Abstract
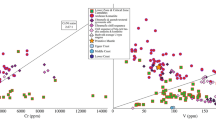
Carbonatites in the Maoniuping REE deposit, Sichuan Province, which are spatially and temporally associated with rare earth mineralization, were emplaced at the time of Himalayan. The rocks are carbonatite-syenite complexes, with the mineral assemblages of calcite-aegirine-acmite-arfvedsonite-mica-orthoclase. The rocks are characterized by the enrichment in incompatible elements, such as Sr, Ba and REE, with C and O isotopic compositions of the “primary igneous carbonatites”, relatively high initial 87Sr/86Sr ratios and low ɛnd values. All of these suggest that the rocks were derived from the metasomatic enriched mantle. It is demonstrated by geological and geochemical evidence that the mixing of the Himalayan subducting crustal materials with mantle source EM1 is probably the main factor responsible for the formation of carbonatites. The carbonatite-syenite complexes were generated from liquid immiscibility of CO2-rich alkalic silicate magma, which was derived from partial melting of the metasomatic mantle.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tilton, G. R., Bryce, J. G., Mateen, A., Pb-Sr-Nd isotope data from 30 and 300 Ma collision zone carbonatites in Northwest Pakistan, J. Petrol., 1998, 39: 1865–1874.
LeBas, M. J., Diversification of carbonatites, in Carbonatites: Genesis and Evolution (ed. Bell, K. ), London: Unwin Hyman, 1989, 427–447.
Doboson, D. P., Jones, A. P., In-situ measurement of viscosity and density of carbonate melts at high pressure, Earth Planet. Sci. Lett., 1996, 143: 207–215.
Wyllie, P. J., Origin of carbonatites: evidence from phase equilibrium studies, in Carbonatites: Genesis and Evolution (ed. Bell, K. ), London: Unwin Hyman, 1989, 15–37.
Treiman, A. H., Schedl, A., Properties of carbonatite magma and processes in carbonatite magma chambers, J. Petrol., 1983, 91: 437–447.
Tu Gruangchi, The unique nature in ore composition, geological background and metallogenic mechanism of nonconventional super-large ore deposits: A preliminary discussion, Science in China, Ser. D, 1998, 41 (Supplement), 1–6.
Pu, G. P., Discovery of an alkali pegmatite-carbonatite complex zone in Maoniuping, Southwestern Sichuan Province, Geological Review (in Chinese), 1988, 34(1): 86–92.
Wang, D. H., Yang, J. M., Yan, S. H., A special orogenic type REE deposit in Maoniuping, Sichuan, China: Geology and geochemistry, Resource Geology, 2001, 51(3): 177–188.
Yuan, Z. X., Shi, Z. M., Bai, G. et al., Rare Earth Element Deposit in Maoniuping Mianning in Sichuan Province (in Chinese), Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 1995, 89–102.
Pu, G. P., The evolution history of REE mineralization and major features of Himalayan REE deposit in thr Panzhihua-Xichang area, Sichuan, in Study on Himalayan endognic mineralization (eds. Chen, Y. C., Wang, D. H.) (in Chinese), Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2001, 104–116.
Qi, L., Hu, J., Gregoire, D. C., Determination of trace elements in granites by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry, Talanta, 2000, 51: 507–513.
Samoilov, V. S., The main geochemical features of carbonatites, Journal of Geochemical Exploration, 1991, 40: 251–262.
Yang, X. M., Yang, X. Y., Geological and geochemical characteristics of carbonatites and their implication for tectonic settings, Advance in Earth Sciences (in Chinese), 1998, 13(5): 457–466.
Sun, S. S., McDonoigh, W. F., Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts: Implications for mantle compositions and processes, in Magmatism in the Oceanic Basins, Geological Society (ed. Saunders, A. D.), London: Special Publication, 1989, 313–345.
Boynton, W. V., Cosmochemistry of the rare earth elements: Meteorite studies, Dev. Geochem., 1984, 2: 63–114.
Keller, J., Hoefs, J., Stable isotope characteristics of recent natrocarbonatites from Oldoinyo Lengai, in Carbonatites Volcanism: Oldoinyo Lengai and Petrogenesis of Natrocarbonatites, IAVCEI Proceeding in Volcanology (ed. Bell, K. ), Berlin: Springer, 1995, 113–123.
Friedman, I., Oneil, J. R., Compilation of stable isotope fractionation fraction factors of geochemical interest, in Data of Geochemistry (ed. Fleischer, M.), 6th ed., Geology Survey Professional Paper, 1977, 117–117.
Epaolo, D. J., Implications of correlated Nd and Sr isotopic variations for the chemical evolution of crust and mantle, Earth Planet. Sci. Lett., 1979, 43: 201–211.
Jachson, S. B., Wasserburg, J. G., Sm-Nd isotopic evolution of chondrites, Earth Planet. Sci. Lett., 1980, 50: 139–155.
Toyoda, K., Horuchi, H., Tokonami, M., Dupal anomaly of Brazilian carbonatites: Geochemocal correlations with hotspots in the South Atlantic and implications for the mantle source, Earth Planet. Sci. Lett., 1994, 126: 315–331.
Simonetti, A., Bell, K., Nd, Pd, and Sr isotope systematics of fluorite at the Amba Dongar carbonatite complex, India: Evidence for hydrothermal and crustal fluid mixing, Econ. Geol., 1995, 90: 2018–2027.
Harmer, R. E., Gittins, J., The case for primary, mantle-derived carbonatite magma, J. Petrol., 1998, 39: 1895–1903.
Hart, S. R., Hauri, E. H., Oschmann, L. A., Mantle plume and entrainment isotopic evidence, Science, 1992, 256: 517–520.
Lee, W. J., Wyllie, P. J., Experimental data bearing on liquid immiscibility, crystal fraction, and the origin of calciocar-bonatites and natrocarbonatites, International Geology Review, 1994, 36: 797–819.
Kjarsgaard, B. A., Hamilton, D. L., The genesis of carbonatites by immiscibility, in Carbonatites: Genesis and Evolution (ed. Bell, K. ), London: Unwin Hyman, 1989, 388–404.
Huang, Z. L., Liu, C. Q., Xiao, H. Y. et al., Study on the carbonate ocelli-bearing lamprophyre dyke in the Ailaoshan gold deposit zone, Yunnan Province, Science in China, Ser. D, 2002, 45(6): 494–502.
Bell, K., Radiogenic isotope constraints on relationships between carbonatites and associated silicate rocks—A brief review, J. Petrol., 1998, 39: 1987–1996.
Veksler, I. V., Petibon, C., Jenner, G. A., Trace element partitioning in immiscible silicate-carbonate liquids: An initial experimental study using a centrifuge autoclave, J. Petrol., 1998, 39: 2095–2104.
Wendlant, R. F., Harrison, W. J., Rare earth partitioning between immiscible carbonate and silicate liquids and CO2 vapor: results and implications for the formation of light earth-enriched rocks, Contrib. Mineral. Petrol., 1979, 69: 409–419.
Ionov, D. A., Dupuy, C., Oreilly, S. Y., Carbonated peridotite xenoliths from Spitsbergen: Implications for trace element signature of mantle carbonate metasomatism, Earth Planet. Sci. Lett., 1993, 119: 283–297.
Hart, S. R., Heterogeneous mantle domains: signatures, genesis and mixing chronologies, Earth Planet. Sci. Lett., 1988, 90: 273–296.
Zhang, Y. X., Lu, Y. N., Yang, C. X. et al., The Panxi Rift (in Chinese), Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 1988, 224–270.
Hu, S. X., Zhao, Y. B., Lu, B. et al., Evidence for the Jiangsu-Shandong ultra-high-pressure metamorphic belt returning from the upper mantle to the earth surface in the Mesozoic-Cenozoic, Acta Geologica Sinica (in Chinese), 1997, 71(3): 245–253.
Chen, Y. J., Constraints and their mechanism on the petrogenic and metallogenic model for collision orogenesis, Earth Science Frontiers (in Chinese), 1998, 5(Supplement): 109–118.
Sui, Y. H., Wang, H. H., Gao, X. L. et al., Ore fluid of the Tieluping silver deposit of Henan Province and its illustration of the tectonic model for collisional petrogenesis, metallogenesis and fluidization, Science in China, Ser. D, 2000, 43(Supplement): 108–121.
Chen, Y. J., Li, C., Zhang, J., Sr and Nd isotopic characteristics of porphyries in the Qinling molybdenum deposit belt and their implication to genetic mechanism and type, Science in China, Ser. D, 2000, 43(Supplement): 82–94.
Xu, Z. Q., Yang, J. S., Jiang, M. et al., Continental subduction and uplifting of the orogenic belts at the margin of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, Earth Science Frontiers (in Chinese ), 1999, 6(3): 139–150.
Luo, Y., Yu, R. L., Major features and dynamic model of the Himalayan tectonic-magmatism in the intracontinental orogenic belt in Longmenshan-Jinpingshan, Sichuan Province, in Study on Himalayan Endogenic Mineralization (in Chinese) (eds. Chen, Y. C., Wang, D. H.), Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2001, 88–96.
Rock, N. M. S., Lamprophyres, Glasgow: Blackie, 1990.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, C., Huang, Z., Liu, C. et al. Geochemistry of carbonatites in Maoniuping REE deposit, Sichuan province, China. Sci. China Ser. D-Earth Sci. 46, 246–256 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1360/03yd9023
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1360/03yd9023