Abstract
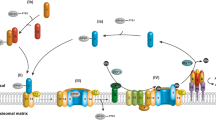
Peroxisomal matrix proteins are synthesized on free cytosolic ribosomes and posttranslationally imported into the organelle. Translocation of these newly synthesized proteins across the peroxisomal membrane requires the concerted action of many different proteins, the majority of which were already identified. However, not much is known regarding the mechanism, of protein translocation across this membrane system. Here, we discuss recent mechanistic and structural data. These results point to a model in which proteins en route to the peroxisomal matrix are translocated across the organelle membrane by their own receptor in a process that occurs, through a large membrane protein assembly.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Purdue, P. E., and Lazarow, P. B. (2001) Peroxisome biogenesis. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 17, 701–752.
Subramani, S. (1993) Protein import into peroxisomes and biogenesis of the organelle. Annu. Rev. Cell Biol. 9, 445–478.
Sacksteder, K. A. and Gould, S. J. (2000) The genetics of peroxisome biogenesis. Annu. Rev. Genet. 34, 623–652.
Sparkes, I. A., and Baker, A. (2002) Peroxisome biogenesis and protein import in plants animals and yeasts: enigma and variations. Mol. Membr. Biol. 19, 171–185.
Eckert, J. H., and Erdmann, R. (2003) Peroxisome biogenesis. Rev. Physiol. Biochem. Pharmacol. 147, 75–121.
Gould, S. J., and Valle, D. (2000) Peroxisome biogenesis disorders: genetics and cell biology. Trends Genet. 16, 340–345.
Gould, S. J., Reymond, G. V., and Valle, D. (2001) The peroxisome biogenesis disorders, in The Metabolic and Molecular Bases of Inherited Disease (Scriver CR, Beadet AL, Sly WS and Valle, D., eds.) McGraw-Hill, New York, pp. 3181–3217.
Raymond, G. V. (2001) Peroxisomal disorders. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 14, 783–787.
Weller, S., Gould, S. J., and Valle, D. (2003) Peroxisome biogenesis disorders. Annu. Rev. Genomics Hum. Genet. 4, 165–211.
Honsho, M., Tamura, S., Shimozawa, N., Suzuki, Y., Kondo, N., and Fujiki, Y. (1998) Mutation in PEX16 is causal in the peroxisome-deficient Zellweger syndrome of complementation group D. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 63, 1622–1630.
Shimozawa, N., Suzuki, Y., Zhang, Z., Imamura, A., Kondo, N., Kinoshita, N., et al. (1998) Genetic basis of peroxisome-assembly mutants of humans, Chinese hamster ovary cells, and yeast: identification of a new complementation group of peroxisome-biogenesis disorders apparently lacking peroxisomal-membrane ghosts. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 63, 1898–1903.
Matsuzono, Y., Kinoshita, N., Tamura, S., Shimozawa, N., Hamasaki, M., Ghaedi, K., et al. (1999) Human PEX19: cDNA cloning by functional complementation, mutation analysis in a patient with Zellweger syndrome, and potential role in peroxisomal membrane assembly. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U S A 96, 2116–2121.
South, S. T., and Gould, S. J. (1999) Peroxisome synthesis in the absence of preexisting peroxisomes. J. Cell Biol. 144, 255–266.
Ghaedi, K., Honsho, M., Shimozawa, N., Suzuki, Y., Kondo, N., and Fujiki, Y. (2000) PEX3 is the causal gene responsible for peroxisome membrane assembly-defective Zellweger syndrome of complementation group G. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 67, 976–981.
Sacksteder, K. A., Jones, J. M., South, S. T., Li, X., Liu, Y., and Gould, S. J. (2000) PEX19 binds multiple peroxisomal membrane proteins, is predominantly cytoplasmic, and is required for peroxisome membrane synthesis. J. Cell Biol. 148, 931–944.
Tam, Y. Y., Torres-Guzman, J. C., Vizeacoumar, F. J., Smith, J. J., Marelli, M., Aitchison, J. D., et al. (2003) Pex11-related proteins in peroxisome dynamics: a role for the novel peroxin Pex27p in controlling peroxisome size and number in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol. Biol. Cell 14, 4089–4102.
Vizeacoumar, F. J., Torres-Guzman, J. C., Tam, Y. Y., Aitchison, J. D., and Rachubinski, R. A. (2003) YHR150w and YDR479c encode peroxisomal integral membrane proteins involved in the regulation of peroxisome number, size, and distribution in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J. Cell Biol. 161, 321–332.
Distel, B., Erdmann, R., Gould, S. J., Blobel, G., Crane, D. I., Cregg, J. M., et al. (1996) A unified nomenclature for peroxisome biogenesis factors. J. Cell Biol. 135, 1–3.
Lazarow, P. B. (2003) Peroxisome biogenesis: advances and conundrums. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 15, 489–497.
Lazarow, P. B. and Fujiki, Y. (1985) Biogenesis of peroxisomes. Annu. Rev. Cell Biol. 1, 489–530.
Gould, S. J., Keller, G. A., Hosken, N., Wilkinson, J., and Subramani, S. (1989) A conserved tripeptide sorts proteins to peroxisomes. J. Cell Biol. 108, 1657–1664.
Miura, S., Kasuya-Arai, I., Mori, H., Miyazawa, S., Osumi, T., Hashimoto, T., et al. (1992) Carboxyl-terminal consensus Ser-Lys-Leu-related tripeptide of peroxisomal proteins functions in vitro as a minimal peroxisome-tar-geting signal. J. Biol. Chem. 267, 14405–14411.
Elgersma, Y. and Tabak, H. F. (1996) Proteins involved in peroxisome biogenesis and functioning. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1286, 269–283.
Lametschwandtner, G., Brocard, C., Fransen, M., Van Veldhoven, P., Berger, J., and Hartig, A. (1998) The difference in recognition of terminal tripeptides as peroxisomal targeting signal 1 between yeast and human is due to different affinities of their receptor Pex5p to the cognate signal and to residues adjacent to it. J. Biol. Chem. 273, 33635–33643.
Subramani, S., Koller, A., and Snyder, W. B. (2000) Import of peroxisomal matrix and membrane proteins. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 69, 399–418.
Swinkels, B. W., Gould, S. J., Bodnar, A. G., Rachubinski, R. A., and Subramani, S. (1991) A novel, cleavable peroxisomal targeting signal at the amino-terminus of the rat 3-ketoacyl-CoA thiolase. EMBO J. 10, 3255–3262.
Osumi, T., Tsukamoto, T., Hata, S., Yokota, S., Miura, S., Fujiki, Y., et al. (1991) Amino-terminal presequence of the precursor of peroxisomal 3-ketoacyl-CoA thiolase is a cleavable signal peptide for peroxisomal targeting. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 181, 947–954.
Rehling, P., Marzioch, M., Niesen, F., Wittke, E., Veenhuis, M., and Kunau, W. H. (1996) The import receptor for the peroxisomal targeting signal 2 (PTS2) in Saccharomyces cerevisiae is encoded by the PAS7 gene. EMBO J. 15, 2901–2913.
Miura, S., Mori, M., Takiguchi, M., Tatibana, M., Furuta, S., Miyazawa, S., et al. (1984) Biosynthesis and intracellular transport of enzymes of peroxisomal beta-oxidation. J. Biol. Chem. 259, 6397–6402.
McNew, J. A., and Goodman, J. M. (1994) An oligomeric protein is imported into peroxisomes in vivo. J. Cell Biol. 127, 1245–1257.
Glover, J. R., Andrews, D. W., and Rachubinski, R. A. (1994) Saccharomyces cerevisiae peroxisomal thiolase is imported as a dimer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U S A 91, 10541–10545.
Stewart, M. Q., Esposito, R. D., Gowani, J., and Goodman, J. M. (2001) Alcohol oxidase and dihydroxyacetone synthase, the abundant peroxisomal proteins of methylotrophic yeasts, assemble in different cellular compartments. J. Cell Sci. 114, 2863–2868.
Walton, P. A., Hill, P. E., and Subramani, S. (1995) Import of stably folded proteins into peroxisomes. Mol. Biol. Cell 6, 675–683.
Agarraberes, F. A., and Dice, J. F. (2001) Protein translocation across membranes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1513, 1–24.
Bellion, E., and Goodman, J. M. (1987) Proton ionophores prevent assembly of a peroxisomal protein. Cell 48, 165–73.
Wendland, M. and Subramani, S. (1993) Cytosol-dependent peroxisomal protein import in a permeabilized cell system. J. Cell Biol. 120, 675–685.
Soto, U., Pepperkok, R., Ansorge, W., and Just, W. W. (1993) Import of firefly luciferase into mammalian peroxisomes in vivo requires nucleoside triphosphates. Exp. Cell Res. 205, 66–75.
Fransen, M., Brees, C., Ghys, K., Amery, L., Mannaerts, G. P., Ladant, D., et al. (2002) Analysis of mammalian peroxin interactions using a non-transcription-based bacterial two-hybrid assay. Mol. Cell. Proteomics 1, 243–252.
Gouveia, A. M., Reguenga, C., Oliveira, M. E., Sá-Miranda, C., and Azevedo, J. E. (2000) Characterization of peroxisomal Pex5p from rat liver. Pex5p in the Pex5p-Pex14p membrane complex is a transmembrane protein. J. Biol. Chem. 275, 32444–32451.
Reguenga, C., Oliveira, M. E., Gouveia, A. M., Sá-Miranda, C., and Azevedo, J. E. (2001) Characterization of the mammalian peroxisomal import machinery: Pex2p, Pex5p, Pex12p, and Pex14p are subunits of the same protein assembly. J. Biol. Chem. 276, 29935–29942.
Agne, B., Meindl, N. M., Niederhoff, K., Einwachter, H., Rehling, P., Sickmann, A., et al. (2003) Pex8p: an intraperoxisomal organizer of the peroxisomal import machinery. Mol. Cell 11, 635–646.
Brocard, C., Kragler, F., Simon, M. M., Schuster, T., and Hartig, A. (1994) The tetratri-copeptide repeat-domain of the PAS10 protein of Saccharomyces cerevisiae is essential for binding the peroxisomal targeting signal-SKL. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 204, 1016–1022.
Dodt, G., Braverman, N., Wong, C., Moser, A., Moser, H. W., Watkins, P., et al. (1995) Mutations in the PTS1 receptor gene, PXR1, define complementaion group 2 of the peroxisome biogenesis disorders. Nat. Genet. 9, 115–125.
Fransen, M., Brees, C., Baumgart, E., Vanhooren, J. C., Baes, M., Mannaerts, G. P., et al. (1995) Identification and characterization of the putative human peroxisomal C-terminal targeting signal import receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 270, 7731–7736.
Terlecky, S. R., Nuttley, W. M., McCollum, D., Sock, E., and Subramani, S. (1995) The Pichia pastoris peroxisomal protein PAS8p is the receptor for the C-terminal tripeptide peroxisomal targeting signal. EMBO J. 14, 3627–3634.
Gatto, G. J., Jr., Geisbrecht, B. V., Gould, S. J., and Berg, J. M. (2000) A proposed model for the PEX5-peroxisomal targeting signal-1 recognition complex. Proteins 38, 241–246.
Gatto, G. J., Jr., Geisbrecht, B. V., Gould, S. J., and Berg, J. M. (2000) Feroxisomal targeting signal-1 recognition by the TPR domains of human PEX5. Nat. Struct. Biol. 7, 1091–1095.
Klein, A. T., Barnett, P., Bottger, G., Konings, D., Tabak, H. F., and Distel, B. (2001) Recognition of peroxisomal targeting signal type 1 by the import receptor Pex5p. J. Biol. Chem. 276, 15034–15041.
Otera, H., Setoguchi, K., Hamasaki, M., Kumashiro, T., Shimizu, N., and Fujiki, Y. (2002) Peroxisomal targeting signal receptor Pex5p interacts with cargoes and import machinery components in a spatiotemporally differentiated manner: conserved Pex5p WXXXF/Y motifs are critical for matrix protein import. Mol. Cell Biol. 22, 1639–1655.
Schliebs, W., Saidowsky, J., Agianian, B., Dodt, G., Herberg, F. W., and Kunau, W. H. (1999) Recombinant human peroxisomal targeting signal receptor PEX5. Structural basis for interaction of PEX5 with PEX14. J. Biol. Chem. 274, 5666–5673.
Saidowsky, J., Dodt, G., Kirchberg, K., Wegner, A., Nastainczyk, W., Kunau, W. H., et al. (2001) The di-aromatic pentapeptide repeats of the human peroxisome import receptor PEX5 are separate high affinity binding sites for the peroxisomal membrane protein PEX14. J. Biol. Chem. 276, 34524–34529.
Elgersma, Y., Kwast, L., Klein, A., Voorn-Brouwer, T., van den Berg, M., Metzig, B., et al. (1996) The SH3 domain of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae peroxisomal membrane protein Pex13p functions as a docking site for Pex5p, a mobile receptor for the import PTS1-containing proteins. J. Cell Biol. 135, 97–109.
Erdmann, R. and Blobel, G. (1996) Identification of Pex13p a peroxisomal membrane receptor for the PTS1 recognition factor. J. Cell Biol. 135, 111–121.
Gould, S. J., Kalish, J. E., Morrell, J. C., Bjorkman, J., Urquhart, A. J., and Crane, D. I. (1996) Pex13p is an SH3 protein of the peroxi-some membrane and a docking factor for the predominantly cytoplasmic PTS1 receptor. J. Cell Biol. 135, 85–95.
Bottger, G., Barnett, P., Klein, A. T., Kragt, A., Tabak, H. F., and Distel, B. (2000) Saccharomyces cerevisiae PTS1 receptor Pex5p interacts with the SH3 domain of the peroxisomal membrane protein Pex13p in an unconventional, non-PXXP-related manner. Mol. Biol. Cell 11, 3963–3976.
Braverman, N., Dodt, G., Gould, S. J., and Valle, D. (1998) An isoform of pex5p, the human PTS1 receptor, is required for the import of PTS2 proteins into peroxisomes. Hum. Mol. Genet. 7, 1195–1205.
Otera, H., Harano, T., Honsho, M., Chaedi, K., Mukai, S., Tanaka, A., et al. (2000) The mammalian peroxin Pex5pL, the longer isoform of the mobile peroxisome targeting signal (PTS) type 1 transporter, translocates the Pex7p.PTS2 protein complex into peroxisomes via its initial docking site, Pex14p. J. Biol. Chem. 275, 21703–21714.
Matsumura, T., Otera, H., and Fujiki, Y. (2000) Disruption of the interaction of the longer isoform of Pex5p, Pex5pL, with Pex7p abolishes peroxisome targeting signal type 2 protein import in mammals. Study with a novel Pex5-impaired Chinese hamster ovary cell mutant. J. Biol. Chem. 275, 21715–21721.
Dodt, G, Warren D, Becker E, Rehling P and Gould SJ. (2001) Domain mapping of human PEX5 reveals functional and structural similarities to Saccharomyces cerevisiae Pex18p and Pex21p. J. Biol. Chem. 276, 41769–41781.
Nito, K., Hayashi, M., and Nishimura, M. (2002) Direct interaction and determination of binding domains among peroxisomal import factors in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant. Cell Physiol. 43, 355–366.
Zhang, J. W. and Lazarow, P. B. (1996) Peb1p (Pas7p) is an intraperoxisomal receptor for the NH2-terminal, type 2, peroxisomal targeting sequence of thiolase: Peb1p itself is targeted to peroxisomes by an NH2-terminal peptide. J. Cell Biol. 132, 325–334.
Elgersma, Y., Elgersma-Hooisma, M., Wenzel, T., McCaffery, J. M., Farquhar, M. G., and Subramani, S. (1998) A mobile PTS2 receptor for peroxisomal protein import in Pichia pastoris. J. Cell. Biol. 140, 807–820.
Purdue, P. E., Yang, X., and Lazarow, P. B. (1998) Pex 18p and Pex21p, a novel pair of related peroxins essential for peroxisomal targeting by the PTS2 pathway. J. Cell Biol. 143, 1859–1869.
Titorenko, V. I., Smith, J. J., Szilard, R. K., and Rachubinski, R. A. (1998) Pex20p of the yeast Yarrowia lipolytica is required for the oligomerization of thiolase in the cytosol and for its targeting to the peroxisome. J. Cell Biol. 142, 403–420.
Sichting, M., Schell-Steven, A., Prokisch, H., Erdmann, R., and Rottensteiner, H. (2003) Pex7p and Pex20p of Neurospora crassa function together in PTS2-dependent protein import into peroxisomes. Mol. Biol. Cell 14, 810–821.
Einwachter, H., Sowinski, S., Kunau, W. H., and Schliebs, W. (2001) Yarrowia lipolytica Pex20p, Saccharomyces cerevisiae Pex18p/Pex21p and mammalian Pex5pL fulfil a common function in the early steps of the peroxisomal PTS2 import pathway. EMBO Rep. 2, 1035–1039.
Hettema, E. H., Distel, B., and Tabak, H. F. (1999) Import of proteins into peroxisomes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1451, 17–34.
Marzioch, M., Erdmann, R., Veenhuis, M., and Kunau, W. H. (1994) PAS7 encodes a novel yeast member of the WD-40 protein family essential for import of 3-oxoacyl-CoA thiolase, a PTS2-containing protein, into peroxisomes. EMBO J. 13, 4908–4918.
Dodt, G. and Gould, S. J. (1996) Multiple PEX genes are required for proper subcellular distribution and stability of Pex5p, the PTS1 receptor: evidence that PTS1 protein import is mediated by a cycling receptor. J. Cell Biol. 135, 1763–1774.
Dammai, V. and Subramani, S. (2001) The human peroxisomal targeting signal receptor, Pex5p, is translocated into the peroxisomal matrix and recycled to the cytosol. Cell 105, 187–196.
Fransen, M., Terlecky, S. R., and Subramani, S. (1998) Identification of a human PTS1 receptor docking protein directly required for peroxisomal protein import. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 95, 8087–8092.
Urquhart, A. J., Kennedy, D., Gould, S. J., and Crane, D. I. (2000) Interaction of Pex5p, the type 1 peroxisome targeting signal receptor, with the peroxisomal membrane proteins Pex14p and Pex13p. J. Biol. Chem. 275, 4127–4136.
Choe, J., Moyersoen, J., Roach, C., Carter, T. L., Fan, E., Michels, P. A., et al. (2003) Analysis of the sequence motifs responsible for the interactions of peroxins 14 and 5, which are involved in glycosome biogenesis in Trypanosoma brucei. Biochemistry 42, 10915–10922.
Albertini, M., Rehling, P., Erdmann, R., Girzalsky, W., Kiel, J. A., Veenhuis, M., et al. (1997) Pex14p, a peroxisomal membrane protein binding both receptors of the two PTS-dependent import pathways. Cell 89, 83–92.
Brocard, C., Lametschwandtner, G., Koudelka, R., and Hartig, A. (1997) Pex14p is a member of the protein linkage map of Pex5p. EMBO J. 16, 5491–5500.
Girzalsky, W., Rehling, P., Stein, K., Kipper, J., Blank, L., Kunau, W. H., et al. (1999) Involvement of Pex13p in Pex14p localization and peroxisomal targeting signal 2-dependent protein import into peroxisomes. J. Cell Biol. 144, 1151–1162.
Pires, J. R., Hong, X., Brockmann, C., Volkmer-Engert, R., Schneider-Mergener, J., Oschkinat, H., et al. (2003) The ScPex13p SH3 domain exposes two distinct binding sites for Pex5p and Pex14p. J. Mol. Biol. 326, 1427–1435.
Oliverira, M. E., Reguenga, C., Gouveia, A. M., Guimaräes, C. P., Schliebs, W., Kunau, W. H., et al. (2002) Mammalian Pex14p: membrane topology and characterisation of the Pex14p-Pex14p interaction. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1567, 13–22.
Shimizu, N., Itoh, R., Hirono, Y., Otera, H., Ghaedi, K., Tateishi, K., et al. (1999) The peroxin Pex14p. cDNA cloning by functional complementation on a Chinese hamster ovary cell mutant, characterization, and functional analysis. J. Biol. Chem. 274, 12593–12604.
Will, G. K., Soukupova, M., Hong, X., Erdmann, K. S., Kiel, J. A., Dodt, G., et al. (1999) Identification and characterization of the human orthologue of yeast Pex14p. Mol. Cell. Biol. 19, 2265–2277.
Toyama, R., Mukai, S., Itagaki, A., Tamura, S., Shimozawa, N., Suzuki, Y., et al. (1999) Isolation, characterization, and mutation analysis of PEX13-defective Chinese hamster ovary cell mutants. Hum. Mol. Genet. 8, 1673–1681.
Kalish, J. E., Theda, C., Morrell, J. C., Berg, J. M., and Gould, S. J. (1995) Formation of the peroxisome lumen is abolished by loss of Pichia pastoris Pas7p, a zinc-binding integral membrane protein of the peroxisome. Mol. Cell Biol. 15, 6406–6419.
Kalish, J. E., Keller, G. A., Morrell, J. C., Mihalik, S. J., Smith, B., Cregg, J. M., et al. (1996) Characterization of a novel component of the peroxisomal protein import apparatus using fluorescent peroxisomal proteins. EMBO J. 15, 3275–3285.
Chang, C. C., Lee, W. H., Moser, H., Valle, D., and Gould, S. J. (1997) Isolation of the human PEX12 gene, mutated in group 3 of the peroxisome biogenesis disorders. Nat. Genet. 15, 385–388.
Okumoto, K., Shimozawa, N., Kawai, A., Tamura, S., Tsukamoto, T., Osumi, T., et al. (1998) PEX12, the pathogenic gene of group III Zellweger syndrome: cDNA cloning functional complementation on a CHO cell mutant, patient analysis, and characterization of PEX12p. Mol. Cell Biol. 18, 4324–4336.
Warren, D. S., Morrell, J. C., Moser, H. W., Valle, D., and Gould, S. J. (1998) Identification of PEX10, the gene defective in complementation group 7 of the peroxisome-biogenesis disorders. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 63, 347–359.
Harano, T., Shimizu, N., Otera, H., and Fujiki, Y. (1999) Transmembrane topology of the peroxin, Pex2p, an essential component for the peroxisome assembly. J. Biochem. (Tokyo) 125, 1168–1174.
Huang, Y., Ito, R., Miura, S., Hashimoto, T., and Ito, M. (2000) A missense mutation in the RING finger motif of PEX2 protein disturbs the import of peroxisome targeting signal 1 (PTS1)-containing protein but not the PTS2-containing protein. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 270, 717–721.
Borden, K. L. (2000) RING domains: master builders of molecular scaffolds? J. Mol. Biol. 295, 1103–1112.
Chang, C. C., Warren, D. S., Sacksteder, K. A., and Gould, S. J. (1999) PEX12 interacts with PEX5 and PEX10 and acts downstream of receptor docking in peroxisomal matrix protein import. J. Cell Biol. 147, 761–774.
Albertini, M., Girzalsky, W., Veenhuis, M., and Kunau, W. H. (2001) Pex12p of Saccharomyces cerevisiae is a component of a multi-protein complex essential for peroxisomal matrix protein import. Eur. J. Cell Biol. 80, 257–270.
Erdmann, R., Wiebel, F. F., Flessau, A., Rytka, J., Beyer, A., Frohlich, K. U., et al. (1991) PAS1, a yeast gene required for peroxisome biogenesis, encodes a member of a novel family of putative ATPases. Cell 64, 499–510.
Spong, A. P. and Subramani, S. (1993) Cloning and characterization of PAS5: a gene required for peroxisome biogenesis in the methylotrophic yeast Pichia pastoris. J. Cell Biol. 123, 535–548.
Patel, S. and Latterich, M. (1998) The AAA team: related ATPases with diverse functions. Trends Cell. Biol. 8, 65–71.
Collins, C. S., Kalish, J. E., Morrell, J. C., McCaffery, J. M. and Gould, S. J. (2000) The peroxisome biogenesis factors pex4p, pex22p, pex1p, and pex6p act in the terminal steps of peroxisomal matrix protein import. Mol. Cell Biol. 20, 7516–7526.
Titorenko, V. I. and Rachubinski, R. A. (2000) Peroxisomal membrane fusion requires two AAA family ATPases, Pex1p and Pex6p. J. Cell Biol. 150, 881–886.
Faber, K. N., Heyman, J. A., and Subramani, S. (1998) Two AAA family peroxins, PpPex1p and PpPex6p, interact with each other in an ATP-dependent manner and are associated with different subcellular membranous structures distinct from peroxisomes. Mol. Cell Biol. 18, 936–943.
Geisbrecht, B. V., Collins, C. S., Reuber, B. E., and Gould, S. J. (1998) Disruption of a PEX1-PEX6 interaction is the most common cause of the neurologic disorders Zellweger syndrome, neonatal adrenoleukodystrophy, and infantile Refsum disease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U S A 95, 8630–8635.
Kiel, J. A., Hilbrands, R. E., van der Klei, I. J., Rasmussen, S. W., Salomons, F. A., van der Heide, M., et al. (1999) Hansenula polymorpha Pex1p and Pex6p are peroxisome-associated AAA proteins that functionally and physically interact. Yeast 15, 1059–1078.
Gould, S. J. and Collins, C. S. (2002) Opinion: peroxisomal-protein import: is it really that complex? Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol., 3, 382–389.
Birschmann, I., Stroobants, A. K., van den Berg, M., Schafer, A., Rosenkranz, K., Kunau, W. H., et al. (2003) Pex15p of Saccharomyces cerewisiae provides a molecular basis for recruitment of the AAA peroxin Pex6p to pertoxisomal membranes. Mol. Biol. Cell 14, 2226–2236.
Matsumoto, N., Tamura, S., and Fujiki Y. (2003) The pathogenic peroxin Pex26p recruits the Pex1p-Pex6p AAA ATPase complexes to peroxisomes. Nat. Cell Biol. 5, 454–460.
Huhse, B., Rehling, P., Albertini, M., Blank, L., Meller, K., and Kunau, W. H. (1998) Pex17p of Saccharomyces cerevisiae is a novel peroxin and component of the peroxisomal protein translocation machinery. J. Cell Biol. 140, 49–60.
Rehling, P., Skaletz-Rorowski, A., Girzalsky, W., Voorn-Brouwer, T., Franse, M. M., Distel, B., et al. (2000) Pex8p, an intraperoxisomal peroxin of Saccharomyces cerevisiae required for protein transport into peroxisomes binds the PTS1 receptor pex5p. J. Biol. Chem. 275, 3593–3602.
Eckert, J. H. and Johnsson, N. (2003) Pex10p links the ubiquitin conjugating enzyme Pex4p to the protein import machinery of the peroxisome. J. Cell Sci. 116, 3623–3634.
Wiener, E. A., Terlecky, S. R., Nuttley, W. M., and Subramani, S. (1995) Characterization of the yeast and human receptors for the carboxy-terminal tripeptide peroxisomal targeting signal. Cold Spring Harb. Symp. Quant. Biol. 60, 637–648.
Gouveia, A. M., Guimarães, C. P., Oliveira, M. E., Reguenga, C., Sá-Miranda, C., and Azevedo, J. E. (2003) Characterization of the peroxisomal cycling receptor, Pex5p, using a cell-free in vitro import system. J. Biol. Chem. 278, 226–232.
Fujiki, Y. and Lazarow, P. B. (1985) Pos-translational import of fatty acyl-CoA oxidase and catalase into peroxisomes of rat liver in vitro. J. Biol. Chem. 260, 5603–5609.
Imanaka, T., Small, G. M., and Lazarow, P. B. (1987) Translocation of acyl-CoA oxidase into peroxisomes requires ATP hydrolysis but not a membrane potential. J. Cell Biol. 105, 2915–2922.
Miura, S., Miyazawa, S., Osumi, T., Hashimoto T., and Fujiki, Y. (1994) Post-translational import of 3-ketoacyl-CoA thiolase into rat liver peroxisomes in vitro. J. Biochem. 115, 1064–1068.
Walton, P. A., Wendland, M., Subramani, S., Rachubinski, R. A., and Welch, W. J. (1994) Involvement of 70-kD heat-shock proteins in peroxisomal import. J. Cell Biol. 125, 1037–1046.
Wiemer, E. A., Nuttley, W. M., Bertolaet, B. L., Li, X., Francke, U., Wheelock, M. J., et al. (1995) Human peroxisomal targeting signal-1 receptor restores peroxisomal protein import in cells from patients with fatal peroxisomal disorders. J. Cell Biol. 130, 51–65.
Terlecky, S. R., Wiemer, E. A., Nuttley, W. M., Walton, P. A., and Subramani, S. (1996) Signals, receptors, and cytosolic factors involved in peroxisomal protein import. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 804, 11–20.
Crookes, W. J., and Olsen, L. J. (1998) The effects of chaperones and the influence of protein assembly on peroxisomal protein import. J. Biol. Chem. 273, 17236–17242.
Lopez-Huertas, E., Oh, J., and Baker, A. (1999) Antibodies against pex14p block ATP-independent binding of matrix proteins to peroxisomes in vitro FEBS Lett. 459, 227–229.
Legakis, J. E., and Terleck, S. R. (2001) PTS2 protein import into mammalian peroxisomes. Traffic 2, 252–260.
Terlecky, S. R., Legakis, J. E., Hueni, S. E., and Subramani, S. (2001) Quantitative analysis of peroxisomal protein import in vitro. Exp. Cell Res. 263, 98–106.
Gouveia, A. M., Guimarães, C. P., Oliveira, M. E., Sá-Miranda, C., and Azevedo, J. E. (2003) Insertion of Pex5p into the peroxisomal membrane is cargo protein-dependent. J. Biol. Chem. 278, 4389–4392.
Harano, T., Nose, S., Uezu, R., Shimizu, N., and Fujiki, Y. (2001) Hsp70 regulates the interaction between the peroxisome targeting signal type 1 (PTS1)-receptor Pex5p and PTS1. Biochem. J. 357, 157–165.
Oliveira, M. E., Gouveia, A. M., Pinto, R. A., Sá-Miranda, C., and Azevedo, J. E. (2003) The energetics of Pex5p-mediated peroxisomal protein import. J. Biol. Chem. 278, 39483–39488.
Salomons, F. A., Kiel, J. A., Faber, K. N., Veenhuis, M., and van der Klei, I. J. (2000) Overproduction of Pex5p stimulates import of alcohol oxidase and dihydroxyacetone synthase in a Hansenula polymorpha Pex14 null mutant. J. Biol. Chem. 275, 12603–12611.
van der Klei, I. J., Hilbrands, R. E., Kiel, J. A., Rasmussen, S. W., Cregg, J. M., and Veenhuis, M. (1998) The ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme Pex4p of Hansenula polymorpha is required for efficient functioning of the PTS1 import machinery. EMBO J. 17, 3608–3618.
Kunau, W. H. (2001) Peroxisomes: the extended shuttle to the peroxisome matrix. Curr. Biol. 11, 659–662.
van der Klei, I. J., Hilbrands, R. E., Swaving, G. J., Waterham, H. R., Vrieling, E. G., Titorenko, V. I., et al. (1995) The Hansenula polymorpha PER3 gene is essential for the import of PTS1 proteins into the peroxisomal matrix. J. Biol. Chem. 270, 17229–17236.
Heyman, J. A., Monosov, E., and Subramani, S. (1994) Role of the PAS1 gene of Pichia pastoris in peroxisome biogenesis. J. Cell Biol. 127, 1259–1273.
Portsteffen, H., Beyer, A., Becker, E., Epplen, C., Pawlak, A., Kunau, W. H., et al. (1997) Human PEX1 is mutated in complementation group 1 of the peroxisome biogenesis disorders. Nat. Genet. 17, 449–452.
Reuber, B. E., Germain-Lee, E., Collins, C. S., Morrell, J. C., Ameritunga, R., Moser, H. W., et al. (1997) Mutations in PEX1 are the most common cause of peroxisome biogenesis disorders. Nat. Genet. 17, 445–448.
Tamura, S., Okumoto, K., Toyama, R., Shimozawa, N., Tsukamoto, T., Suzuki, Y., et al. (1998) Human PEX1 cloned by functional complementation on a CHO cell mutant is responsible for peroxisome-deficient Zellweger syndrome of complementation group I. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U S A 95, 4350–4355.
Titorenko, V. I., Chan, H., and Rachubinski, R. A. (2000) Fusion of small peroxisomal vesicles in vitro reconstructs an early step in the in vivo multistep peroxisome assembly pathway of Yarrowia lipolytica. J. Cell Biol. 148, 29–44.
Tsukamoto, T., Miura, S., and Fujiki, Y. (1991) Restoration by a 35K membrane protein of peroxisome assembly in a peroxisome-deficient mammalian cell mutant. Nature 350, 77–81.
Shimozawa, N., Tsukamoto, T., Suzuki, Y., Orii, T., Shirayoshi, Y., Mori, T., et al. (1992) A human gene responsible for Zellweger syndrome that affects peroxisome assembly. Science 255, 1132–1134.
Eitzen, G. A., Titorenko, V. I., Smith, J. J., Veenhuis, M., Szilard, R. K., and Rachubinski, R. A. (1996) The Yarrowia lipolytica gene PAY5 encodes a peroxisomal integral membrane protein homologous to the mammalian peroxisome assembly factor PAF-1. J. Biol. Chem. 271, 20300–20306.
Liu, Y., Gu, K. L., and Dieckmann, C. L. (1996) Independent regulation of full-length and 5′-truncated PAS5 mRNAs in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Yeast 12, 135–143.
Waterham, H. R., de Vries, Y., Russel, K. A., Xie, W., Veenhuis, M., and Cregg, J. M. (1996) The Pichia pastoris PER6 gene product is a peroxisomal integral membrane protein essential for peroxisome biogenesis and has sequence similarity to the Zellweger syndrome protein PAF-1. Mol. Cell. Biol. 16, 2527–2536.
van der Leij, I., Franse, M. M., Elgersma, Y., Distel, B., and Tabak, H. F. (1993) PAS10 is a tetratricopeptide-repeat protein that is essential for the import of most matrix proteins into peroxisomes of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U S A 90, 11782–11786.
McCollum, D., Monosov, E., and Subramani, S. (1993) The pas8 mutant of Pichia pastoris exhibits the peroxisomal protein import deficiencies of Zellweger syndrome cells—the PAS8 protein binds to the COOH-terminal tripeptide peroxisomal targeting signal, and is a member of the TPR protein family. J. Cell Biol. 121, 761–774.
Nuttley, W. M., Szilard, R. K., Smith, J. J., Veenhuis, M., and Rachubinski, R. A. (1995) The PAH2 gene is required for peroxisome assembly in the methylotrophic yeast Hansenula polymorpha and encodes a member of the tetratricopeptide repeat family of proteins. Gene 160, 33–39.
Yahraus, T., Braverman, N., Dodt, G., Kalish, J. E., Morrell, J. C., Moser, H. W., et al. (1996) The peroxisome biogenesis disorder group 4 gene, PXAAA1, encodes a cytoplasmic ATPase required for stability of the PTS1 receptor. EMBO J. 15, 2914–2923.
Voorn-Brouwer, T., van der Leij, I., Hemrika, W., Distel, B., and Tabak, H. F. (1993) Sequence of the PAS8 gene, the product of which is essential for biogenesis of peroxisomes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1216, 325–328.
Nuttley, W. M., Brade, A. M., Eitzen, G. A., Veenhuis, M., Aitchison, J. D., Szilard, R. K., et al. (1994) PAY4, a gene required for peroxisome assembly in the yeast Yarrowia lipolytica, encodes a novel member of a family of putative ATPases. J. Biol. Chem. 269, 556–566.
Fukuda, S., Shimozawa, N, Suzuki Y, Zhang, Z, Tomatsu, S, Tsukamoto T, Hashiguchi N, Osumi, T. Masuno, M., Imaizumi, K., Kuroki, Y., Fujiki, Y., Orii, T., et al. (1996) Human peroxisome assembly factor-2 (PAF-2): a gene responsible for group C peroxisome biogenesis disorder in humans. Am. J. Hum. Genet., 59, 1210–1220.
Zhang, J. W., and Lazarow, P. B. (1995) PEB1 (PAS7) in Saccharomyces cerevisiae encodes a hydrophilic, intra-peroxisomal protein that is a member of the WD repeat family and is essential for the import of thiolase into peroxisomes. J. Cell Biol. 129, 65–80.
Braverman, N., Steel, G., Obie, C., Moser, A., Moser, H., Gould, S. J., et al. (1997) Human PEX7 encodes the peroxisomal PTS2 receptor and is responsible for rhizomelic chondrodysplasia punctata. Nat. Genet. 15, 369–376.
Motley, A. M., Hettema, E. H., Hogenhout, E. M., Brites, P., ten Asbroek, A. L., Wijburg, F. A., et al. (1997) Rhizomelic chondrodysplasia punctata is a peroxisomal protein targeting disease caused by a non-functional PTS2 receptor. Nat. Genet. 15, 377–380.
Purdue, P. E., Zhang, J. W., Skoneczny, M., and Lazarow, P. B. (1997) Rhizomelic chondrodysplasia punctata is caused by deficiency of human PEX7, a homologue of the yeast PTS2 receptor. Nat. Genet. 15, 381–384.
Tan, X., Waterham, H. R., Veenhuis, M., and Cregg, J. M. (1995) The Hansenula polymorpha PER8 gene encodes a novel peroxisomal integral membrane protein involved in proliferation. J. Cell Biol. 128, 307–319.
Okumoto, K., Itoh, R., Shimozawa, N., Suzuki, Y., Tamura, S., Kondo, N., et al. (1998) Mutations in PEX10 is the cause of Zellweger peroxisome deficiency syndrome of complementation group B. Hum. Mol. Genet. 7, 1399–1405.
Bjorkman, J., Stetten, G., Moore, C. S., Gould, S. J., and Crane, D. I. (1998) Genomic structure of PEX13, a candidate peroxisome biogenesis disorder gene. Genomics 54, 521–528.
Komori, M., Rasmussen, S. W., Kiel, J. A., Baerends, R. J., Cregg, J. M., van der Klei, I. J., et al. (1997) The Hansenula polymorpha PEX14 gene encodes a novel peroxisomal membrane protein essential for peroxisome biogenesis. EMBO J. 16, 44–53.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Azevedo, J.E., Costa-Rodrigues, J., Guimarães, C.P. et al. Protein translocation across the peroxisomal membrane. Cell Biochem Biophys 41, 451–468 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1385/CBB:41:3:451
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1385/CBB:41:3:451