- J-STAGE home
- /
- Biological and Pharmaceutical ...
- /
- Volume 44 (2021) Issue 10
- /
- Article overview
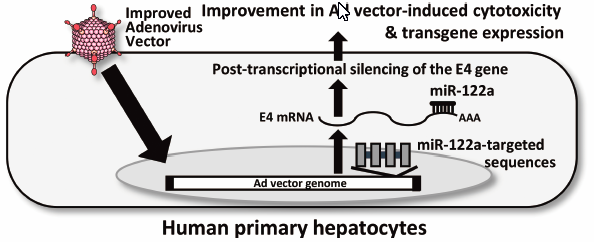
-
Fuminori Sakurai
Corresponding author
Laboratory of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Graduate School of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Osaka University
-
Tomohito Tsukamoto
Laboratory of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Graduate School of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Osaka University
-
Ryosuke Ono
Laboratory of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Graduate School of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Osaka University
-
Fumitaka Nishimae
Laboratory of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Graduate School of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Osaka University
-
Aoi Shiota
Laboratory of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Graduate School of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Osaka University
-
Shunsuke Iizuka
Laboratory of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Graduate School of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Osaka University
-
Kahori Shimizu
Laboratory of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Graduate School of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Osaka University
-
Eiko Sakai
Laboratory of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Graduate School of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Osaka University
-
Yuji Ishida
PhoenixBio Co., Ltd. Collaborative Research Laboratory of Medical Innovation, Hiroshima University
-
Chise Tateno
PhoenixBio Co., Ltd. Collaborative Research Laboratory of Medical Innovation, Hiroshima University
-
Kazuaki Chayama
Collaborative Research Laboratory of Medical Innovation, Hiroshima University Research Center for Hepatology and Gastroenterology, Hiroshima University RIKEN Center for Integrative Medical Sciences
-
Hiroyuki Mizuguchi
Laboratory of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Graduate School of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Osaka University Laboratory of Hepatocyte Regulation, National Institutes of Biomedical Innovation, Health and Nutrition Global Center for Medical Engineering and Informatics, Osaka University Integrated Frontier Research for Medical Science Division, Institute for Open and Transdisciplinary Research Initiatives (OTRI), Osaka University
2021 Volume 44 Issue 10 Pages 1506-1513
- Published: October 01, 2021 Received: May 06, 2021 Released on J-STAGE: October 01, 2021 Accepted: July 15, 2021 Advance online publication: - Revised: -
(compatible with EndNote, Reference Manager, ProCite, RefWorks)
(compatible with BibDesk, LaTeX)