Abstract
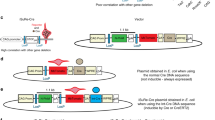
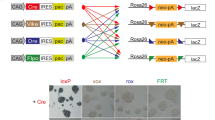
Cre recombinase has become an important tool in the precise manipulation of the genome, and its adoption has led to the development of increasingly accurate mouse models for the understanding of gene function. Although much of current work exploits the alacrity and precision with which Cre catalyzes excisive DNA recombination, Cre also is adept at the insertion of heterologous DNA into the genome. The precision and efficiency with which Cre can target DNA to a predesignated locus in the genome promises to facilitate understanding of mutant genes and allelic variants in their natural chromosomal context.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Capecchi, M. R. (1994). Sci. Am. 270, 52–59.
Sternberg, N., Sauer, B., Hoess, R., and Abremski, K. (1986). J. Mol. Biol. 187, 197–212.
Rajewsky, K., Gu, H., Kühn, R., et al. (1996). J. Clin. Invest. 98, 600–603.
Metzger, D. and Feil, R. (1999). Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 10, 470–476.
Sauer, B. (2002). In: Mobile DNA II. Craig, N. L., Craigie, R., Gellert, M., and Lambowitz, A. M. (eds.). ASM Press: Washington, DC.
Argos, P., Landy, A., Abremski, K., et al. (1986). EMBO J. 5, 433–440.
Hoess, R. H., Ziese, M., and Sternberg, N. (1982). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 79, 3398–3402.
Hoess, R. H. and Abremski, K. (1984). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 81, 1026–1029.
Abremski, K., Hoess, R., and Sternberg, N. (1983). Cell 32, 1301–1311.
Sauer, B. (1987). Mol. Cell. Biol. 7, 2087–2096.
Sauer, B. and Henderson, N. (1988). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 85, 5166–5170.
Sauer, B. and Henderson, N. (1989). Nucleic Acids Res. 17, 147–161.
Le, Y., Gagneten, S., Tombaccini, D., Bethke, B., and Sauer, B. (1998). Nucleic Acids Res. 24, 4703–4709.
Sauer, B. and Henderson, N. (1990). New Biol. 2, 441–449.
Lakso, M., Sauer, B., Mosinger, J. B., et al. (1992). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 89, 6232–6236.
Orban, P. C., Chui, D., and Marth, J. D. (1992). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 89, 6861–6865.
Gu, H., Marth, J. D., Orban, P. C., Mossmann, H., and Rajewsky, K. (1994). Science 265, 103–106.
Tsien, J. Z., Chen, D. F., Gerber, D., et al. (1996). Cell 87, 1317–1326.
Tsien, J. Z., Huerta, P. T., and Tonegawa, S. (1996). Cell 87, 1327–1338.
Gagneten, S., Le, Y., Miller, J., and Sauer, B. (1997). Nucleic Acids Res. 25, 3326–3331.
Le, Y., Miller, J. L., and Sauer, B. (1999). Anal. Biochem. 270, 334–336.
Baubonis, W. and Sauer, B. (1993). Nucleic Acids Res. 21, 2025–2029.
Fukushige, S. and Sauer, B. (1992). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 89, 7905–7909.
Sauer, B., Baubonis, W., Fukushige, S., and Santomenna, L. (1992). Methods 4, 143–149.
Rucker, E. B. and Piedrahita, J. A. (1997). Mol. Reprod. Dev. 48, 324–331.
Kolb, A. F., Ansell, R., McWhir, J., and Siddell, S. G. (1999). Gene 227, 21–31.
Kolb, A. F. and Siddell, S. G. (1997). Gene 203, 209–216.
Choi, S., Begum, D., Koshinsky, H., Ow, D. W., and Wing, R. A. (2000). Nucleic Acids Res. 28, e19.
Call, L. M., Moore, C. S., Stetten, G., and Gearhart, J. D. (2000). Hum. Mol. Genet. 9, 1745–1751.
Sternberg, N., Hoess, R., and Abremski, K. (1983). In: Mechanisms of DNA replication and recombination, UCLA symposia on molecular and cellular biology, Vol. 10. Cozzarelli, N. R. (ed.). Alan R. Liss: New York.
Abremski, K. and Hoess, R. (1985). J. Mol. Biol. 184, 211–220.
Albert, H., Dale, E. C., Lee, E., and Ow, D. W. (1995). Plant J. 7, 649–659.
Araki, K., Araki, M., and Yamamura, K. (1997). Nucleic Acids Res. 25, 868–872.
Hoess, R. H., Wierzbicki, A., and Abremski, K. (1986). Nucleic Acids Res. 14, 2287–2300.
Artelt, P., Grannemann, R., Stocking, C., Friel, J., Bartsch, J., and Hauser, H. (1991). Gene 99, 249–254.
Rijli, F. M., Dollé, P., Fraulob, V., Lemeur, M., and Chambon, P. (1994). Dev. Dyn. 201, 366–377.
Feiring, S., Kim, C. G., Epner, E. M., and Groudine, M. (1993). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 90, 8469–8473.
Bethke, B. and Sauer, B. (1997). Nucleic Acids Res. 25, 2828–2834.
Bouhassira, E. E., Westerman, K., and Leboulch, P. (1997). Blood 90, 3332–3344.
Soukharev, S., Miller, J. L., and Sauer, B. (1999). Nucleic Acids Res. 27, e21.
Feng, Y.-Q., Seibler, J., Alami, R., et al. (1999). J. Mol. Biol. 292, 779–785.
Lewandoski, M. and Martin, G. R. (1997). Nat. Genet. 17, 223–225.
Lee, G. and Saito, I. (1998). Gene 216, 55–65.
Kolb, A. (2001). Anal. Biochem. 290, 260–271.
Siegel, R. W., Jain, R., and Bradbury, A. (2001). FEBS Lett. 505, 467–473.
Aranda, M., Kanellopoulou, C., Christ, N., Peitz, M., Rajewsky, K., and Droge, P. (2001). J. Mol. Biol. 311, 453–459.
Seibler, J. and Bode, J. (1997). Biochemistry 36, 1740–1747.
Seibler, J., Schubeler, D., Fiering, S., Groudine, M., and Bode, J. (1998). Biochemistry 37, 6229–6234.
Baer, A. and Bode, J. (2001). Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 12, 473–480.
Thyagarajan, B., Guimarães, M. J., Groth, A. C., and Calos, M. P. (2000). Gene 244, 47–54.
Sauer, B. (1996). Nucleic Acids Res. 24, 4608–4613.
Schmidt, E. E., Taylor, D. S., Prigge, J. R., Barnett, S., and Capecchi, M. R. (2000). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 97, 13702–13707.
Loonstra, A., Vooijs, M., Beverloo, H. B., et al. (2001). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 98, 9209–9214.
Sauer, B. (1992). J. Mol. Biol. 223, 911–928.
Shimshek, D. R., Kim, J., Hubner, M. R., et al. (2002). Genesis 32, 19–26.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sauer, B. Cre/Iox: One more step in the taming of the genome. Endocr 19, 221–227 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1385/ENDO:19:3:221
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1385/ENDO:19:3:221