Abstract
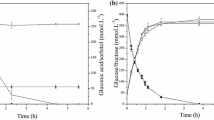
Immobilization of Zymomonas mobilis by different methods was investigated. Experiments were performed order to choose the most appropriate support for the immobilization of the cells. The most advantageous option was to use permeabilized cells in the bore of microporous hollow fibers. Whereas the reaction rate was about 33 g of gluconate/ (g of protein·h) using hollow fibers, which is comparable to that observed by using free cells, the calcium alginate immobilized cells presented a reaction rate of 4 g of gluconate/ (g of protein·h). These results can be explained by the mass transfer resistance effect, which, indeed, was much lower in the case of hollow-fiber membranes than in the alginate gel beads. A loss of enzymatic activity during the reaction was observed in all experiments, which was attributed to the lactone produced as an intermediate of the reaction.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mattey, M. (1992), Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 12(1/2), 87–132.
Zachariou, M. and Scopes, R. K. (1986), J. Bacteriol. 167(3), 863–869.
Ro, H. S. and Kim, H. S. (1991), Enzyme Microb. Biotechnol. 13, 920–924.
Scopes, R. K., Rogers, P. L., and Leigh, D. A. (1988), US patent no. 4755467.
Bringer-Meyer, S. and Sahm, H. (1991), US patent no. 5017485.
Kim, H.-S. and Park, J.-S. (1993), US patent no. 5177012.
Rehr, B. and Sahm, H. (1992), US patent no. 5102795.
Hardman, J. and Scopes, R. K. (1988), Eur. J. Biochem. 173, 203–209.
Loos, H., Krämer, R., Sahm, H., et al. (1994), J. Bacteriol. 176(24), 7688–7693.
Parker, C., Peekhaus, N., Zhang, X., et al. (1997), Appl. Envir. Microbiol. 63(9), 3519–3525.
Fürlinger, M., Haltrich, D., Kulbe, D., et al. (1998), Eur. J. Biochem. 251, 955–963.
Chun, U. H. and Rogers, P. L. (1988), Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 29, 19–24.
Rehr, B., Wilhelm, C., and Sahm, H. (1991), Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 35, 144–148.
Jang, K. H., Park, C. J., and Chun, U. H. (1992), Biotechnol. Lett. 14(4), 311–316.
Gollhofer, D., Nidetzky, B., Fürlinger, M., et al. (1995), Enzyme Microb. Technol. 17, 235–240.
Cabral, J. M. S. (1986), Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 23, 157–162.
Woodward, J. (1988), J. Microbiol. Meth. 8, 91–102.
Doelle, H. W., Kirk, L., Crittenden, R., et al. (1993), Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 13(1), 57–98.
Bunch, A. W. (1988), J. Microbiol. Meth. 8, 103–119.
Prazeres, D. M. F. and Cabral, J. M. S. (1994), Enzyme Microb. Technol. 16, 738–750.
Paterson, S. L., Fane, A. G., Fell, C. J. D., et al. (1988), Biocatalysis 1, 217–229.
Bailey, J. E. and Ollis, D. F. (1986) in Biochemical Engineering Funamentals, 2nd ed., McGraw-Hill, New York.
Bradford, M. M. (1976), Anal. Biochem. 72, 248–254.
Cordeiro, C. and Freire, A. P. (1994), Anal. Biochem. 223, 321–323.
Milson, P. E. and Meers, J. L. (1985), in Comprehensive Biotechnology, Moo-Young, M., ed., Pergamon, New York, pp. 598–600.
Degrassi, A., Toffanin, R., Paoletti, S., et al. (1998), Carbohydr. Res. 306, 19–26.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ferraz, H.C., Borges, C.P. & Alves, T.L.M. Sorbitol and gluconic acid production using permeabilized Zymomonas mobilis cells confined by hollow-fiber membranes. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 89, 43–53 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1385/ABAB:89:1:43
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1385/ABAB:89:1:43