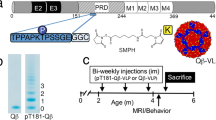
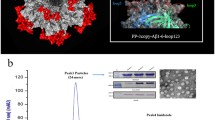
Abstract
Active vaccination with amyloid peptides shows promise for the treatment and prevention of Alzheimer’s disease (AD). Several studies in transgenic mouse models of AD have revealed the potency of vaccination to prevent or even clear amyloid plaques from mouse brain. However, the idea that soluble oligomeric species of β-amyloid (Aβ), rather than plaques, trigger the disease has gained momentum, and current active vaccination strategies affect the levels of total or soluble brain Aβ little or not at all. We describe an active vaccination method based on Aβ1-16 presented on the surface of virosomes, which triggered a dramatic decrease in both soluble Aβ40 (75% reduction; p=0.01) and soluble Aβ42 (62% reduction; p=0.03) in a double transgenic mouse model of AD. Whereas Aβ40 and Aβ42 levels in the insoluble fraction tended to be reduced (by 30% and 27%, respectively), the number of thioflavine-S-positive amyloid plaques was not affected. The high specific antibody responses, obtained without eliciting T-cell reactivity, demonstrate that immunostimulating reconstituted influenza virosomes are a promising antigen carrier system against the neuropathology of AD.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dewachter I. and Van Leuven F. (2002) Secretases as targets for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease: the prospects. Lancet Neurol. 1(7), 409–416.
Dewachter I., Reverse D., Caluwaerts N., Ris L., Kuiperi C., Van Den Haute C., et al. (2002) Neuronal deficiency of presenilin 1 inhibits amyloid plaque formation and corrects hippocampal long-term potentiation but not a cognitive defect of amyloid precursor protein [V717I] transgenic mice. J. Neurosci. 22, 3445–3453.
Dewachter I., Van Dorpe J., Smeijers L., Gilis M., Kuiperi C., Laenen I., et al. (2000) Aging increased amyloid peptide and caused amyloid plaques in brain of old APP/V717I transgenic mice by a different mechanism than mutant presenilin 1. J. Neurosci. 20(17), 6452–6458.
Etcheberrigaray R., Tan M., Dewachter I., Kuiperi C., Van Der Auwera I., Wera S., et al. (2004) Therapeutic effects of PKC activators in Alzheimer’s disease transgenic mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 101, 11141–11146.
Frenkel D., Dewachter I., Van Leuven F., and Solomon B. (2003) Reduction of β-amyloid plaques in brain of transgenic mouse models of Alzheimer’s disease by EFRH-phage immunization. Vaccine 21, 1060–1065.
Hock C., Konietzko U., Papassortiropoulos A., Wollmer A., Streffer J., Von Rotz R. C., et al. (2002) Generation of antibodies specific for beta-amyloid by vaccination of patients with Alzheimer disease. Nat. Med. 8(11), 1270–1275.
Holzer B. R., Hatz C., Schmidt-Sissolak D., Glück R., Althaus B., and Egger M. (1996) Immunogenicity and adverse effects of inactivated virosome versus alum-adsorbed hepatitis A vaccine: a randomized controlled trial. Vaccine 14, 982–986.
Janus C., Pearson J., Mclaurin J., Mathews P. M., Jiang Y., Schmidt S. D., et al. (2000) A peptide immunization reduces behavioural impairment and plaques in a model of Alzheimer’s disease. Nature 408, 979–982.
Lambert M. P., Barlow A. K., Chromy B. A., Edwards C., Freed R., Liosatos M., et al. (1998) Diffusible, non-fibrillar ligands derived from Abeta1-42 are potent central nervous system neurotoxins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 95(11), 6448–6453.
Lavie V., Becker M., Cohen-Kupiec R., Yacoby I., Koppel R., Wedenig M., et al. (2004) EFRH-Phage immunization of Alzheimer’s disease animal model improves behavioral performance in Morris water maze trials. J. Mol. Neurosci. 24, 105–113.
Moechars D., Dewachter I., Lorent K., Reverse D., Baekelandt V., Naidu A., et al. (1999) Early phenotypic changes in transgenic mice that overexpress different mutants of amyloid precursor protein in brain. J. Biol. Chem. 274(10), 6483–6492.
Moechars D., Gilis M., Kuiperi C., Laenen I., and Van Leuven F. (1998) Aggressive behaviour in transgenic mice expressing APP is alleviated by serotonergic drugs. Neuroreport 9(16), 3561–3564.
Monsonego A., Zota V., Karni A., Krieger J. I., Bar-Or A., Bitan G., et al. (2003) Increased T cell reactivity to amyloid beta protein in older humans and patients with Alzheimer disease. J. Clin. Invest. 112(3), 415–422.
Morgan D., Diamond D. M., Gottschalk P. E., Ugen K. E., Dickey C., Hardy J., et al. (2000) A beta peptide vaccination prevents memory loss in an animal model of Alzheimer’s disease. Nature 408(6815), 982–985.
Mueller M. S., Renard A., Boato F., Vogel D., Naegeli M., Zurbriggen R., et al. (2003) Induction of parasite growth-inhibitory antibodies by a virosomal formulation of a peptidomimetic of loop I from domain III of Plasmodium falciparum apical membrane antigen 1. Infect. Immun. 71(8), 4749–4758.
Nicolau C., Greferath R., Balaban T. S., Lazarte J. E., and Hopkins R. J. (2002) A liposome-based therapeutic vaccine against β-amyloid plaques on the pancreas of transgenic NORBA mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 99(4), 2332–2337.
Permanne B., Adessi C. Saborio G. P., Fraga S., Frossard M. J., Van Dorpe J., et al. (2002) Reduction of amyloid load and cerebral damage in a transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease by treatment with a beta-sheet breaker peptide. FASEB J. 16(8), 860–862.
Postina R., Schroeder A., Dewachter I., Bohl J., Schmitt U., Kojro E., et al. (2004) A disintegrin-metalloproteinase prevents amyloid plaque formation and hippocampal defects in an Alzheimer’s disease mouse model. J. Clin. Invest. 113, 1456–1464.
Schenk D., Barbou R., Dunn W., Gordon G., Grajeda H., Guido T., et al. (1999) Immunization with amyloid-β attenuates Alzheimer-disease-like pathology in the PDAPP mouse. Nature 400, 173–177.
Sigurdsson E. M., Scholtzova H., Mehta P. D., Frangione B., and Wisniewski T. (2001) Immunization with a non-toxic/nonfibrillar amyloid-beta homologous peptide reduces Alzheimer’s disease-associated pathology in transgenic mice. Am. J. Pathol. 159(2), 439–447.
Van Dorpe J., Smeijers L., Dewachter I., Nuyens D., Spittaels K., Van Den Haute C., et al. (2000) Prominent cerebral amyloid angiopathy in transgenic mice overexpressing the London mutant of human APP in neurons. Am. J. Pathol. 157, 1283–1298.
Walsh D. M., Klyubin I., Fadeeva J. V., Cullen W. K., Anwyl R., Wolfe M. S., et al. (2002) Naturally secreted oligomers of amyloid beta protein potently inhibit hippocampal long-term potentiation in vivo. Nature 416(6880), 535–539.
Willem M., Dewachter I., Smyth N., Van Dooren T., Borghgraef P., Haass C., and Van Leuven F. (2004) Betasite amyloid precursor protein cleaving enzyme 1 increases amyloid deposition in brain parenchyma but reduces cerebrovascular amyloid angiopathy in aging BACE × APP [V717I] double-transgenic mice. Am. J. Pathol. 165(5), 1621–1631.
Zhang J., Wu X., Qin C., Qi J., Ma S., Zhang H., et al. (2003) A novel recombinant adeno-associated virus vaccine reduces behavioral impairment and beta-amyloid plaques in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol. Dis. 14(3), 365–379.
Zurbriggen R., Novak-Hofer I., Seelig A., and Gluck R. (2000). IRIV-adjuvanted hepatitis A vaccine: in vivo absorption and biophysical characterization. Prog. Lipid Res. 39, 3–18.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zurbriggen, R., Amacker, M., Kammer, A.R. et al. Virosome-based active immunization targets soluble amyloid species rather than plaques in a transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. J Mol Neurosci 27, 157–166 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1385/JMN:27:2:157
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1385/JMN:27:2:157