ray A. M., Lee J. C., Kassis S., Kumar S., et al. (2001) Inhibition of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase provides neuroprotection in cerebral focal ischemia. Med. Res. Rev. 21, 129–145.
Batistatou A. and Greene L. A. (1991) Aurintricarboxylic acid rescues PC12 cells and sympathetic neurons from cell death caused by nerve growth factor deprivation: correlation with suppression of endonuclease activity. J. Cell Biol. 115, 461–471.
Berger R. and Garnier Y. (2000) Perinatal brain injury. J. Perinat. Med. 28, 261–285.
Bloch-Shilderman E., Jiang H., Abu-Raya S., Linial M., and Lazarovici P. (2001) Involvement of extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) in pardaxin-induced dopamine release from PC12 cells. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 296, 704–711.
Bloch-Shilderman E., Jiang H., and Lazarovici P. (2002) Pardaxin, an ionophore neurotoxin, induces PC12 cell death: activation of stress kinases and production of reactive oxygen species. J. Nat. Toxins 11, 71–85.
Boniece I. R. and Wagner J. A. (1993) Growth factors protect PC12 cells against ischemia by a mechanism that is independent of PKA, PKC, and protein synthesis. J. Neurosci. 13, 4220–4228.
Boniece I. R. and Wagner J. A. (1995) NGF protects PC12 cells against ischemia by a mechanism that requires the N-kinase. J. Neurosci. Res. 40, 1–9.
Bradford M. M. (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 72, 248–254.
Brightman F. A. and Fell D. A. (2000) Differential feedback regulation of the MAPK cascade underlies the quantitative differences in EGF and NGF signalling in PC12 cells. FEBS Lett.. 482, 169–174.
Buchanan J. D. and Armstrong D. A. (1976) Free radical inactivation of lactate dehydrogenase. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. Relat. Stud. Phys. Chem. Med. 30, 115–127.
Chang L. and Karin M. (2001) Mammalian MAP kinase signalling cascades. Nature 410, 37–40.
Cowan K. J. and Storey K. B. (2003) Mitogen-activated protein kinases: new signaling pathways functioning incellular responses to environmental stress. J. Exp. Biol. 206, 1107–1115.
Deshmukh M. and Johnson E. M. (1997) Programmed cell death in neurons: focus on the pathway of nerve growth factor deprivation-induced death of sympathetic neurons. Mol. Pharmacol. 51, 897–906.
Enokido Y. and Hatanaka H. (1990) High oxygen atmosphere for neuronal cell culture with nerve growth factor. II. Survival and growth of clonal rat pheochromocytoma PC12h cells. Brain Res. 536, 23–29.
Fischer S. J., Podratz J. L., and Windebank A. J. (2001) Nerve growth factor rescue of cisplatin neurotoxicity is mediated through the high affinity receptor: studies in PC12 cells and p75 null mouse dorsal root ganglia. Neurosci. Lett. 308, 1–4.
Fujita K., Lazarovici P., and Guroff G. (1989) Regulation of the differentiation of PC12 pheochromocytoma cells. Environ. Health Perspect. 80, 127–142.
Goldberg M. P., Strasser U., and Dugan L. L. (1997) Techniques for assessing neuroprotective drugs in vitro, in Neuroprotective agents and cerebral ischaemia, Green, A. R., and Cross A. J., eds., Academic Press, San Diego, CA, pp. 69–93.
Haviv R. and Stein R. (1999) Nerve growth factor inhibits apoptosis induced by tumor necrosis factor in PC12 cells. J. Neurosci. Res. 55, 269–277.
Han B. H. and Holtzman D. M. (2000) BDNF protects the neonatal brain from hypoxic-ischemic injury in vivo via the ERK pathway. J. Neurosci. 20, 5775–5781.
Han B. H., D’Costa A., Back S. A., Parsadanian M., Patel S., Shah A. et al. (2000) BDNF blocks caspase-3 activation in neonatal hypoxia-ischemia. Neurobiol. Dis. 7, 38–53.
Irving E. A. and Bamford M. (2002) Role of mitogen- and stress-activated kinases in ischemic injury. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 22, 631–647.
Irving E. A., Barone F. C., Reith A. D., Hadingham S. J., and Parsons A. A. (2000) Differential activation of MAPK/ERK and p38/SAPK in neurons and glia following focal cerebral ischaemia in the rat. Brain Res. Mol. Brain Res. 77, 65–75.
Itano Y., Kitamura Y., and Nomura Y. (1994) 1-Methyl-4-phenylpyridinium (MPP+)-induced cell death in PC12 cells: inhibitory effects of several drugs. Neurochem. Int. 25, 419–424.
Kaplan D. R. and Miller F.D. (2000) Neurotrophin signal transduction in the nervous system. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 10, 381–391.
Khokhlatchev A., Xu S., English J., Wu P., Schaefer E., and Cobb M. H. (1997) Reconstitution of mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphorylation cascades in bacteria. Efficient synthesis of active protein kinases. J. Biol. Chem. 272, 11057–11062.
Koh J. Y. and Choi D. W. (1987) Quantitative determination of glutamate mediated cortical neuronal injury in cell culture by lactate dehydrogenase efflux assay. J. Neurosci. Methods 20, 83–90.
Kyriakis J. M. and Avruch J. (2001) Mammalian mitogenactivated protein kinase signal transduction pathways activated by stress and inflammation. Physiol. Rev. 81, 807–869.
Lee N. H., Weinstock K. G., Kirkness E. F., Earle-Hughes J. A., Fuldner R. A., Marmaros S., et al. (1995) Comparative expressed-sequence-tag analysis of differential gene expression profiles in PC-12 cells before and after nerve growth factor treatment. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 92, 8303–8307.
Maroney A. C., Glicksman M. A., Basma A. N., Walton K. M., Knight E., Jr., Murphy C. A., et al. (1998) Motoneuron apoptosis is blocked by CEP-1347 (KT 7515), a novel inhibitor of the JNK signaling pathway. J. Neurosci. 18, 104–111.
Martin L. J., Al-Abdulla N. A., Brambrink A. M., Kirsch J. R., Sieber F. E., and Portera-Cailliau C. (1998) Neurodegeneration in excitotoxicity, global cerebral ischemia, and target deprivation: A perspective on the contributions of apoptosis and necrosis. Brain Res. Bull. 46, 281–309.
Menei P., Pean J. M., Nerriere-Daguin V., Jollivet C., Brachet P., and Benoit J. P. (2000) Intracerebral implantation of NGF-releasing biodegradable microspheres protects striatum against excitotixic damage. Exp. Neurol. 161, 259–272.
Mielke K. and Herdegen T. (2000) JNK and p38 stress kinases—degenerative effectors of signal-transduction-cascades in the nervous system. Prog. Neurobiol. 61, 45–60.
Murray B., Alessandrini A., Cole A. J., Yee A. G., and Furshpan E. J. (1998) Inhibition of the p44/42 MAP kinase pathway protects hippocampal neurons in a cell-culture model of seizure activity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 95, 11975–11980.
Nakajima W., Ishida A., Lange M. S., Gabrielson K. L., Wilson M. A., Martin L. J., et al. (2000) Apoptosis has a prolonged role in the neurodegeneration after hypoxic ischemia in the newborn rat. J. Neurosci. 20, 7994–8004.
Nozaki K., Nishimura M., and Hashimoto N. (2001) Mitogen-activated protein kinases and cerebral ischemia. Mol. Neurobiol. 23, 1–19.
Ohyashiki T., Satoh E., Okada M., Takadera T., and Sahara M. (2002) Nerve growth factor protects against aluminum-mediated cell death. Toxicology 176, 195–207.
Pan Z., Sampath D., Jackson G., Werrbach-Perez K., and Perez-Polo R. (1997a) Nerve growth factor and oxidative stress in the nervous system. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 429, 173–193.
Pan Z., Sampath D., Jackson G., Werrbach-Perez K., and Perez-Polo R. (1997b) Nerve growth factor and oxidative stress in the nervous system, in: Brain Plastisity, Filogamo et al., eds., Plenum Press, NY, pp. 173–193.
Park D. S., Morris E. J., Stefanis L., Troy C. M., Shelanski M. L., Geller H. M., and Greene L. A. (1998) Multiple pathways of neuronal death induced by DNA-damaging agents, NGF deprivation, and oxidative stress. J. Neurosci. 18, 830–840.
Park S. Y., Lee H., Hur J., Kim S. Y., Kim H., Park J. H., et al. (2002) Hypoxia induces nitric oxide production in mouse microglia via p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway. Brain Res. Mol. Brain Res. 107, 9–16.
Raingeaud J., Gupta S., Rogers J. S., Dickens M., Han J., Ulevitch R. J., and Davis R. J. (1995) Pro-inflammatory cytokines and environmental stress cause p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase activation by dual phosphorylation on tyrosine and threonine. J. Biol. Chem. 270, 7420–7426.
Reimann-Philipp U., Ovase R., Weigel P. H., and Grammas P. (2001) Mechanisms of cell death in primary cortical neurons and PC12 cells. J. Neurosci. Res. 64, 654–660.
Rideout H. J., Larsen K. E., Sulzer D., and Stefanis L. (2001) Proteasomal inhibition leads to formation of ubiquitin/alpha-synuclein-immunoreactive inclusions in PC12 cells. J. Neurochem. 78, 899–908.
Rukenstein A., Rydel R. E., and Greene L. A. (1991) Multiple agents rescue PC12 cells from serum-free cell death by translation- and transcription-independent mechanisms. J. Neurosci. 11, 2552–2563.
Satoh T., Yamagata T., Ishikawa Y., Yamada M., Uchiyama Y., and Hatanaka H. (1999) Regulation of reactive oxygen species by nerve growth factor but not Bcl-2 as a novel mechanism of protection of PC12 cells from superoxide anion-induced death. J. Biochem. (Tokyo) 125, 952–959.
Schneider S., Chen W., Hou J., Steenbergen C., and Murphy E. (2001) Inhibition of p38 MAPK alpha/beta reduces ischemic injury and does not block protective effects of preconditioning. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 280, 499–509.
Seta K. A., Spicer Z., Yuan Y., Lu G., and Millhorn D. E. (2002) Responding to hypoxia: lessons from a model cell line. Sci. STKE 146, RE11.
Shimoke K. and Chiba H. (2001) Nerve growth factor prevents 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine-induced cell death via the Akt pathway by suppressing caspase-3-like activity using PC12 cells: relevance to therapeutical application for Parkinson’s disease. J. Neurosci. Res. 63, 402–409.
Siesjo B. K. (1992a) Pathophysiology and treatment of focal cerebral ischemia. Part I: Pathophysiology. J. Neurosurg. 77, 169–184.
Siesjo B. K. (1992b) Pathophysiology and treatment of focal cerebral ischemia. Part II: Mechanisms of damage and treatment. J. Neurosurg. 77, 337–354.
Sofroniew M. V., Howe C. L., and Mobley W. C. (2001) Nerve growth factor signaling, neuroprotection, and neural repair. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 24, 1217–1281.
Sugino T., Nozaki K., Takagi Y., Hattori I., Hashimoto N., Moriguchi T., and Nishida E. (2000) Activation of mitogen-activated protein kinases after transient forebrain ischemia in gerbil hippocampus. J. Neurosci. 20, 4506–4514.
Sweatt J. D. (2001) The neuronal MAP kinase cascade: a biochemical signal integration system subserving synaptic plasticity and memory. J. Neurochem. 76, 1–10.
Tabakman R., Jiang H., Levine R. A., Kohen R., and Lazarovici P. (2004) Aoptotic characteristics of cell death and the neuroprotective effect of homocarnosine on pheochromocytoma PC12 cells exposed to ischemia. J. Neurosci. Res. 75, 499–507.
Tabakman R., Lazarovici P., and Kohen R. (2002) Neuroprotective effects of carnosine and homocarnosine on pheochromocytoma PC12 cells exposed to ischemia. J. Neurosci. Res. 68, 463–469.
Takeda K. and Ichijo H. (2002) Neuronal p38 MAPK signalling: an emerging regulator of cell fate and function in the nervous system. Genes Cells 7, 1099–1111.
Troy C. M., Rabacchi S. A., Xu Z., Maroney A. C., Connors T. J., Shelanski M. L., and Greene L. A. (2001) Beta-Amyloid-induced neuronal apoptosis requires c-Jun N-terminal kinase activation. J. Neurochem. 77, 157–164.
Vartiainen N., Goldsteins G., Keksa-Goldsteine V., Chan P. H., and Koistinaho J. (2003) Aspirin inhibits p44/42 mitogen-activated protein kinase and is protective against hypoxia/reoxygenation neuronal damage. Stroke 34, 752–757.
Vartiainen N., Keksa-Goldsteine V., Goldsteins G., and Koistinaho J. (2002) Aspirin provides cyclin-dependent kinase 5-dependent protection against subsequent hypoxia/reoxygenation damage in culture. J. Neurochem. 82, 329–335.
Vaudry D., Stork P. J., Lazarovici P., and Eiden L. E. (2002) Signaling pathways for PC12 cell differentiation: making the right connections. Science 296, 1648–1649.
Xia Z., Dickens M., Raingeaud J., Davis R. J., and Greenberg M. E. (1995) Opposing effects of ERK and JNK-p38 MAP kinases on apoptosis. Science 270, 1326–1331.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This study is part of a Ph.D. thesis to be submitted to the Hebrew University of Jerusalem by R.T.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tabakman, R., Jiang, H., Schaefer, E. et al. Nerve growth factor pretreatment attenuates oxygen and glucose deprivation-induced c-Jun amino-terminal kinase 1 and stress-activated kinases p38α and p38β activation and confers neuroprotection in the pheochromocytoma PC12 model. J Mol Neurosci 22, 237–249 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1385/JMN:22:3:237
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1385/JMN:22:3:237