Abstract
Background
There is increasing evidence that microRNAs are differentially expressed in many types of cancers. Despite progress in analyses of microRNAs in several types of cancers, the functional contributions of microRNAs to pancreatic cancer remain unclear.
Methods
In the present study, the expression levels of specific microRNAs identified by microarray analyses were examined in a panel of 15 pancreatic cancer cell lines. We then investigated the functional roles of these microRNAs in the proliferation and invasion of pancreatic cancer cells.
Results
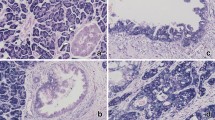
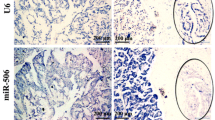
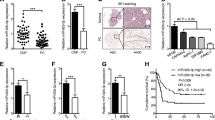
Based on the microarray data, we found frequent and marked overexpression of miR-10a, miR-92, and miR-17-5p in pancreatic cancer cell lines. Microdissection analyses revealed that miR-10a was overexpressed in pancreatic cancer cells isolated from a subset of primary tumors (12 of 20, 60%) compared with precursor lesions and normal ducts (P < .01). In vitro experiments revealed that miR-10a inhibitors decreased the invasiveness of pancreatic cancer cells (P < .01), but had no effect on their proliferation. Inhibition of HOXA1, a target of miR-10a, promoted the invasiveness of pancreatic cancer cells (P < .01).
Conclusions
The present data suggest that miR-10a is overexpressed in a subset of pancreatic cancers and is involved in the invasive potential of pancreatic cancer cells partially via suppression of HOXA1.




Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Hirata K, Egawa S, Kimura Y, Nobuoka T, Oshima H, Katsuramaki T, et al. Current status of surgery for pancreatic cancer. Dig Surg. 2007;24:137–47.
Jemal A, Murray T, Samuels A, Ghafoor A, Ward E, Thun MJ. Cancer statistics, 2003. CA Cancer J Clin. 2003;53:5–26.
Hawes RH, Xiong Q, Waxman I, Chang KJ, Evans DB, Abbruzzese JL. A multispecialty approach to the diagnosis and management of pancreatic cancer. Am J Gastroenterol. 2000;95:17–31.
Matsuno S, Egawa S, Fukuyama S, Motoi F, Sunamura M, Isaji S, et al. Pancreatic cancer registry in Japan: 20 years of experience. Pancreas. 2004;28:219–30.
Neoptolemos JP, Stocken DD, Friess H, Bassi C, Dunn JA, Hickey H, et al. A randomized trial of chemoradiotherapy and chemotherapy after resection of pancreatic cancer. N Engl J Med. 2004;350:1200–10.
Lagos-Quintana M, Rauhut R, Lendeckel W, Tuschl T. Identification of novel genes coding for small expressed RNAs. Science. 2001;294:853–8.
Lau NC, Lim LP, Weinstein EG, Bartel DP. An abundant class of tiny RNAs with probable regulatory roles in Caenorhabditis elegans. Science. 2001;294:858–62.
Lee RC, Ambros V. An extensive class of small RNAs in Caenorhabditis elegans. Science. 2001;294:862–4.
Ambros V. MicroRNA pathways in flies and worms: growth, death, fat, stress, and timing. Cell. 2003;113:673–6.
Johnson SM, Grosshans H, Shingara J, Byrom M, Jarvis R, Cheng A, et al. RAS is regulated by the let-7 microRNA family. Cell. 2005;120:635–47.
Calin GA, Dumitru CD, Shimizu M, Bichi R, Zupo S, Noch E, et al. Frequent deletions and down-regulation of micro- RNA genes miR15 and miR16 at 13q14 in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2002;99:15524–9.
Michael MZ, SM OC, van Holst Pellekaan NG, Young GP, James RJ. Reduced accumulation of specific microRNAs in colorectal neoplasia. Mol Cancer Res. 2003;1:882–91.
Metzler M, Wilda M, Busch K, Viehmann S, Borkhardt A. High expression of precursor microRNA-155/BIC RNA in children with Burkitt lymphoma. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 2004;39:167–9.
Hayashita Y, Osada H, Tatematsu Y, Yamada H, Yanagisawa K, Tomida S, et al. A polycistronic microRNA cluster, miR-17-92, is overexpressed in human lung cancers and enhances cell proliferation. Cancer Res. 2005;65:9628–32.
He L, Thomson JM, Hemann MT, Hernando-Monge E, Mu D, Goodson S, et al. A microRNA polycistron as a potential human oncogene. Nature. 2005;435:828–33.
Liang RQ, Li W, Li Y, Tan CY, Li JX, Jin YX, et al. An oligonucleotide microarray for microRNA expression analysis based on labeling RNA with quantum dot and nanogold probe. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005;33:e17.
Lu J, Getz G, Miska EA, Alvarez-Saavedra E, Lamb J, Peck D, et al. MicroRNA expression profiles classify human cancers. Nature. 2005;435:834–8.
Bloomston M, Frankel WL, Petrocca F, Volinia S, Alder H, Hagan JP, et al. MicroRNA expression patterns to differentiate pancreatic adenocarcinoma from normal pancreas and chronic pancreatitis. JAMA. 2007;297:1901–8.
Szafranska AE, Davison TS, John J, Cannon T, Sipos B, Maghnouj A, et al. MicroRNA expression alterations are linked to tumorigenesis and non-neoplastic processes in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Oncogene. 2007;26:4442–52.
Calvo R, West J, Franklin W, Erickson P, Bemis L, Li E, et al. Altered HOX and WNT7A expression in human lung cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2000;97:12776–81.
Tsou JA, Galler JS, Siegmund KD, Laird PW, Turla S, Cozen W, et al. Identification of a panel of sensitive and specific DNA methylation markers for lung adenocarcinoma. Mol Cancer. 2007;6:70.
Kang GH, Lee S, Cho NY, Gandamihardja T, Long TI, Weisenberger DJ, et al. DNA methylation profiles of gastric carcinoma characterized by quantitative DNA methylation analysis. Lab Invest. 2008;88:161–70.
Sato N, Mizumoto K, Beppu K, Maehara N, Kusumoto M, Nabae T, et al. Establishment of a new human pancreatic cancer cell line, NOR-P1, with high angiogenic activity and metastatic potential. Cancer Lett. 2000;155:153–61.
Furukawa T, Duguid WP, Rosenberg L, Viallet J, Galloway DA, Tsao MS. Long-term culture and immortalization of epithelial cells from normal adult human pancreatic ducts transfected by the E6E7 gene of human papilloma virus 16. Am J Pathol. 1996;148:1763–70.
Ohuchida K, Mizumoto K, Murakami M, Qian LW, Sato N, Nagai E, et al. Radiation to stromal fibroblasts increases invasiveness of pancreatic cancer cells through tumor-stromal interactions. Cancer Res. 2004;64:3215–22.
Ohuchida K, Mizumoto K, Ishikawa N, Fujii K, Konomi H, Nagai E, et al. The role of S100A6 in pancreatic cancer development and its clinical implication as a diagnostic marker and therapeutic target. Clin Cancer Res. 2005;11:7785–93.
Ohuchida K, Mizumoto K, Fujita H, Yamaguchi H, Konomi H, Nagai E, et al. Sonic hedgehog is an early developmental marker of intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms: clinical implications of mRNA levels in pancreatic juice. J Pathol. 2006;210:42–8.
Ohuchida K, Mizumoto K, Egami T, Yamaguchi H, Fujii K, Konomi H, et al. S100P is an early developmental marker of pancreatic carcinogenesis. Clin Cancer Res. 2006;12:5411–6.
Zhang L, Mizumoto K, Sato N, Ogawa T, Kusumoto M, Niiyama H, et al. Quantitative determination of apoptotic death in cultured human pancreatic cancer cells by propidium iodide and digitonin. Cancer Lett. 1999;142:129–37.
Volinia S, Calin GA, Liu CG, Ambs S, Cimmino A, Petrocca F, et al. A microRNA expression signature of human solid tumors defines cancer gene targets. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2006;103:2257–61.
Weiss FU, Marques IJ, Woltering JM, Vlecken DH, Aghdassi A, Partecke LI, et al. Retinoic acid receptor antagonists inhibit miR-10a expression and block metastatic behavior of pancreatic cancer. Gastroenterology. 2009;137:2136–45 e1–7.
Hruban RH, Adsay NV, Albores-Saavedra J, Compton C, Garrett ES, Goodman SN, et al. Pancreatic intraepithelial neoplasia: a new nomenclature and classification system for pancreatic duct lesions. Am J Surg Pathol. 2001;25:579–86.
Garzon R, Pichiorri F, Palumbo T, Iuliano R, Cimmino A, Aqeilan R, et al. MicroRNA fingerprints during human megakaryocytopoiesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2006;103:5078–83.
Hwang HW, Wentzel EA, Mendell JT. Cell-cell contact globally activates microRNA biogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2009;106:7016–21.
Ma L, Teruya-Feldstein J, Weinberg RA. Tumour invasion and metastasis initiated by microRNA-10b in breast cancer. Nature. 2007;449:682–8.
Mertani HC, Zhu T, Goh EL, Lee KO, Morel G, Lobie PE. Autocrine human growth hormone (hGH) regulation of human mammary carcinoma cell gene expression. Identification of CHOP as a mediator of hGH-stimulated human mammary carcinoma cell survival. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:21464–75.
Zhang X, Zhu T, Chen Y, Mertani HC, Lee KO, Lobie PE. Human growth hormone-regulated HOXA1 is a human mammary epithelial oncogene. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:7580–90.
ACKNOWLEDGMENT
Supported in part by a Grant-in-Aid from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology of Japan and a grant from the Kato Memorial Bioscience Foundation. We are grateful to Emiko Manabe, Midori Sato, and Miyuki Omori (Department of Surgery and Oncology, Kyushu University) for skillful technical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
ELECTRONIC SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ohuchida, K., Mizumoto, K., Lin, C. et al. MicroRNA-10a is Overexpressed in Human Pancreatic Cancer and Involved in Its Invasiveness Partially via Suppression of the HOXA1 Gene. Ann Surg Oncol 19, 2394–2402 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-012-2252-3
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-012-2252-3