Abstract
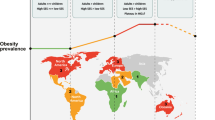
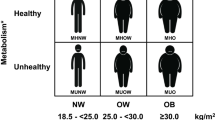
Overweight and obesity are major health problems worldwide. A body mass index of ≥25 has been classified as overweight and of ≥30 as obesity. However, national and epidemiologic data on overweight and obesity are not based on actual measures of body fat because of the difficulty of collecting such data from large groups and especially from the obese. There are now numerous direct and indirect methods to assess body fat. Anthropometric techniques are the most common indirect methods used in epidemiologic and clinical assessments, but these are restricted in the obese to circumferences. The other methods of assessing body fat are bioelectrical impedance, body density, total body water, and dual X-ray absorptiometry, all of which have advantages and limitations when applied to the obese. All these methods make use of statistical models in calculating body composition. There are several sources of available reference data for anthropometric measures for the US population, but no direct measures of body fat are currently available. There is a clear need for continued development and validation of new and existing techniques to determine levels of fat.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Popkin, B. M. (1998). J. Nutr. Biochem. 9, 487–488.
World Health Organization. (1995). Physical status: the use and interpretation of anthropometry. World Health Organization: Geneva.
World Health Organization. (1998). Obestity: preventing and managing the global epidemic. World Health Organization Programme of Nutrition: Geneva.
Shils, M. E., Olson, J. A., and Shike, M. (1994). In: Modern nutrition in health and disease, vol. 2. 8th ed. Pi-Sunyer, F. X. (ed.) Lea & Febiger: Philadelphia.
Bray, G. A. (1994). In: Prasent knowledge in nutrition (seventh edition). Ziegler, E. E. and Filer, L. J. (eds.). International Life Sciences Institute: Washington, DC.
Kuczmarski, R., Flegal, K., Campbell, S., and Johnson, C. (1994). JAMA 272, 205–211.
Ismail, M. N. (1995). Malaysian J. Nutr. 1, 1–10.
Troiano, R. P., Flegal, K. M., Kuczmarski, R. J., Campbell, S. M., and Johnson, C. L. (1995). Arch. Pediatr. Adolesc. Med. 149, 1085–1091.
Lohman, T. G. (1992). Advances in body composition assessment. Human Kinetics: Champaign, IL.
Baumgartner, R. N., Rhyne, R. L., Garry, P. J., and Chumlea, W. C. (1993). In: Human body composition: in vivo methods, models and assessment. Ellis, K. J. and Eastman, J. D., (eds.). Plenum: New York.
Moore, F. D. (1963). The body cell mass and its supporting environment. W. B. Saunders: Philadelphia.
Guo, S., Roche, A. F., and Houtkooper, L. H. (1989). Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 50, 435–443.
Conlisk, E., Haas, J., Martinez, E., Flores, R., Rivera, J., and Martorell, R. (1992). Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 55, 1051–1059.
Guo, S., Chumlea, W. C., Roche, A. F., Gardner, J. D., and Siervogel, R. M. (1994). Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 59, 810–819.
Seim, H. C. and Holtmeier, K. B. (1993). Am. Fam. Phys. 47, 1183–1189.
Salom, I. L. (1997). Geriatrics 52, 33–34.
Chumlea, W. C., Roche, A. F., and Webb, P. (1984). Int. J. Obes. 8, 311–317.
Chumlea, W. C., Baumgartner, R. N., Garry, P. J., Rhyne, R. L., Nicholson, C., and Wayne, S. (1992). Int J. Obes. 16, 125–133.
Seidell, J. C., Oosterlee, A., Thijssen, M. A. O., Burema, J., Deurenberg, P., Hautvast, J. G. A. J., and Ruijs, J. H. J. (1987). Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 45, 7–13.
Fujimoto, W. Y., Newellmorris, L. L., Grote, M., Bergstrom, R. W., and Shuman, W. P. (1991). Int. J. Obes. 15, 41–44.
Pouliot, M., Despres, J., Lemieux, S., Moorjani, S., Bouchard, C., Tremblay, A., Nadeau, A., and Lupien, P. (1994). Am. J. Cardiol. 73, 460–468.
Despres, J., Prudhomme, D., Pouliot, M., Tremblay, A., and Bouchard, C. (1991). Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 54, 471–477.
Chumlea, W. C. and Kuczmarski, R. J. (1995). J. Am. Diet Assoc. 95, 12.
Malina, R. M. and Bouchard, C. (1988). In: Fat distribution during growth and health outcomes. Wiley-Liss: New York.
Brambilla, P., Manzoni, P., and Sironi, S. (1994). Int. J. Obes. 18, 795–800.
Roche, A. F., Siervogel, R. M., Chumlea, W. C., and Webb, P. (1981). Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 34, 2831–2838.
Chumlea, W. C. and Guo, S. (1994). Nutr. Rev. 52, 323–325.
Lukaski H. (1987). Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 46, 537–556.
Baumgartner, R. N., Chumlea, W. C., and Roche, A. F. (1990). Exer sports scirvs. Pandolf, K. B. (ed.) MacMillan: New York.
Jenin, P., Lenoir, J., Routlet, C., Thomasset, A., and Ducrot. H. Aviat. Space Environ. Med. 46, 152–155.
Boulier, A., Thomasset A., and Apfelbaum, M. (1992). Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 55, 761–762.
Guo, S. S. and Chumlea, W. C. (1996). In: Human body composition: methods and findings. Roche, A. F., Heymsfield, S. B., and Lohman, T. G. (eds.) Human Kinetic: Champaign, IL.
National Institutes of Health. (1994). BIA: bioelectrical impedance analysis in body composition measurement. NIH Technology Assessment Statement: Bethesda, MD.
Gray, D. S., Bray, G. A., Gemayel, N. K., and Kaplan, K. (1989). Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2, 255–260.
Kushner, R., Kunigk, A., Alspaugh, M., Andronis, P. T., Leitch, C. A., and Schoeller, D. A. (1990). Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 52, 219–223.
Siri, W. (1961). In: Techniques for measuring body composition vol. 61., Brozek, J. and Henschel, A. (eds.) National Academy Press: Washington, DC.
Brozek, J., Grande, F., Anderson, J., and Keys, A. (1963). Ann. NY Acad. Sci. 110, 113–140.
Guo, S., Schumlea, W. C., Wu, X., Wellens, R., Roche, A. F., and Siervogel, R. M. (1993). In: Human body composition. Ellis, K. J. and Eastman, J. D. (eds.). Plenum: New York:
Dempster, P. and Aitkens, S. (1995). Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 27, 1692–1697.
McCrory, M. A., Gomez, T. D., Bernauer, E. M., and Mole, P. A. (1995). Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 27, 1686–1691.
Roubenoff, R., Kehayias, J., Dawsonhughes, B., and Haymsfield, S. (1993). Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 58, 589–591.
Kohrt, W. M. (1995). Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 58, 589–591.
Guo, S. S., Wisemandle, W., Tyleshevski, F. E., Roche, A. F., Chumlea, W. C., siervogel, R. M., Specker, B., and Heub, J. (1997). J. Nutr. Health Age 1, 29–38.
Tataranni, P. A. and Ravussin, E. (1995). Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 62, 730–734.
Morrison, J. A., Khoury, R. R., Chumlea, W. C., Specker, B., Campaign, B. N., and Guo, S. (1994). Am. J. Hum. Biol. 6, 481–490.
Herman-Giddens, H. E., Slora, E. J., Hasemeier, C. M., and Wasserman, R. C. (1993). Am. J. Dis. Child 147, 455.
Herman-Giddens, M. E., Slora, E. J., Wasserman, R. C., Bourdony, C. J., Bhaplar, M. V., Koch, G. G., and Hasemeier, C. M. (1997). Pediatrics 99, 505–512.
Sparling, P. B., Millardstafford, M., Rosskopf, L. B., Dicarlo, L. J., and Hinson, B. T. (1993). Am. J. Hum. Biol. 5, 111–117.
Zillikens, M. C. and Conway, J. M. (1991). Am. J. Hum. Biol. 3, 25–32.
NCHS. (1994). In: Series 1: programs and collection procedures no. 32 Publication @ PHS 94–1308., NCHS: Hyattsville, MD.
Woteki, C. E., Briefel, R. R., and Kuczmarski, R. M. (1988). Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 47, 320–328.
Lohman, T., Martorell, R., and Roche, A. F. (1988). Anthropometrics standardization reference manual. Human Kinetics: Champaign, IL.
Abraham, S., Johnson, C., and Najjar, M. (1979). In: Vitat and health statistics. DHEW publication no (Phs) 79-1659. series 11, no. 211:1–49. DHEW: Washington, DC.
Stoudt, H., Damon, A., McFarland, R., and Roberts, J. (1965). In: Vital and health statistics, PHS publication no. 1000, series 11, no. 8:1–44. Public Health Service: Washington, DC,
Najjar, M., and Rowland, M. (1987). In: Vital and health statistics. Rublication no 238, series 11, 1–73. National Center for Health Statistics: Washington, DC.
Najjar, M., and Kuczmarski, R. M. (1989). In: Vital and health statistics. Publication no. 239, series 11, 1–106. National Center for Health Statistics: Washington, DC.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cameron, e., Guo, S.S. Assessment and prevalence of obesity. Endocr 13, 135–142 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1385/ENDO:13:2:135
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1385/ENDO:13:2:135