Abstract
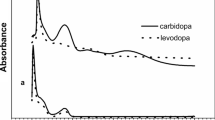
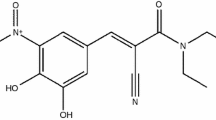
This paper investigates the hydrolysis kinetics of levodopa methyl ester in 0.05–1.5 M HCl between 37 and 75°C. An isocratic HPLC assay was developed for simultaneous determination of levodopa methyl ester and levodopa in the hydrolysate of levodopa methyl ester. A series of hydrolysis rate constants were obtained and the effects of hydrogen ion concentration and temperature on the reaction were evaluated. It was found that pH was a key factor at low temperature, but that when the temperature was raised, temperature became in turn the most influent factor on the hydrolysis. From the measured pseudo-first order reaction rate constants, the activation energy for levodopa methyl ester hydrolysis in 0.5, 1.0 and 1.5 M HCl were calculated to be 71.24, 74.32 and 76.57 kJ mol−1, respectively.
Similar content being viewed by others

References
Connors KA, Amidon GL, Stella VJ, Chemical Stability of pharmaceuticals (1986) A handbook for Pharmacists, 2nd ed., Wiley-Interscience, New York
Bodor NS, Sloan KB, Hussain AA (1976) U.S. Patent 3,939,253
Bodor NS, Sloan KB (1977) U.S. Patent 4,035,507
Juncos JL, Mouradian MM, Fabbrini G, Serrati C, Chasel TN (1987) Neurology 37:1242–1245
Steiger MJ, Stocchi F, Carta A, Ruggieri S, Agnoli A, Quinn NP, Marsden CD (1991) Clin Neuropharmacol 14(3):241–244
Stocchi F, Barbato L, Bramante L , Nordera G, Vacca L, Ruggieri S (1996) J Neurol 243(5):377–380
Stocchi F, Barbato L, Bramante L , Bonamartini A, Ruggieri S (1994) Funct Neurol 9(5):259–264
Cooper DR, Marrel C, Testa B, Waterbeemd HVD, Quinn N, Jenner P, Marsden CD (1984) Clin Neuropharmacol 7 (1):89–98
Composition of L-dopa esters (1993) Eur Patent 0610595 (A2)
United States Pharmacopeial Convention (2004) 27th ed, Description and Solubility , The United States Pharmacopeial Convention, MD, USA, p. 2768
Gomez R, Hagel RB, MacMullan EA (1976) Anal Profiles Drug Subs 5:189–223
Hartmann C, Massart DL, Mcdowall RD (1994) J Pharm Biomed Anal 12(11):1337–1343
United States Pharmacopeial Convention (2004) 27th ed, Validation of Compendial Methods, The United States Pharmacopeial Convention, MD, USA, pp. 2622–2625
Drossman H, Johnson H, Mill T (1988) Chemosphere 17:1509–1530
Adamson AW (1986) A Textbook of Physical Chemistry, 3rd ed., Los Angeles, Ch 14, p. 541
Mabey W, Mill T (1978) J Phys Chem Ref Data 7:383–415
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Revised: 24 May and 15 August 2005
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, J., Zhou, Y. & Fang, Y.Z. Studies of the Rate Constant of Levodopa Methyl Ester Hydrolysis by LC. Chroma 62, 423–428 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1365/s10337-005-0643-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1365/s10337-005-0643-3