Abstract
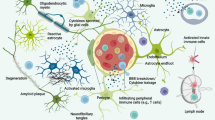
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is the most common dementing illness and is pathologically characterized by deposition of the 40–42 amino acid peptide, amyloid-β (Aβ), as senile plaques. It is well documented that brain inflammatory mechanisms mediated by reactive glia are activated in response to Aβ plaques. A number of reports further suggest that T-cells are activated in AD patients, and that these cells exist both in the periphery and as infiltrates in the brain. We explore the potential role of T-cells in the AD process, a controversial area, by reviewing reports that show disturbed activation profiles and/or altered numbers of various subsets of T-cells in the circulation as well as in the AD brain parenchyma and in cerebral amyloid angiopathy. We also discuss the recent Aβ immunotherapy approach vis-à-vis the activated, autoaggressive T-cell infiltrates that contributed to aseptic meningoencephalitis in a small percentage of patients, and present possible alternative approaches that may be both efficacious and safe. Finally, we explore the use of mouse models of AD as a system within which to definitively test the possible contribution of T-cells to AD pathogenesis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anders K. H., Wang Z. Z., Kornfeld M., et al. (1997) Giant cell arteritis in association with cerebral amyloid angiopathy: immunohistochemical and molecular studies. Hum. Pathol. 28, 1237–1246.
Archambault A. S., Sim J., Gimenez M. A., and Russell J. H. (2005) Defining antigen-dependent stages of T cell migration from the blood to the central nervous system parenchyma. Eur. J. Immunol. 35, 1076–1085.
Baril L., Nicolas L., Croisile B., et al. (2004) Immune response to Abeta-peptides in peripheral blood from patients with Alzheimer’s disease and control subjects. Neurosci. Lett. 355, 226–230.
Becker K. J., McCarron R. M., Ruetzler C., et al. (1997) Immunologic tolerance to myelin basic protein decreases stroke size after transient focal cerebral ischemia. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 94, 10,873–10,878.
Bongioanni P., Boccardi B., Borgna M., Castagna M., and Mondino C. (1997) T-cell interferon gamma binding in patients with dementia of the Alzheimer type. Arch. Neurol. 54, 457–462.
Cribbs D. H., Ghochikyan A., Vasilevko V., et al. (2003) Adjuvant-dependent modulation of Th1 and Th2 responses to immunization with beta-amyloid. Int. Immunol. 15, 505–514.
Das P., Murphy M. P., Younkin L. H., Younkin S. G., and Golde T. E. (2001) Reduced effectiveness of Abeta1-42 immunization in APP transgenic mice with significant amyloid deposition. Neurobiol. Aging 22, 721–727.
Dong C. and Flavell R. A. (2001) Th1 and Th2 cells. Curr. Opin. Hematol. 8, 47–51.
Dutton R. W., Bradley L. M., and Swain S. L. (1998) T cell memory. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 16, 201–223.
Ellis R. J., Olichney J. M., Thal L. J., et al. (1996) Cerebral amyloid angiopathy in the brains of patients with Alzheimer’s disease: the CERAD experience, Part XV. Neurology 46, 1592–1596.
Eng J. A., Frosch M. P., Choi K., Rebeck G. W., and Greenberg S. M. (2004) Clinical manifestations of cerebral amyloid angiopathy-related inflammation. Ann. Neurol. 55, 250–256.
Furlan R., Brambilla E., Sanvito F., et al. (2003) Vaccination with amyloid-beta peptide induces autoimmune encephalomyelitis in C57/BL6 mice. Brain 126, 285–291.
Gruden M. A., Davudova T. B., Malisauskas M., et al. (2004) Autoimmune responses to amyloid structures of Abeta(25–35) peptide and human lysozyme in the serum of patients with progressive Alzheimer’s disease. Dement. Geriatr. Cogn. Disord. 18, 165–171.
Hickey W. F. (2001) Basic principles of immunological surveillance of the normal central nervous system. Glia 36, 118–124.
Huberman M., Sredni B., Stern L., Kott E., and Shalit F. (1995) IL-2 and IL-6 secretion in dementia: correlation with type and severity of disease. J. Neurol. Sci. 130, 161–164.
Hyman B. T., Smith C., Buldyrev I., et al. (2001) Autoantibodies to amyloid-beta and Alzheimer’s disease. Ann. Neurol. 49, 808–810.
Janus C., Pearson J., McLaurin J., et al. (2000) A beta peptide immunization reduces behavioural impairment and plaques in a model of Alzheimer’s disease. Nature 408, 979–982.
Jones T. B., Basso D. M., Sodhi A., et al. (2002) Pathological CNS autoimmune disease triggered by traumatic spinal cord injury: implications for autoimmune vaccine therapy. J. Neurosci. 22, 2690–2700.
Kim H. D., Cao Y., Kong F. K., et al. (2005) Induction of a Th2 immune response by co-administration of recombinant adenovirus vectors encoding amyloid beta-protein and GM-CSF. Vaccine 23, 2977–2986.
Lafaille J. J. (1998) The role of helper T cell subsets in autoimmune diseases. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 9, 139–151.
Lemere C. A., Maron R., Selkoe D. J., and Weiner H. L. (2001) Nasal vaccination with beta-amyloid peptide for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. DNA Cell Biol. 20, 705–711.
Lemere C. A., Maron R., Spooner E. T., et al. (2000) Nasal A beta treatment induces anti-A beta antibody production and decreases cerebral amyloid burden in PD-APP mice. Ann. NY. Acad. Sci. 920, 328–331.
Linton P. J., Haynes L., Klinman N. R., and Swain S. L. (1996) Antigen-independent changes in naive CD4 T cells with aging. J. Exp. Med. 184, 1891–1900.
Lombardi V. R., Fernandez-Novoa L., Etcheverria I., Seoane S., and Cacabelos R. (2004) Association between APOE epsilon4 allele and increased expression of CD95 on T cells from patients with Alzheimer’s disease. Methods Find. Exp. Clin. Pharmacol. 26, 523–529.
Lombardi V. R., Garcia M., Rey L., and Cacabelos R. (1999) Characterization of cytokine production, screening of lymphocyte subset patterns and in vitro apoptosis in healthy and Alzheimer’s Disease (AD) individuals. J. Neuroimmunol. 97, 163–171.
Lopez O. L., Rabin B. S., and Huff F. J. (1991) Serum auto-antibodies in Alzheimer’s disease. Acta Neurol. Scand. 84, 441–444.
McGeer E. G. and McGeer P. L. (1999a) Brain inflammation in Alzheimer disease and the therapeutic implications. Curr. Pharm. Des. 5, 821–836.
McGeer P. L. and McGeer E. G. (1999b) Inflammation of the brain in Alzheimer’s disease: implications for therapy. J. Leukoc. Biol. 65, 409–415.
McGeer P. L. and McGeer E. G. (2002) Innate immunity, local inflammation, and degenerative disease. Sci. Aging Knowledge Environ. 2002(29), re3.
Moalem G., Leibowitz-Amit R., Yoles E., Mor F., Cohen I. R., and Schwartz M. (1999) Autoimmune T cells protect neurons from secondary degeneration after central nervous system axotomy. Nat. Med. 5, 49–55.
Monsonego A., Imitola J., Zota V., Oida T., and Weiner H. L. (2003a) Microglia-mediated nitric oxide cytotoxicity of T cells following amyloid beta-peptide presentation to Th1 cells. J. Immunol. 171, 2216–2224.
Monsonego A., Maron R., Zota V., Selkoe D. J., and Weiner H. L. (2001) Immune hyporesponsiveness to amyloid beta-peptide in amyloid precursor protein transgenic mice: implications for the pathogenesis and treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 98, 10273–10278.
Monsonego A., Zota V., Karni A, et al. (2003b) Increased T cell reactivity to amyloid beta protein in older humans and patients with Alzheimer disease. J. Clin. Invest. 112, 415–422.
Morgan D., Diamond D. M., Gottschall P. E., et al. (2000) A beta peptide vaccination prevents memory loss in an animal model of Alzheimer’s disease. Nature 408, 982–985.
Mruthinti S., Buccafusco J. J., Hill W. D., et al. (2004) Autoimmunity in Alzheimer’s disease: increased levels of circulating IgGs binding Abeta and RAGE peptides. Neurobiol. Aging 25, 1023–1032.
Myagkova M. A., Gavrilova S. I., Lermontova N. N., et al. (2003) Content of autoantibodies to bradykinin and beta-amyloid(1–42) as a criterion for biochemical differences between Alzheimer’s dementias. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 136, 49–52.
Nagelkerken L. (1998) Role of Th1 and Th2 cells in autoimmune demyelinating disease. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 31, 55–60.
Nath A., Hall E., Tuzova M., et al. (2003) Autoantibodies to amyloid beta-peptide (A beta) are increased in Alzheimer’s disease patients and Abeta antibodies can enhance Abeta neurotoxicity: implications for disease pathogenesis and vaccine development. Neuromol. Med. 3, 29–39.
Nicoll J. A., Wilkinson D., Holmes C., Steart P., Markham H., and Weller R. O. (2003) Neuropathology of human Alzheimer disease after immunization with amyloid-beta peptide: a case report. Nat. Med. 9, 448–452.
Peterson D. A., DiPaolo R. J., Kanagawa O., and Unanue E. R. (1999) Quantitative analysis of the T cell repertoire that escapes negative selection. Immunity 11, 453–462.
Pfeifer M., Boncristiano S., Bondolfi L., et al. (2002) Cerebral hemorrhage after passive anti-Abeta immunotherapy. Science 298, 1379.
Qu B., Rosenberg R. N., Li L., Boyer P. J., and Johnston S. A. (2004) Gene vaccination to bias the immune response to amyloid-beta peptide as therapy for Alzheimer disease. Arch. Neurol. 61, 1859–1864.
Rogers J., Luber-Narod J., Styren S. D., and Civin W. H. (1988) Expression of immune system-associated antigens by cells of the human central nervous system: relationship to the pathology of Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol. Aging 9, 339–349.
Rogers J., Webster S., Lue L. F., et al. (1996) Inflammation and Alzheimer’s disease pathogenesis. Neurobiol. Aging 17, 681–686.
Romagnani S. (1992) Human TH1 and TH2 subsets: regulation of differentiation and role in protection and immunopathology. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 98, 279–285.
Romagnani S. (2000) T-cell subsets (Th1 versus Th2) Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 85, 9–18; quiz 18, 21.
Schenk D., Barbour R., Dunn W., et al. (1999) Immunization with amyloid-beta attenuates Alzheimer-disease-like pathology in the PDAPP mouse. Nature 400, 173–177.
Scolding N. J., Joseph F., Kirby P. A., et al. (2005) Abetarelated angiitis: primary angiitis of the central nervous system associated with cerebral amyloid angiopathy. Brain 128, 500–515.
Shalit F., Sredni B., Stern L., Kott E., and Huberman M. (1994) Elevated interleukin-6 secretion levels by mononuclear cells of Alzheimer’s patients. Neurosci. Lett. 174, 130–132.
Tan J., Town T., Abdullah L., et al. (2002a) CD45 isoform alteration in CD4+ T cells as a potential diagnostic marker of Alzheimer’s disease. J. Neuroimmunol. 132, 164–172.
Tan J., Town T., Crawford F., et al. (2002b) Role of CD40 ligand in amyloidosis in transgenic Alzheimer’s mice. Nat. Neurosci. 5, 1288–1293.
Tan J., Town T., and Mullan M. (2002c) CD40-CD40L interaction in Alzheimer’s disease. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2, 445–451.
Tan J., Town T., Paris D., et al. (1999a) Microglial activation resulting from CD40-CD40L interaction after beta-amyloid stimulation. Science 286, 2352–2355.
Tan J., Town T., Suo Z., et al. (1999b) Induction of CD40 on human endothelial cells by Alzheimer’s beta-amyloid peptides. Brain Res. Bull. 50, 143–148.
Tarkowski E., Wallin A., Regland B., Blennow K., and Tarkowski A. (2001) Local and systemic GM-CSF increase in Alzheimer’s disease and vascular dementia. Acta. Neurol. Scand. 103, 166–174.
Togo T., Akiyama H., Iseki E., et al. (2002) Occurrence of T cells in the brain of Alzheimer’s disease and other neurological diseases. J. Neuroimmunol. 124, 83–92.
Town T., Tan J., and Mullan M. (2001a) CD40 signaling and Alzheimer’s disease pathogenesis. Neurochem. Int. 39, 371–380.
Town T., Tan J., Sansone N., Obregon D., Klein T., and Mullan M. (2001b) Characterization of murine immunoglobulin G antibodies against human amyloid-beta1-42 Neurosci. Lett. 307, 101–104.
Town T., Vendrame M., Patel A., et al. (2002) Reduced Th1 and enhanced Th2 immunity after immunization with Alzheimer’s beta-amyloid(1–42). J. Neuroimmunol. 132, 49–59.
Townsend K. P., Town T., Mori T., et al. (2005) CD40 signaling regulates innate and adaptive activation of microglia in response to amyloid beta-peptide. Eur. J. Immunol. 35, 901–910.
Weiner H. L., Lemere C. A., Maron R., et al. (2000) Nasal administration of amyloid-beta peptide decreases cerebral amyloid burden in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Ann. Neurol. 48, 567–579.
Wyss-Coray T., Lin C., Yan F., et al. (2001) TGF-beta1 promotes microglial amyloid-beta clearance and reduces plaque burden in transgenic mice. Nat. Med. 7, 612–618.
Yamada M., Itoh Y., Shintaku M., et al. (1996) Immune reactions associated with cerebral amyloid angiopathy. Stroke 27, 1155–1162.
Zhang J., Wu X., Qin C., et al. (2003) A novel recombinant adeno-associated virus vaccine reduces behavioral impairment and beta-amyloid plaques in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol. Dis. 14, 365–379.