Abstract
Background
Extramammary Paget’s disease (EMPD) is a rare cutaneous malignancy; however, the standard treatment of EMPD has not been established. In this study, we applied mapping biopsy to penoscrotal EMPD and evaluated its effects.
Methods
A retrospective chart review was performed to determine the outcomes of patients with primary penoscrotal EMPD who underwent surgery at our institution between 2007 and 2014. Patients were divided into two groups (one group underwent mapping biopsy, while the other group did not), and the difference between the two groups was analyzed. The 5-year tumor-free rate was estimated using the Kaplan–Meier method, and the risk factors for local recurrence were also estimated.
Results
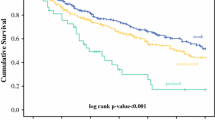
A total of 44 patients were analyzed, and the mean follow-up of patients was 50.27 months. Patients who underwent mapping biopsy showed significantly lower tumor involvement at permanent and frozen biopsies and a lower local recurrence rate than those who did not undergo mapping biopsy. The 5-year tumor-free rate was significantly higher in the mapping biopsy group than in the non-mapping biopsy group. Multivariable analysis demonstrated that age at operation, mapping biopsy, and false-negative results at frozen biopsy were associated with local recurrence.
Conclusions
Mapping biopsy is beneficial to reduce local recurrence in penoscrotal EMPD.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lloyd J, Flanagan AM. Mammary and extramammary Paget’s disease. J Clin Pathol 2000;53:742–9.
Tulchinsky H, Zmora O, Brazowski E, Goldman G, Rabau M. Extramammary Paget’s disease of the perianal region. Colorectal Dis 2004;6:206–9.
Yang WJ, Kim DS, Im YJ, Cho KS, Rha KH, Cho NH, et al. Extramammary Paget’s disease of penis and scrotum. Urology 2005;65:972–5.
Whorton CM, Patterson JB. Carcinoma of moll’s glands with extramammary Paget’s disease of the eyelid. Cancer 1955;8:1009–15.
Changus GW, Yonan TN, Bartolome J. Extramammary Paget’s disease of the tongue. Laryngoscope 1971;81:1621–25.
Fligiel Z, Kaneko M. Extramammary Paget’s disease of the external ear canal in association with ceruminous gland carcinoma. A case report. Cancer 1975;36:1072–6.
Kanitakis J. Mammary and extramammary Paget’s disease. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol 2007;21: 581-90.
Wright JL, Morgan TM, Lin DW. Primary scrotal cancer: disease characteristics and increasing incidence. Urology 2008; 72: 1139-43.
Herrel LA, Weiss AD, Goodman M, Johnson TV, Osunkoya AO, Delman KA, et al. Extramammary Paget’s disease in males: survival outcomes in 495 patients. Ann Surg Oncol 2014; 22: 1625-30.
Hatta N, Yamada M, Hirano T, Fujimoto A, Morita R. Extramammary Paget’s disease: treatment, prognostic factors and outcome in 76 patients. Br J Dermatol 2008;158: 313-8.
Abide JM, Nahai F, Bennett RG. The meaning of surgical margins. Plast Reconstr Surg 1984; 73: 492-7.
Mohs FE, Blanchard L. Microscopically controlled surgery for extramammary Paget’s disease. Arch Dermatol 1979;115: 706-8.
Murata Y, Kumano K. Extramammary Paget’s disease of the genitalia with clinically clear margins can be adequately resected with 1 cm margin. Eur J Dermatol 2005; 15: 168-70.
Gunn RA, Gallager HS. Vulvar Paget’s disease: a topographic study. Cancer 1980; 46: 590-4.
Chan JYW, Li GKH, Chung JHP, Chow VLY. Extramammary Paget’s disease: 20 years of experience in Chinese population. Int J Surg Oncol 2012; 2012: 1-5.
O’Connor WJ, Lim KK, Zalla MJ, Gagnot M, Otley CC, Nguyen TH, et al. Comparison of Mohs micrographic surgery and wide excision for extramammary Paget’s disease. Dermatol Surg 2003; 29: 723-7.
Lee KY, Roh MR, Chung WG, Chung KY. Comparison of Mohs micrographic surgery and wide excision for extramammary Paget’s disease: Korean experience. Dermatol Surg 2009; 35: 34-40.
Hendi A, Brodland DG, Zitelli JA. Extramammary Paget’s disease: surgical treatment with Mohs micrographic surgery. J Am Acad Dermatol 2004; 51: 767-73.
Kim BJ, Park SK, Chang H. The effectiveness of mapping biopsy in patients with extramammary Paget’s disease. Arch Plast Surg 2014; 41: 753-6.
Beilan J, McCormick B, Baumgarten A, Mosiello G, Dhillon J, Spiess P. Mapping biopsies: a new tactic in the surgical management of extramammary Paget’s disease. J Urol 2016; 195: e773.
Appert DL, Otley CC, Phillips PK. Role of multiple scouting biopsies before Mohs micrographic surgery for extramammary Paget’s disease. Dermatol Surg 2005; 31: 1417-22.
Park S, Grossfeld GD, McAninch JW, Santucci R. Extramammary Paget’s disease of the penis and scrotum: excision, reconstruction and evaluation of occult malignancy. J Urol 2001;166: 2112-6.
Lai Y-L, Yang W-G, Tsay P-K, Swei H, Chuang S-S, Wen C-J. Penoscrotal extramammary Paget’s disease: a review of 33 cases in a 20-year experience. Plast Reconstr Surg 2003; 112: 1017-23.
Coldiron BM, Goldsmith BA, Robinson JK. Surgical treatment of extramammary Paget’s disease. A report of six cases and a reexamination of Mohs micrographic surgery compared with conventional surgical excision. Cancer 1991;67:933-38.
Petrie MS, Hess S, Benedetto AV. Automated 15-minute cytokeratin 7 immunostaining potocol for extramammary Pagetʼs disease in Mohs micrographic surgery. Dermatol Surg 2011;37:1811-15.
Zhu Y, Ye DW, Chen ZW, Zhang SL, Qin XJ. Frozen section-guided wide local excision in the treatment of penoscrotal extramammary Paget’s disease. BJU Int 2007;100:1282-87.
Urist MM, Balch CM, Soong S, Shaw HM, Milton GW, Maddox WA. The influence of surgical margins and prognostic factors predicting the risk of local recurrence in 3445 patients with primary cutaneous melanoma. Cancer 1985;55:1398-1402.
Khan L, Breen D, Zhang L, et al. Predictors of recurrence after radiotherapy for non-melanoma skin cancer. Curr Oncol 2014;21:e326-9.
Disclosure
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Park, S.O., Ha, J.H., Hong, K.Y. et al. Usefulness of Mapping Biopsy in the Treatment of Penoscrotal Extramammary Paget’s Disease. Ann Surg Oncol 24, 3229–3236 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-017-5947-7
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-017-5947-7