Summary
Background. EGF and EGF-R are frequently overexpressed in the tissue of patients suffering from ductal pancreatic cancer and to lesser degree in patients with chronic pancreatitis. The aim of this study was to determine the value of serum measurements in these patients to detect malignant pancreatic disease. In cases of pancreatic cancer, the tissue expression of EGF and EGF-R was evaluated by immunohistochemistry.
Method. Thirty-five patients with chronic pancreatitis and 31 patients with pancreatic cancer were evaluated; 71 patients admitted for routine surgery (hernia repair, cholecystectomy, goiter surgery) served as controls.
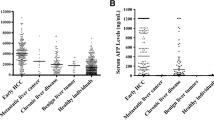
Results. EGF and EGF-R values were not significantly different in pancreatic cancer as compared to controls and did not correlate with other tumor markers (CA 19-9, carcinoembryonic antigen [CEA], tumor polypeptide antigen [TPA]) or with the stage of the disease. Fourteen patients (67%) with pancreatic cancer displayed tissue overexpression for EGF and 11 patients for EGF-R (52%). These patients, however, also failed to exhibit any significant pathological changes in serum concentration. In chronic pancreatitis, EGF and EGF-R were significantly decreased as compared to pancreatic cancer and controls. This was an unexpected finding. There was a positive correlation to clinical exocrine insufficiency.
Conclusion. The results of this study show that routine measurements of epidermal growth factor (EGF) and epidermal growth factor receptor (EGF-R) cannot improve screening for pancreatic cancer despite the frequently present tissue overexpression. Both values fail to reveal this malignancy in a serum test. Patients with chronic pancreatitis exhibit no or very low concentrations of EGF. In cases where preoperative diagnosis is difficult the noninvasive EGF and EGF-R serum measurements may be helpful in discriminating between pancreatic cancer and chronic pancreatitis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fallon JH, Seroogy KB, Louglin SE, Morrison RS, Bradshaw RA, Knauer DJ, et al. Epidermal growth factor immuno-reactive material in the central nervous system: location and development. Science 1984; 224: 1107–1109.
Gregory H, Walsh S, Hopkins CR. The identification of urogastrone in serum, saliva and gastric juice. Gastroenterology 1979; 77: 313–318.
Costrini NV, Beck R. Epidermal growth factor urogastrone receptors in normal human liver and hepatoma. Cancer 1983; 51: 2191–2196.
Marti U, Burwein SJ, Jones AL. The biological effects of eridermal growth factor receptor, with emphasis on the gastrointestinal tract and liver. An update. Hepatology 1989; 9: 126–138.
Hollenberg MD. Growth factors, their receptors and development. Am J Med Genet 1989; 24: 35–42.
Scheving LA, Scheving LE, Willingham MC, Veseley DL. Epidermal growth factor enhances guanylate cyclase activity in vivo and in vitro. Endocrinology 1985; 116: 332–336.
National Cancer Institute. Annual cancer statistics review 1973–1987. Department of Health and Human Services, Bethesda, MD: 1991; NIH publication no. 91-2789.
Korc M. Growth factors and pancreatic cancer. Int J Pancreatol 1991; 9: 87–91.
Korc M, Chandrrasekar B, Yamananka Y, Friess H, Buechler M, Beger HG. Overexpression of epidermal growth factor receptor in human pancreatic cancer is associated with concomittant increase in the levels of epidermal growth factor and transforming growth factor alpha. J Clin Invest 1992; 90(4): 1352–1360.
Korc M. The role of growth factors in pancreatic cancer. Surg Oncol Clin North Am 1998; 7: 25–41.
Bleday R, Tzanakakis GN, Schwalke MA, Wanebo HJ, Vezeredis MP. Epidermal growth factor stimulation and metastatic rate in human pancreatic carcinoma cell lines. J Surg Res 1990; 49(3): 276–279.
Yamananka Y, Friess H, Kobrin MS, Büchler M, Beger HG, Korc M. Coexpression of epidermal growth factor receptor and ligands in human pancreatic cancer is associated with enhanced tumor aggressivness. Anticancer Res 1993; 13(3): 565–569.
Uegaki K, Nio Y, Inoue Y, Minari Y, Sato, Y, Song MH, et al. Clinicopathological significance of epidermal growth factors and its receptor in human pancreatic cancer. Anticancer Res 1997; 17(5): 3841–3847.
Lemoine NR, Lobresco M, Leung H, Barton C, Hughes CM, Prigent SA, et al. The erbB-3 gene in human pancreatic cancer. J Pathol 1992 (3): 269–273.
Baselega J, Norton L, Masui H, Pandiella A, Coplan K, Miller WH, et al. Antitumor effect of doxorubicin in combination with anti-epidermal growth factor receptor monoclonal antibody. J Natl Cancer Inst 1993; 85(16): 1327–1333.
Szepeshazi K, Scally AV, Halmos G, Groot K, Radulovic S. Growth inhibtion of estrogen-dependant and estrogen independant MXT ammary cancers in mice by the bombesin and gastrin releasing peptide antagonist RC-3095. J Natl Cancer Inst 1992; 84(24): 1915–1922.
Safi F, Roscher R, Beger HG. Tumor markers in pancreatic cancer. Sensitivity and specificity of CA 19/9. Hepato-Gastroenterology 1991; 26: 419–423.
Niederau C, Grendell JH. Diagnosis of pancreatic carcinoma. Imaging techniques and tumor markers. Pancreas 1992; 7: 66–86.
Schölmerich J. Diagnosis of pancreatic cancer, in: Beger HG, Büchler M, Malfertheimer P, eds. Standards in Pancreatic Surgery. Springer Verlag, Berlin 1993; pp. 578–590.
Briese V, Müller H. Fetomaternale Signal Transduktion durch Wachstumsfaktoren. Zentrbl Gynäkol 1992; 114: 219–223.
Hirata Y, Moore GW, Bertagna C, Orth DN. Plasma concentrations of immunoreactive human epidermal growth factor in man. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1980; 50: 440–444.
Oka Y, Orth DN. Human plasma epidermal growth factor is associated with blood platlets. J Clin Invest 1983; 72: 249–259.
Starkey RH, Orth DN. Radioimmunoassay of human epidermal growth factor. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1977; 45: 1144–1153.
Mattila AL, Viininka L, Saario I, Perheentupa J. Human epidermal growth factor receptors in human transitional cell carcinoma. Regul Pept 1988; 23: 89–93.
Savage CR, Imamgami T, Cohen S. The primary structure of epidermal growth factor. J Biol Chem 1972; 248: 7669–7672.
Savage AP, Chatterjee VK, Gregory H, Bloom SR. Epidermal growth factor in blood. Regul Pept 1986; 16: 199–206.
Birk D, Gansauge F, Formentini A, Safi F, Beger HG. Expression of epidermal growth factors and their ligands in experimental pancreatic cancer. Digestion 1995; 52(6): 312.
Konturek SJ, Tasler J, Bielanski W, Cieszkowski M, Pawlik W. Role of liver and intestines in the degradation of epidermal growth factor. Digestion 1990; 45(4): 202–211.
Jaworek J, Konturek SJ. Distribution, release and secretory activity of epidermal growth factor in the pancreas. Int J Pancreatol 1990; 6(3): 189–205.
Konturek JW, Buesing M, Hopt UT, Stachura J, Becker HD, Konturek SJ. Secretion of protein and epidermal growth factor by transplanted human pancreas. Int J Pancreatol 1992; 12(1): 23–29.
Skov Olson P. Role of epidermal growth factor in gastroduodenal mucosal protection. J Clin Gastroenterol 1988; (Suppl 1),10: 146–148.
Dembinski A, Gregory H, Konturek SJ, Polanski M. Trophic action of epidermal growth factor on the pancreas and the gastroduodenal mucosa in rats. J Physiol 1982; 325: 35–42.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Birk, D., Gansauge, F., Gansauge, S. et al. Serum and correspondent tissue measurements of epidermal growth factor (EGF) and epidermal growth factor receptor (EGF-R). International Journal of Pancreatology 25, 89–96 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1385/IJGC:25:2:89
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1385/IJGC:25:2:89