-
摘要:
电磁超构表面是一类由单层或多层亚波长人工微结构组成的平面电磁材料,可以在亚波长尺度下实现对电磁波的振幅、相位、波前、色散、偏振态以及角动量等多个维度的精准调控,其中无反射电磁超构表面为实现高效率电磁器件提供了新理论与新方案。本文综述了无反射电磁超构表面的理论与应用,从惠更斯原理、电磁谐振、布儒斯特效应三个方面阐明了无反射超构表面的基本原理,介绍了相关的重要应用,包括异常折射、偏振操控、超构减反膜、电磁波完美吸收等,并对该领域面临的挑战和发展前景进行了总结与展望。
Abstract:Electromagnetic metasurfaces, as a class of planar electromagnetic materials consisting of single-layer or multilayer subwavelength artificial micro-structures, can precisely control the amplitude, phase, wavefront, dispersion, polarization, and angular momentum of electromagnetic waves in the subwavelength scale. In particular, reflectionless electromagnetic metasurfaces provide new theories and schemes for realizing high-efficiency electromagnetic devices. In this review, we elaborate the underlying mechanism of reflectionless metasurfaces from the perspective of the Huygens principle, electromagnetic resonances and the Brewster effect. We also discuss the important applications including anomalous refraction, polarization manipulation, meta-antireflection coatings, and perfect electromagnetic absorption, and point out the challenges and potentials of this field.
-
Overview: Electromagnetic devices that manipulate the propagation of electromagnetic waves are ubiquitous in today's society. The high-efficiency control of electromagnetic waves has been a hot topic among researchers in the past few decades. Electromagnetic metasurfaces, as a class of planar electromagnetic materials consisting of single-layer or multilayer subwavelength artificial micro-structures, can precisely control the amplitude, phase, wavefront, dispersion, polarization, and angular momentum of electromagnetic waves in the subwavelength scale. However, the phenomenon of reflection is inevitable in the design and application of metasurfaces. In addition to reflection-based metasurfaces that manipulate electromagnetic waves through reflection, for transmission-based metasurfaces with broad application prospects, their efficiency is mainly limited by losses and reflection. The reflected electromagnetic waves are difficult to be utilized by the system. Therefore, reducing or even eliminating reflection to enhance electromagnetic control efficiency is a key scientific problem in the field of metasurfaces. Designing reflectionless metasurfaces can provide new theories and approaches for achieving high-efficiency electromagnetic devices. The mechanism and design research of reflectionless metasurfaces are one of the important research directions in the field of metasurfaces. This article reviews the theory and applications of reflectionless electromagnetic metasurfaces, elucidating the basic principles of reflectionless metasurfaces from three aspects: Huygens' principle, electromagnetic resonance, and Brewster effect. Specifically, it includes Huygens metasurfaces, multilayer reflectionless metasurfaces, and Brewster metasurfaces. This article also introduces important applications of reflectionless metasurfaces, including anomalous refraction, polarization control, antireflection metasurfaces, and perfect absorption of electromagnetic waves. In addition, this article summarizes and prospects the challenges and development prospects in this field. The future focus will be on reducing reflection to improve the efficiency of metasurfaces, and further exploration of new physical effects and applications is still needed.
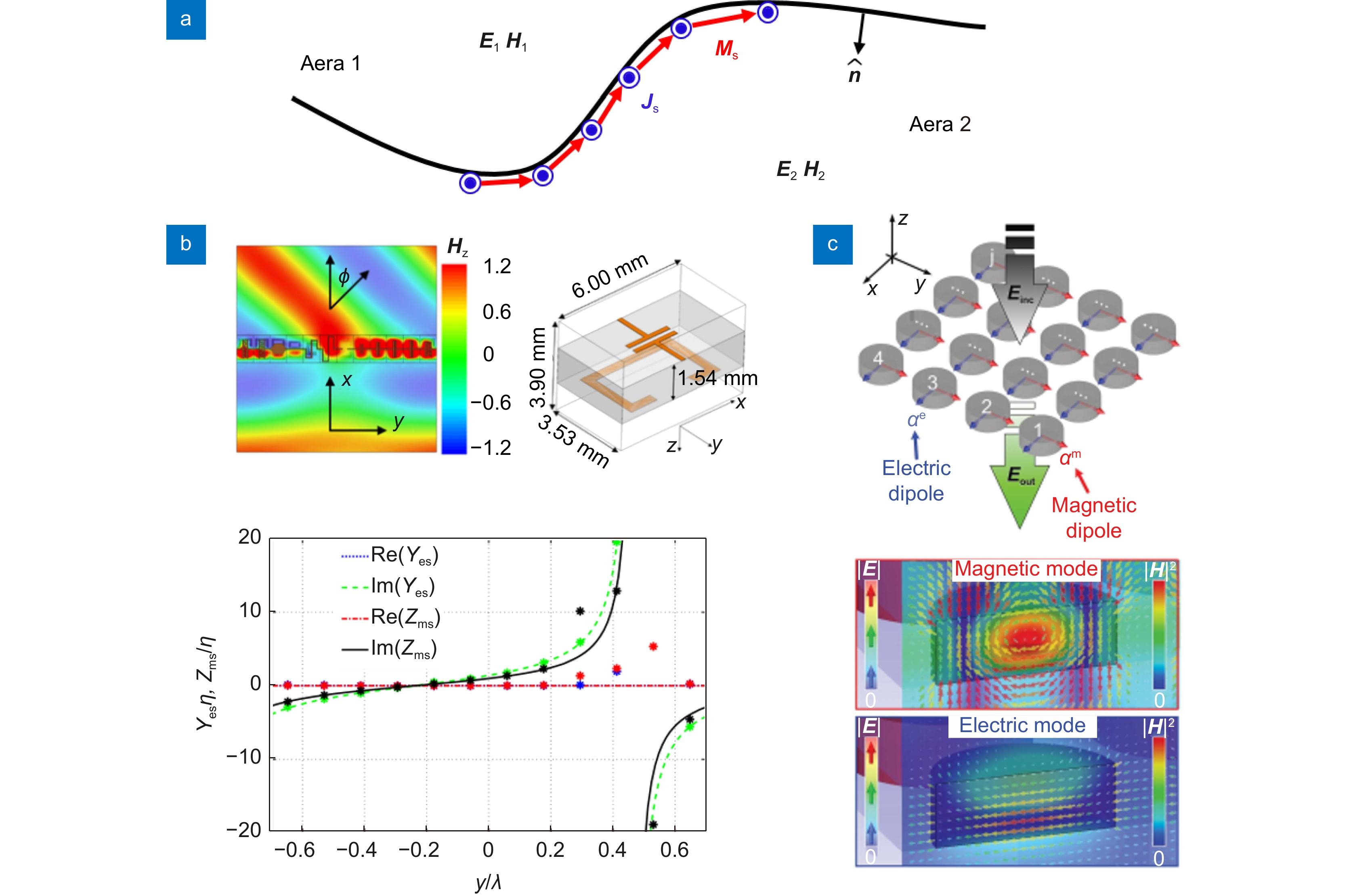
-

-
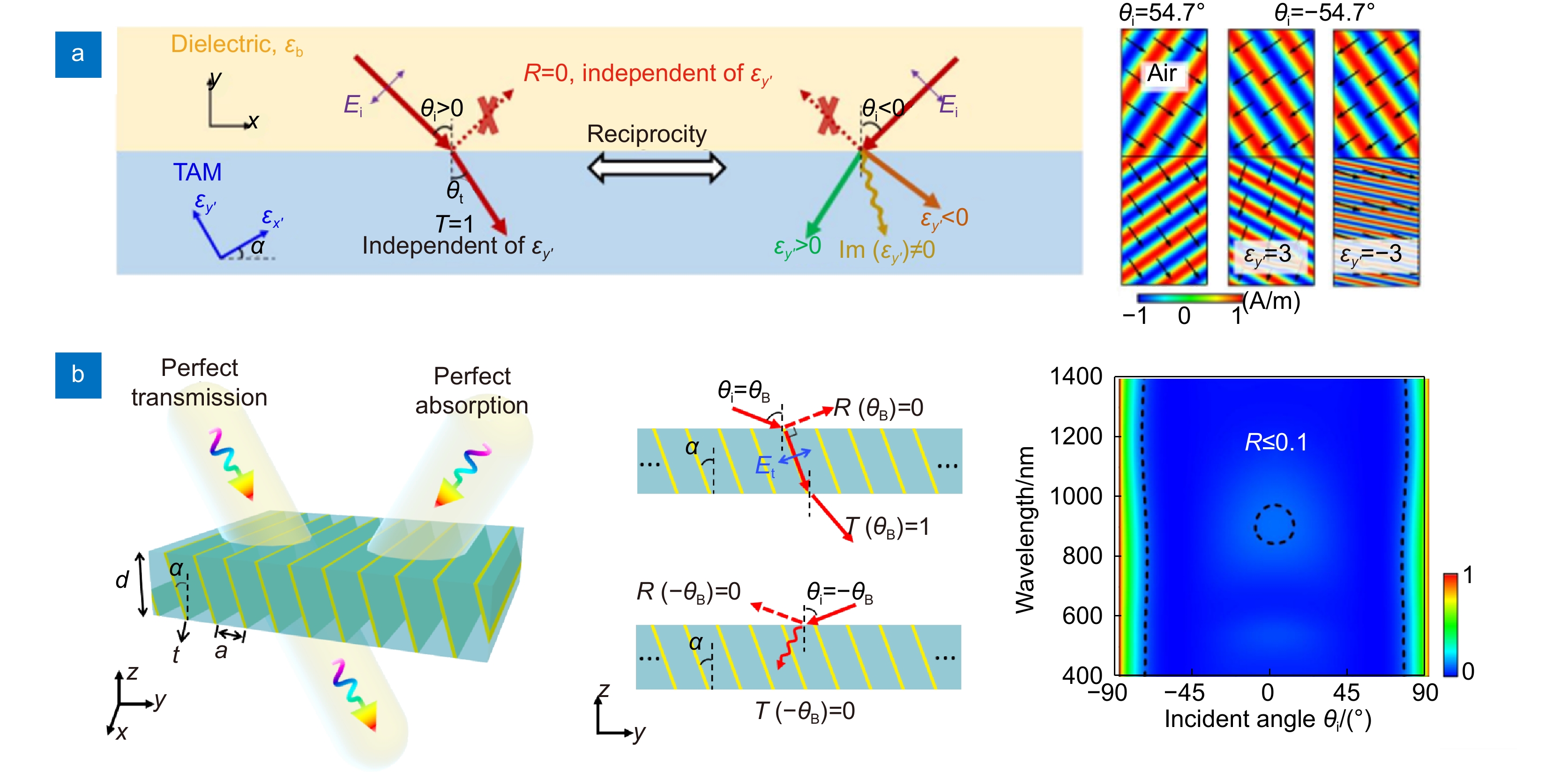
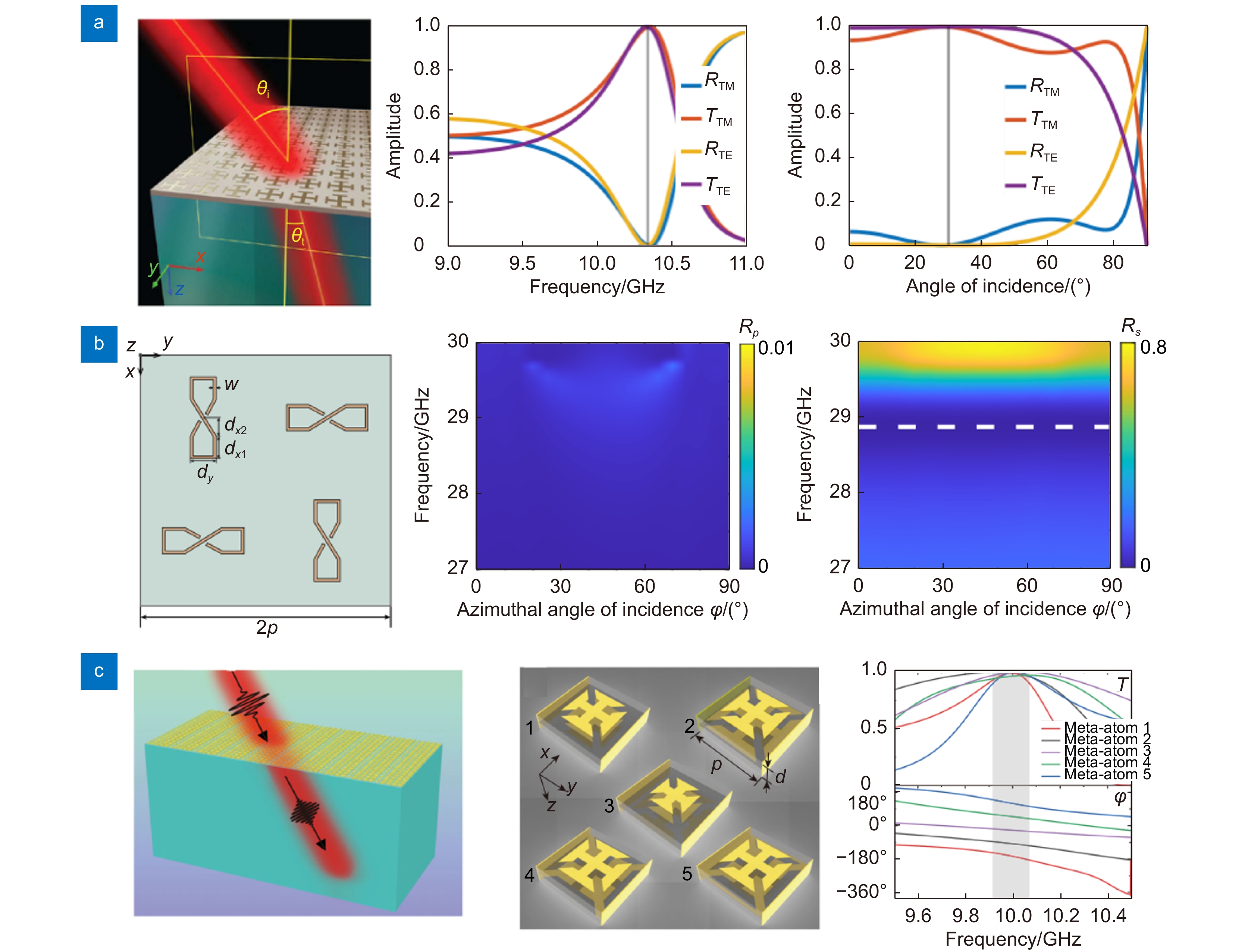
图 3 布儒斯特超构表面。(a) 布儒斯特超构表面的机理及其对折射波的无反射操控[53];(b) 光学布儒斯特超构表面的设计及宽频无反射特性[54]
Figure 3. Brewster metasurfaces. (a) The underlying physics of Brewster metasurfaces and their applications for reflectionless manipulation of refracted waves[53]; (b) The design and broadband reflection property of optical Brewster metasurfaces[54]
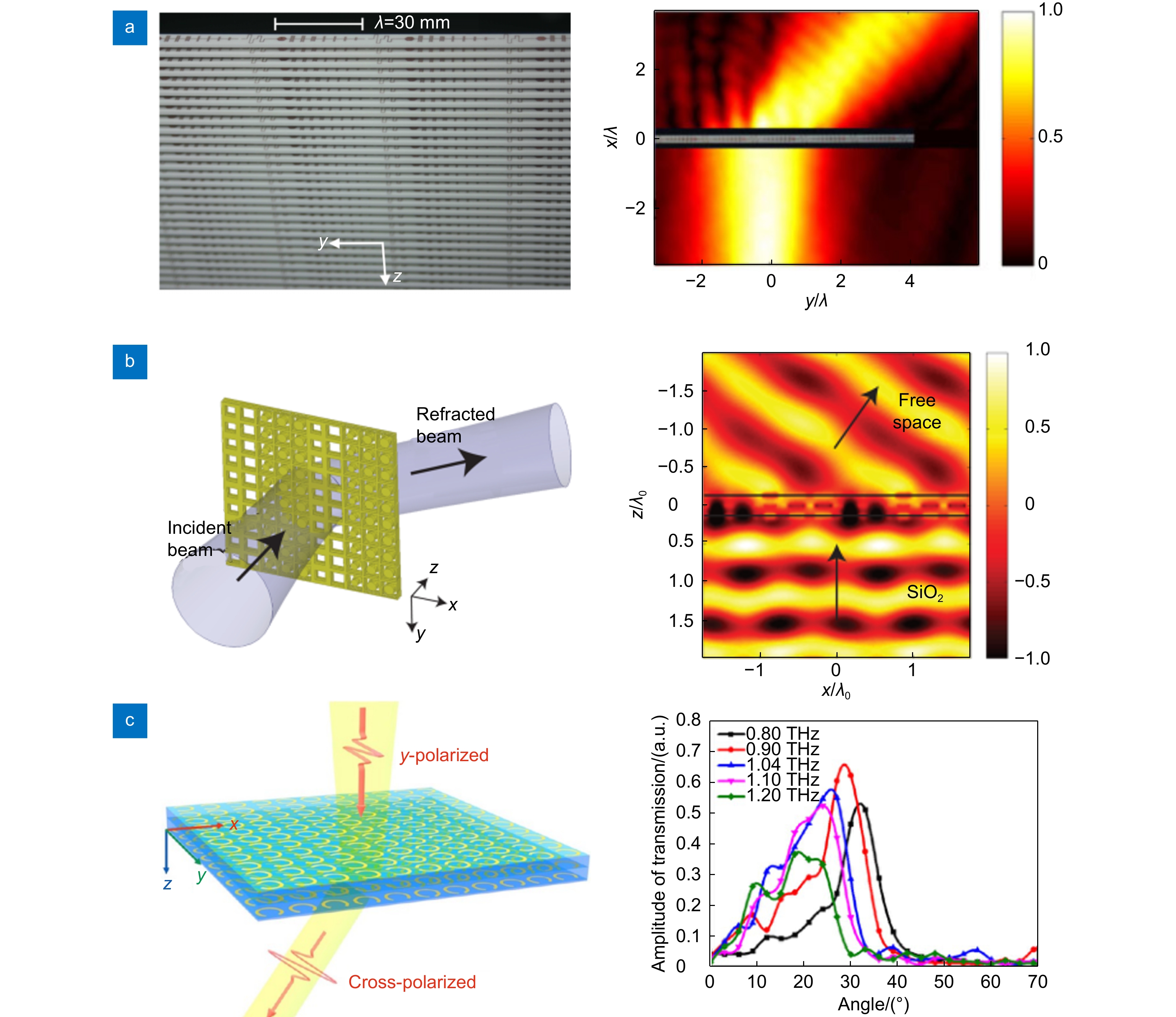
图 5 宽频无反射超构表面。(a) 基于螺旋型微结构单元的宽频无反射微波超构表面[99];(b) 利用优化算法设计的宽带低反射的太赫兹超构表面[157];(c) 由双层微结构单元组成的超宽频无反射超构表面[158]
Figure 5. Broadband reflectionless metasurfaces. (a) Broadband reflectionless microwave metasurfaces consisting of double-turn helix units[99]; (b) Broadband low-reflection terahertz metasurfaces based on optimization methods[157]; (c) Ultra-broadband reflectionless microwave metasurfaces consisting of double-layer units[158]
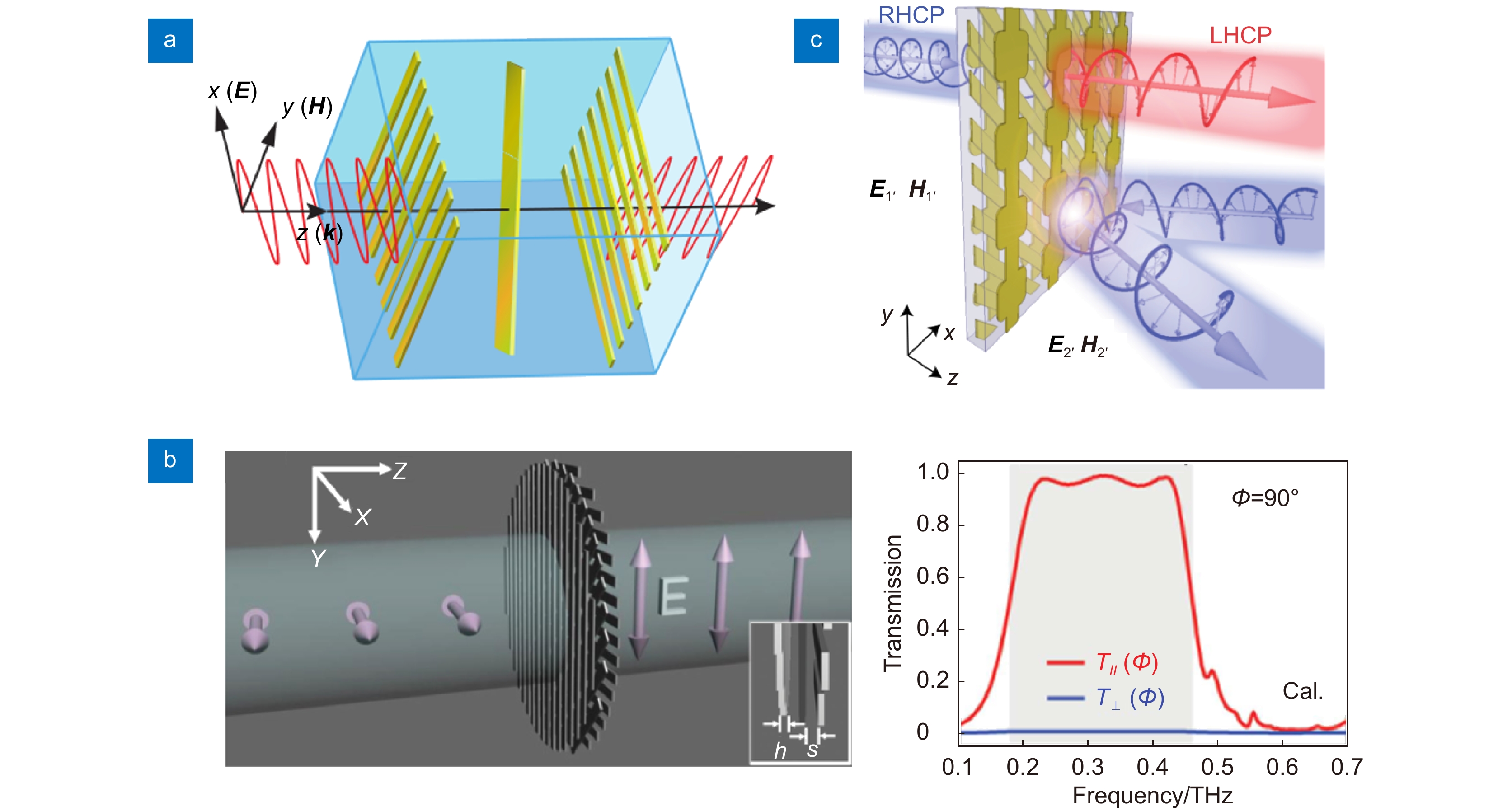
图 7 偏振操控。(a) 太赫兹各向异性超构表面偏振转换器[72];(b) 可调控的太赫兹各向异性超构表面偏振转换器[74];(c) 双各向异性超构表面偏振转换器[73]
Figure 7. Polarization manipulation. (a) Terahertz anisotropic metasurface as polarization converter[72]; (b) Tunable terahertz anisotropic metasurface as polarization converter[74]; (c) Bianisotropic metasurface as polarization converter[73]
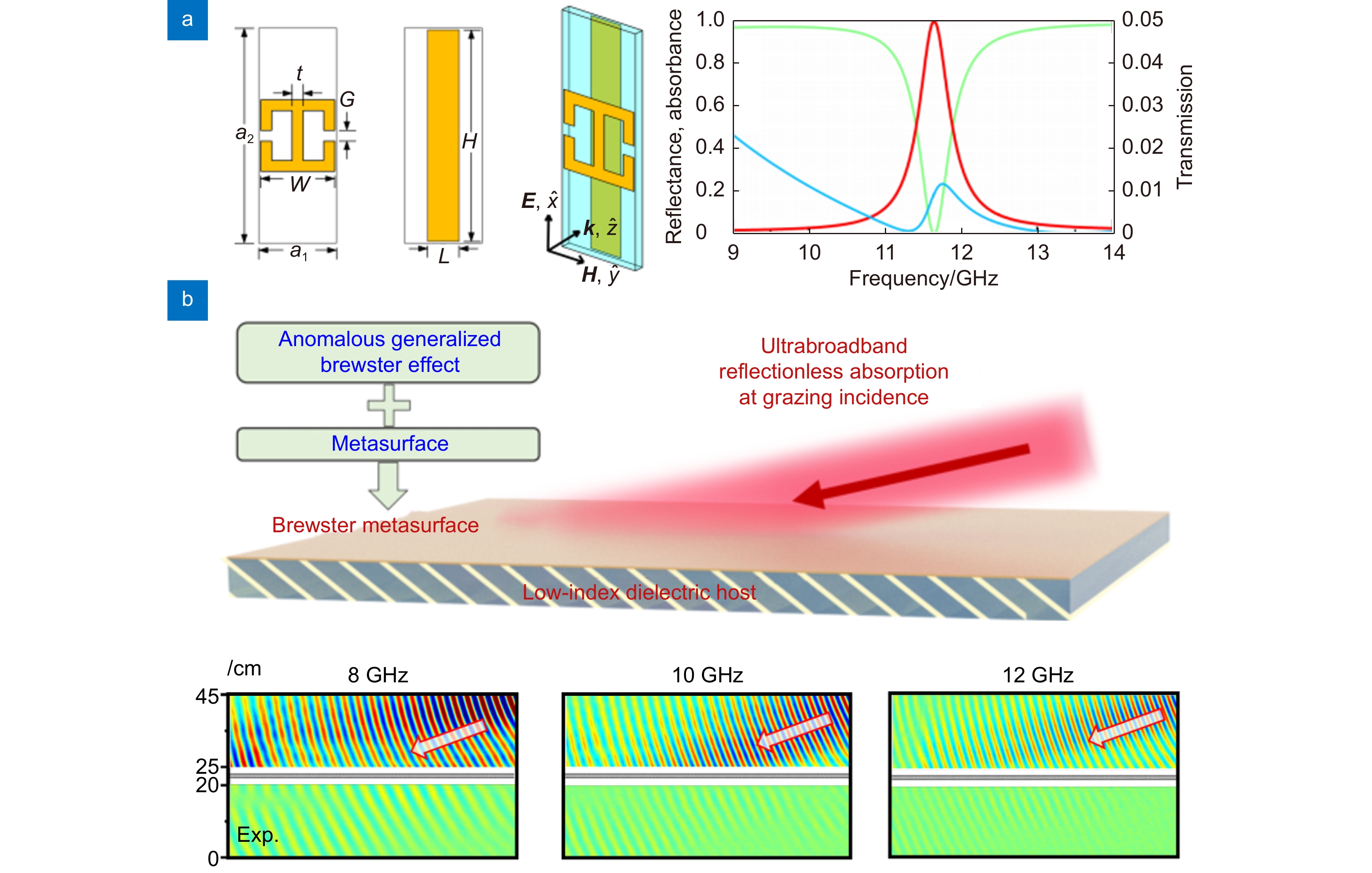
图 8 超构减反膜。(a) H形金属结构构成的双各向异性超构减反膜[194];(b) S形金属结构构成双各向异性超构减反膜[195];(c)同时消除反射和调控波前的超构减反膜[123]
Figure 8. Meta-antireflection coatings. (a) Bianisotropic meta-antireflection coating using H-shaped metallic units[194]; (b) Bianisotropic meta-antireflection coating using S-shaped metallic units[195]; (c) Meta-antireflection coating for simultaneous reflection elimination and wavefront control[123]
-
[1] Cui T J, Smith D R, Liu R P. Metamaterials: Theory, Design, and Applications[M]. New York: Springer, 2010.
[2] Cai W S, Shalaev V. Optical Metamaterials[M]. New York: Springer, 2010.
[3] Zheludev N I, Kivshar Y S. From metamaterials to metadevices[J]. Nat Mater, 2012, 11(11): 917−924. doi: 10.1038/nmat3431
[4] Veselago V G. The electrodynamics of substances with simultaneously negative values of ϵ and μ[J]. Sov Phys Usp, 1968, 10(4): 509−514. doi: 10.1070/PU1968v010n04ABEH003699
[5] Pendry J B. Negative refraction makes a perfect lens[J]. Phys Rev Lett, 2000, 85(18): 3966−3969. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.85.3966
[6] Zhang X, Liu Z W. Superlenses to overcome the diffraction limit[J]. Nat Mater, 2008, 7(6): 435−441. doi: 10.1038/nmat2141
[7] Lu D, Liu Z W. Hyperlenses and metalenses for far-field super-resolution imaging[J]. Nat Commun, 2012, 3(1): 1205. doi: 10.1038/ncomms2176
[8] Pendry J B, Schurig D, Smith D R. Controlling electromagnetic fields[J]. Science, 2006, 312(5781): 1780−1782. doi: 10.1126/science.1125907
[9] Schurig D, Mock J J, Justice B J, et al. Metamaterial electromagnetic cloak at microwave frequencies[J]. Science, 2006, 314(5801): 977−980. doi: 10.1126/science.1133628
[10] Leonhardt U. Optical conformal mapping[J]. Science, 2006, 312(5781): 1777−1780. doi: 10.1126/science.1126493
[11] Lai Y, Chen H Y, Zhang Z Q, et al. Complementary media invisibility cloak that cloaks objects at a distance outside the cloaking shell[J]. Phys Rev Lett, 2009, 102(9): 093901. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.102.093901
[12] Yu N F, Genevet P, Kats M A, et al. Light propagation with phase discontinuities: generalized laws of reflection and refraction[J]. Science, 2011, 334(6054): 333−337. doi: 10.1126/science.1210713
[13] Ni X J, Emani N K, Kildishev A V, et al. Broadband light bending with plasmonic nanoantennas[J]. Science, 2012, 335(6067): 427. doi: 10.1126/science.1214686
[14] Kildishev A V, Boltasseva A, Shalaev V M. Planar photonics with metasurfaces[J]. Science, 2013, 339(6125): 1232009. doi: 10.1126/science.1232009
[15] Yu N F, Capasso F. Flat optics with designer metasurfaces[J]. Nat Mater, 2014, 13(2): 139−150. doi: 10.1038/nmat3839
[16] Meinzer N, Barnes W L, Hooper I R. Plasmonic meta-atoms and metasurfaces[J]. Nat Photonics, 2014, 8(12): 889−898. doi: 10.1038/nphoton.2014.247
[17] Turpin J P, Bossard J A, Morgan K L, et al. Reconfigurable and tunable metamaterials: a review of the theory and applications[J]. Int J Antennas Propag, 2014, 2014: 429837. doi: 10.1155/2014/429837
[18] Cheng H, Liu Z C, Chen S Q, et al. Emergent functionality and controllability in few-layer metasurfaces[J]. Adv Mater, 2015, 27(36): 5410−5421. doi: 10.1002/adma.201501506
[19] Walia S, Shah C M, Gutruf P, et al. Flexible metasurfaces and metamaterials: a review of materials and fabrication processes at micro- and nano-scales[J]. Appl Phys Rev, 2015, 2(1): 011303. doi: 10.1063/1.4913751
[20] Pu M B, Li X, Ma X L, et al. Catenary optics for achromatic generation of perfect optical angular momentum[J]. Sci Adv, 2015, 1(9): e1500396. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.1500396
[21] Luo X G. Principles of electromagnetic waves in metasurfaces[J]. Sci China Phys Mech Astron, 2015, 58(9): 594201. doi: 10.1007/s11433-015-5688-1
[22] Chen H T, Taylor A J, Yu N F. A review of metasurfaces: physics and applications[J]. Rep Prog Phys, 2016, 79(7): 076401. doi: 10.1088/0034-4885/79/7/076401
[23] Zhang L, Mei S T, Huang K, et al. Advances in full control of electromagnetic waves with metasurfaces[J]. Adv Opt Mater, 2016, 4(6): 818−833. doi: 10.1002/adom.201500690
[24] Glybovski S B, Tretyakov S A, Belov P A, et al. Metasurfaces: from microwaves to visible[J]. Phys Rep, 2016, 634: 1−72. doi: 10.1016/j.physrep.2016.04.004
[25] Xu Y D, Fu Y Y, Chen H Y. Planar gradient metamaterials[J]. Nat Rev Mater, 2016, 1(12): 16067. doi: 10.1038/natrevmats.2016.67
[26] Liu S, Cui T J. Concepts, working principles, and applications of coding and programmable metamaterials[J]. Adv Opt Mater, 2017, 5(22): 1700624. doi: 10.1002/adom.201700624
[27] Genevet P, Capasso F, Aieta F, et al. Recent advances in planar optics: from plasmonic to dielectric metasurfaces[J]. Optica, 2017, 4(1): 139−152. doi: 10.1364/OPTICA.4.000139
[28] Kamali S M, Arbabi E, Arbabi A, et al. A review of dielectric optical metasurfaces for wavefront control[J]. Nanophotonics, 2018, 7(6): 1041−1068. doi: 10.1515/nanoph-2017-0129
[29] He Q, Sun S L, Xiao S Y, et al. High-efficiency metasurfaces: principles, realizations, and applications[J]. Adv Opt Mater, 2018, 6(19): 1800415. doi: 10.1002/adom.201800415
[30] Minovich A E, Miroshnichenko A E, Bykov A Y, et al. Functional and nonlinear optical metasurfaces[J]. Laser Photonics Rev, 2015, 9(2): 195−213. doi: 10.1002/lpor.201400402
[31] Li G X, Zhang S, Zentgraf T. Nonlinear photonic metasurfaces[J]. Nat Rev Mater, 2017, 2(5): 17010. doi: 10.1038/natrevmats.2017.10
[32] Krasnok A, Tymchenko M, Alù A. Nonlinear metasurfaces: a paradigm shift in nonlinear optics[J]. Mater Today, 2018, 21(1): 8−21. doi: 10.1016/j.mattod.2017.06.007
[33] Neshev D, Aharonovich I. Optical metasurfaces: new generation building blocks for multi-functional optics[J]. Light Sci Appl, 2018, 7(1): 58. doi: 10.1038/s41377-018-0058-1
[34] Xie X, Li X, Pu M B, et al. Plasmonic metasurfaces for simultaneous thermal infrared invisibility and holographic illusion[J]. Adv Funct Mater, 2018, 28(14): 1706673. doi: 10.1002/adfm.201706673
[35] Sun S L, He Q, Hao J M, et al. Electromagnetic metasurfaces: physics and applications[J]. Adv Opt Photonics, 2019, 11(2): 380−479. doi: 10.1364/AOP.11.000380
[36] Shaltout A M, Shalaev V M, Brongersma M L. Spatiotemporal light control with active metasurfaces[J]. Science, 2019, 364(6441): eaat3100. doi: 10.1126/science.aat3100
[37] Cui T, Bai B F, Sun H B. Tunable metasurfaces based on active materials[J]. Adv Funct Mater, 2019, 29(10): 1806692. doi: 10.1002/adfm.201806692
[38] Hu Y Q, Wang X D, Luo X H, et al. All-dielectric metasurfaces for polarization manipulation: principles and emerging applications[J]. Nanophotonics, 2020, 9(12): 3755−3780. doi: 10.1515/nanoph-2020-0220
[39] Zang X F, Yao B S, Chen L, et al. Metasurfaces for manipulating terahertz waves[J]. Light Adv Manuf, 2021, 2: 10. doi: 10.37188/LAM.2021.010
[40] Xie X, Pu M B, Jin J J, et al. Generalized pancharatnam-berry phase in rotationally symmetric meta-atoms[J]. Phys Rev Lett, 2021, 126(18): 183902. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.126.183902
[41] Guo Y H, Zhang S C, Pu M B, et al. Spin-decoupled metasurface for simultaneous detection of spin and orbital angular momenta via momentum transformation[J]. Light Sci Appl, 2021, 10(1): 63. doi: 10.1038/S41377-021-00497-7
[42] Du K, Barkaoui H, Zhang X D, et al. Optical metasurfaces towards multifunctionality and tunability[J]. Nanophotonics, 2022, 11(9): 1761−1781. doi: 10.1515/nanoph-2021-0684
[43] 杨港, 郭迎辉, 蒲明博, 等. 基于相关性选择的微型计算光谱探测技术[J]. 光电工程, 2022, 49(10): 220130. doi: 10.12086/oee.2022.220130
Yang G, Guo Y H, Pu M B, et al. Miniature computational spectral detection technology based on correlation value selection[J]. Opto-Electron Eng, 2022, 49(10): 220130. doi: 10.12086/oee.2022.220130
[44] Epstein A, Eleftheriades G V. Huygens' metasurfaces via the equivalence principle: design and applications[J]. J Opt Soc Am B, 2016, 33(2): A31−A49. doi: 10.1364/JOSAB.33.000A31
[45] Chen M, Kim M, Wong A M H, et al. Huygens' metasurfaces from microwaves to optics: a review[J]. Nanophotonics, 2018, 7(6): 1207−1231. doi: 10.1515/nanoph-2017-0117
[46] Ataloglou V G, Chen M, Kim M, et al. Microwave Huygens' metasurfaces: fundamentals and applications[J]. IEEE J Microw, 2021, 1(1): 374−388. doi: 10.1109/JMW.2020.3034578
[47] Huang L L, Chen X Z, Mühlenbernd H, et al. Dispersionless phase discontinuities for controlling light propagation[J]. Nano Lett, 2012, 12(11): 5750−5755. doi: 10.1021/nl303031j
[48] Sun S L, He Q, Xiao S Y, et al. Gradient-index meta-surfaces as a bridge linking propagating waves and surface waves[J]. Nat Mater, 2012, 11(5): 426−431. doi: 10.1038/nmat3292
[49] Liu S, Cui T J, Xu Q, et al. Anisotropic coding metamaterials and their powerful manipulation of differently polarized terahertz waves[J]. Light Sci Appl, 2016, 5(5): e16076. doi: 10.1038/lsa.2016.76
[50] Cui T J, Qi M Q, Wan X, et al. Coding metamaterials, digital metamaterials and programmable metamaterials[J]. Light Sci Appl, 2014, 3(10): e218. doi: 10.1038/lsa.2014.99
[51] Pfeiffer C, Grbic A. Metamaterial Huygens' surfaces: tailoring wave fronts with reflectionless sheets[J]. Phys Rev Lett, 2013, 110(19): 197401. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.110.197401
[52] Pfeiffer C, Grbic A. Millimeter-wave transmitarrays for wavefront and polarization control[J]. IEEE Trans Microwave Theory Techn, 2013, 61(12): 4407−4417. doi: 10.1109/TMTT.2013.2287173
[53] Luo J, Chu H C, Peng R W, et al. Ultra-broadband reflectionless Brewster absorber protected by reciprocity[J]. Light Sci Appl, 2021, 10(1): 89. doi: 10.1038/S41377-021-00529-2
[54] Fan H Y, Li J S, Lai Y, et al. Optical Brewster metasurfaces exhibiting ultrabroadband reflectionless absorption and extreme angular asymmetry[J]. Phys Rev Appl, 2021, 16(4): 044064. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevApplied.16.044064
[55] Ma Z K, Fan H Y, Zhou H, et al. Broadband perfect transparency-to-absorption switching in tilted anisotropic metamaterials based on the anomalous Brewster effect[J]. Opt Express, 2021, 29(24): 39186−39199. doi: 10.1364/OE.443790
[56] Fan H Y, Chu H C, Luo H, et al. Brewster metasurfaces for ultrabroadband reflectionless absorption at grazing incidence[J]. Optica, 2022, 9(10): 1138−1148. doi: 10.1364/OPTICA.472221
[57] Huang L L, Chen X Z, Bai B F, et al. Helicity dependent directional surface plasmon polariton excitation using a metasurface with interfacial phase discontinuity[J]. Light Sci Appl, 2013, 2(3): e70. doi: 10.1038/lsa.2013.26
[58] Pors A, Nielsen M G, Bernardin T, et al. Efficient unidirectional polarization-controlled excitation of surface plasmon polaritons[J]. Light Sci Appl, 2014, 3(8): e197. doi: 10.1038/lsa.2014.78
[59] Sun W J, He Q, Sun S L, et al. High-efficiency surface plasmon meta-couplers: concept and microwave-regime realizations[J]. Light Sci Appl, 2016, 5(1): e16003. doi: 10.1038/lsa.2016.3
[60] Chen H T, Zhou J F, O'Hara J F, et al. Antireflection coating using metamaterials and identification of its mechanism[J]. Phys Rev Lett, 2010, 105(7): 073901. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.105.073901
[61] Kang M, Feng T H, Wang H T, et al. Wave front engineering from an array of thin aperture antennas[J]. Opt Express, 2012, 20(14): 15882−15890. doi: 10.1364/OE.20.015882
[62] Aieta F, Genevet P, Kats M A, et al. Aberration-free ultrathin flat lenses and axicons at telecom wavelengths based on plasmonic metasurfaces[J]. Nano Lett, 2012, 12(9): 4932−4936. doi: 10.1021/nl302516v
[63] Lin D M, Fan P Y, Hasman E, et al. Dielectric gradient metasurface optical elements[J]. Science, 2014, 345(6194): 298−302. doi: 10.1126/science.1253213
[64] Khorasaninejad M, Chen W T, Devlin R C, et al. Metalenses at visible wavelengths: diffraction-limited focusing and subwavelength resolution imaging[J]. Science, 2016, 352(6290): 1190−1194. doi: 10.1126/science.aaf6644
[65] Arbabi A, Horie Y, Ball A J, et al. Subwavelength-thick lenses with high numerical apertures and large efficiency based on high-contrast transmitarrays[J]. Nat Commun, 2015, 6(1): 7069. doi: 10.1038/ncomms8069
[66] Khorasaninejad M, Capasso F. Metalenses: versatile multifunctional photonic components[J]. Science, 2017, 358(6367): eaam8100. doi: 10.1126/science.aam8100
[67] Chen K, Feng Y J, Monticone F, et al. A reconfigurable active Huygens' metalens[J]. Adv Mater, 2017, 29(17): 1606422. doi: 10.1002/adma.201606422
[68] Wang S M, Wu P C, Su V C, et al. A broadband achromatic metalens in the visible[J]. Nat Nanotechnol, 2018, 13(3): 227−232. doi: 10.1038/s41565-017-0052-4
[69] Lin R J, Su V C, Wang S M, et al. Achromatic metalens array for full-colour light-field imaging[J]. Nat Nanotechnol, 2019, 14(3): 227−231. doi: 10.1038/s41565-018-0347-0
[70] Li L, Liu Z X, Ren X F, et al. Metalens-array–based high-dimensional and multiphoton quantum source[J]. Science, 2020, 368(6498): 1487−1490. doi: 10.1126/science.aba9779
[71] Pan M Y, Fu Y F, Zheng M J, et al. Dielectric metalens for miniaturized imaging systems: progress and challenges[J]. Light Sci Appl, 2022, 11(1): 195. doi: 10.1038/s41377-022-00885-7
[72] Grady N K, Heyes J E, Chowdhury D R, et al. Terahertz metamaterials for linear polarization conversion and anomalous refraction[J]. Science, 2013, 340(6138): 1304−1307. doi: 10.1126/science.1235399
[73] Pfeiffer C, Zhang C, Ray V, et al. High performance bianisotropic metasurfaces: asymmetric transmission of light[J]. Phys Rev Lett, 2014, 113(2): 023902. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.113.023902
[74] Fan R H, Zhou Y, Ren X P, et al. Freely tunable broadband polarization rotator for terahertz waves[J]. Adv Mater, 2015, 27(7): 1201−1206. doi: 10.1002/adma.201404981
[75] Xu H X, Tang S W, Wang G M, et al. Multifunctional microstrip array combining a linear polarizer and focusing metasurface[J]. IEEE Trans Antennas Propagat, 2016, 64(8): 3676−3682. doi: 10.1109/TAP.2016.2565742
[76] Ma X L, Pu M B, Li X, et al. All-metallic wide-angle metasurfaces for multifunctional polarization manipulation[J]. Opto-Electron Adv, 2019, 2(3): 180023. doi: 10.29026/oea.2019.180023
[77] Landy N I, Sajuyigbe S, Mock J J, et al. Perfect metamaterial absorber[J]. Phys Rev Lett, 2008, 100(20): 207402. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.100.207402
[78] Chen H T, O'Hara J F, Azad A K, et al. Manipulation of terahertz radiation using metamaterials[J]. Laser Photonics Rev, 2011, 5(4): 513−533. doi: 10.1002/lpor.201000043
[79] Watts C M, Liu X L, Padilla W J. Metamaterial electromagnetic wave absorbers[J]. Adv Mater, 2012, 24(23): OP98−OP120. doi: 10.1002/adma.201200674
[80] Cui Y X, He Y R, Jin Y, et al. Plasmonic and metamaterial structures as electromagnetic absorbers[J]. Laser Photonics Rev, 2014, 8(4): 495−520. doi: 10.1002/lpor.201400026
[81] Ra’di Y, Simovski C R, Tretyakov S A. Thin perfect absorbers for electromagnetic waves: theory, design, and realizations[J]. Phys Rev Appl, 2015, 3(3): 037001. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevApplied.3.037001
[82] Alaee R, Albooyeh M, Rockstuhl C. Theory of metasurface based perfect absorbers[J]. J Phys D:Appl Phys, 2017, 50(50): 503002. doi: 10.1088/1361-6463/aa94a8
[83] Feng L, Huo P C, Liang Y Z, et al. Photonic metamaterial absorbers: morphology engineering and interdisciplinary applications[J]. Adv Mater, 2020, 32(27): 1903787. doi: 10.1002/adma.201903787
[84] 蓝翔, 邓钦荣, 张汶婷, 等. 基于扭转悬链线结构的高效手性吸波器[J]. 光电工程, 2022, 49(10): 220157. doi: 10.12086/oee.2022.220157
Lan X, Deng Q R, Zhang W T, et al. Efficient chiral absorber based on twisted catenary structure[J]. Opto-Electron Eng, 2022, 49(10): 220157. doi: 10.12086/oee.2022.220157
[85] Ni X J, Wong Z J, Mrejen M, et al. An ultrathin invisibility skin cloak for visible light[J]. Science, 2015, 349(6254): 1310−1314. doi: 10.1126/science.aac9411
[86] Sounas D L, Fleury R, Alù A. Unidirectional cloaking based on metasurfaces with balanced loss and gain[J]. Phys Rev Appl, 2015, 4(1): 014005. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevApplied.4.014005
[87] Chu H C, Li Q, Liu B B, et al. A hybrid invisibility cloak based on integration of transparent metasurfaces and zero-index materials[J]. Light Sci Appl, 2018, 7(1): 50. doi: 10.1038/s41377-018-0052-7
[88] Huang Y J, Pu M B, Zhang F, et al. Broadband functional metasurfaces: achieving nonlinear phase generation toward achromatic surface cloaking and lensing[J]. Adv Opt Mater, 2019, 7(7): 1801480. doi: 10.1002/adom.201801480
[89] Luo J, Li X, Zhang X Y, et al. Deep-learning-enabled inverse engineering of multi-wavelength invisibility-to-superscattering switching with phase-change materials[J]. Opt Express, 2021, 29(7): 10527−10537. doi: 10.1364/OE.422119
[90] Cai T, Wang G M, Tang S W, et al. High-efficiency and full-space manipulation of electromagnetic wave fronts with metasurfaces[J]. Phys Rev Appl, 2017, 8(3): 034033. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevApplied.8.034033
[91] Akram M R, Mehmood M Q, Bai X D, et al. High efficiency ultrathin transmissive metasurfaces[J]. Adv Opt Mater, 2019, 7(11): 1801628. doi: 10.1002/adom.201801628
[92] Decker M, Staude I, Falkner M, et al. High-efficiency dielectric Huygens' surfaces[J]. Adv Opt Mater, 2015, 3(6): 813−820. doi: 10.1002/adom.201400584
[93] Selvanayagam M, Eleftheriades G V. Discontinuous electromagnetic fields using orthogonal electric and magnetic currents for wavefront manipulation[J]. Opt Express, 2013, 21(12): 14409−14429. doi: 10.1364/OE.21.014409
[94] Wong J P S, Selvanayagam M, Eleftheriades G V. Design of unit cells and demonstration of methods for synthesizing Huygens metasurfaces[J]. Photonics Nanostruct Fundam Appl, 2014, 12(4): 360−375. doi: 10.1016/j.photonics.2014.07.001
[95] Pfeiffer C, Emani N K, Shaltout A M, et al. Efficient light bending with isotropic metamaterial Huygens' surfaces[J]. Nano Lett, 2014, 14(5): 2491−2497. doi: 10.1021/nl5001746
[96] Chen W T, Yang K Y, Wang C M, et al. High-efficiency broadband meta-hologram with polarization-controlled dual images[J]. Nano Lett, 2014, 14(1): 225−230. doi: 10.1021/nl403811d
[97] Kim M, Wong A M H, Eleftheriades G V. Optical Huygens' metasurfaces with independent control of the magnitude and phase of the local reflection coefficients[J]. Phys Rev X, 2014, 4(4): 041042. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevX.4.041042
[98] Sautter J, Staude I, Decker M, et al. Active tuning of all-dielectric metasurfaces[J]. ACS Nano, 2015, 9(4): 4308−4315. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.5b00723
[99] Asadchy V S, Faniayeu I A, Ra’di Y, et al. Broadband reflectionless metasheets: frequency-selective transmission and perfect absorption[J]. Phys Rev X, 2015, 5(3): 031005. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevX.5.031005
[100] Asadchy V S, Ra'di Y, Vehmas J, et al. Functional metamirrors using bianisotropic elements[J]. Phys Rev Lett, 2015, 114(9): 095503. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.114.095503
[101] Wong J P S, Selvanayagam M, Eleftheriades G V. Polarization considerations for scalar Huygens metasurfaces and characterization for 2-D refraction[J]. IEEE Trans Microwave Theory Techn, 2015, 63(3): 913−924. doi: 10.1109/TMTT.2015.2392931
[102] Iyer P P, Butakov N A, Schuller J A. Reconfigurable semiconductor phased-array metasurfaces[J]. ACS Photonics, 2015, 2(8): 1077−1084. doi: 10.1021/acsphotonics.5b00132
[103] Chong K E, Wang L, Staude I, et al. Efficient polarization-insensitive complex wavefront control using Huygens' metasurfaces based on dielectric resonant meta-atoms[J]. ACS Photonics, 2016, 3(4): 514−519. doi: 10.1021/acsphotonics.5b00678
[104] Paniagua-Domínguez R, Yu Y F, Miroshnichenko A E, et al. Generalized Brewster effect in dielectric metasurfaces[J]. Nat Commun, 2016, 7(1): 10362. doi: 10.1038/ncomms10362
[105] Babicheva V E, Evlyukhin A B. Resonant lattice Kerker effect in metasurfaces with electric and magnetic optical responses[J]. Laser Photonics Rev, 2017, 11(6): 1700132. doi: 10.1002/lpor.201700132
[106] Wong A M H, Christian P, Eleftheriades G V. Binary Huygens' metasurfaces: experimental demonstration of simple and efficient near-grazing retroreflectors for TE and TM polarizations[J]. IEEE Trans Antennas Propagat, 2018, 66(6): 2892−2903. doi: 10.1109/TAP.2018.2816792
[107] Abujetas D R, Sánchez-Gil J A, Sáenz J J. Generalized Brewster effect in high-refractive-index nanorod-based metasurfaces[J]. Opt Express, 2018, 26(24): 31523−31541. doi: 10.1364/OE.26.031523
[108] Liu W, Kivshar Y S. Generalized Kerker effects in nanophotonics and meta-optics [Invited][J]. Opt Express, 2018, 26(10): 13085−13105. doi: 10.1364/OE.26.013085
[109] Wong A M H, Eleftheriades G V. Perfect anomalous reflection with a bipartite Huygens' metasurface[J]. Phys Rev X, 2018, 8(1): 011036. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevX.8.011036
[110] Chen M, Abdo-Sánchez E, Epstein A, et al. Theory, design, and experimental verification of a reflectionless bianisotropic Huygens' metasurface for wide-angle refraction[J]. Phys Rev B, 2018, 97(12): 125433. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.97.125433
[111] Kwon D H, Ptitcyn G, Díaz-Rubio A, et al. Transmission magnitude and phase control for polarization-preserving reflectionless metasurfaces[J]. Phys Rev Appl, 2018, 9(3): 034005. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevApplied.9.034005
[112] Liu C, Chen L, Wu T S, et al. All-dielectric three-element transmissive Huygens' metasurface performing anomalous refraction[J]. Photonics Res, 2019, 7(12): 1501−1510. doi: 10.1364/PRJ.7.001501
[113] Chen M, Epstein A, Eleftheriades G V. Design and experimental verification of a passive Huygens' metasurface lens for gain enhancement of frequency-scanning slotted-waveguide antennas[J]. IEEE Trans Antennas Propagat, 2019, 67(7): 4678−4692. doi: 10.1109/TAP.2019.2911591
[114] Sun Z W, Sima B, Zhao J M, et al. Electromagnetic polarization conversion based on Huygens' metasurfaces with coupled electric and magnetic resonances[J]. Opt Express, 2019, 27(8): 11006−11017. doi: 10.1364/OE.27.011006
[115] Lin Z M, Li X W, Zhao R Z, et al. High-efficiency Bessel beam array generation by Huygens metasurfaces[J]. Nanophotonics, 2019, 8(6): 1079−1085. doi: 10.1515/nanoph-2019-0085
[116] Hao W M, Deng M, Chen S Q, et al. High-efficiency generation of airy beams with Huygens' metasurface[J]. Phys Rev Appl, 2019, 11(5): 054012. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevApplied.11.054012
[117] Fathnan A A, Liu M K, Powell D A. Achromatic Huygens' metalenses with deeply subwavelength thickness[J]. Adv Opt Mater, 2020, 8(22): 2000754. doi: 10.1002/adom.202000754
[118] Rahimzadegan A, Arslan D, Dams D, et al. Beyond dipolar Huygens' metasurfaces for full-phase coverage and unity transmittance[J]. Nanophotonics, 2020, 9(1): 75−82. doi: 10.1515/nanoph-2019-0239
[119] Chen M, Eleftheriades G V. Omega-bianisotropic wire-loop Huygens' metasurface for reflectionless wide-angle refraction[J]. IEEE Trans Antennas Propagat, 2020, 68(3): 1477−1490. doi: 10.1109/TAP.2019.2948708
[120] Howes A, Zhu Z H, Curie D, et al. Optical limiting based on Huygens' metasurfaces[J]. Nano Lett, 2020, 20(6): 4638−4644. doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.0c01574
[121] Wang Z C, Liu J, Ding X M, et al. Three-dimensional microwave holography based on broadband Huygens' metasurface[J]. Phys Rev Appl, 2020, 13(1): 014033. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevApplied.13.014033
[122] Ang P, Xu G Y, Eleftheriades G V. Invisibility cloaking with passive and active Huygens's metasurfaces[J]. Appl Phys Lett, 2021, 118(7): 071903. doi: 10.1063/5.0041996
[123] Chu H C, Zhang H Y, Zhang Y, et al. Invisible surfaces enabled by the coalescence of anti-reflection and wavefront controllability in ultrathin metasurfaces[J]. Nat Commun, 2021, 12(1): 4523. doi: 10.1038/S41467-021-24763-9
[124] Song W T, Liang X N, Li S Q, et al. Large-scale Huygens' metasurfaces for holographic 3D near-eye displays[J]. Laser Photonics Rev, 2021, 15(9): 2000538. doi: 10.1002/lpor.202000538
[125] Derafshi I, Komjani N. A new high aperture efficiency transmitarray antenna based on Huygens metasurfaces[J]. IEEE Trans Antennas Propagat, 2022, 70(7): 5458−5467. doi: 10.1109/TAP.2022.3161480
[126] Zhang T, Duan Y P, Huang L X, et al. Huygens' metasurface based on induced magnetism: enhance the microwave absorption performance of magnetic coating[J]. Adv Mater Interfaces, 2022, 9(12): 2102559. doi: 10.1002/admi.202102559
[127] Yang Z W, Liu M K, Komar A, et al. Phase‐only tuning of extreme Huygens metasurfaces enabled by optical anisotropy[J]. Adv Opt Mater, 2022, 10(2): 2101893. doi: 10.1002/adom.202101893
[128] Li H J, Wei G G, Zhou H M, et al. Polarization-independent near-infrared superabsorption in transition metal dichalcogenide Huygens metasurfaces by degenerate critical coupling[J]. Phys Rev B, 2022, 105(16): 165305. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.105.165305
[129] Hassanfiroozi A, Cheng Y C, Huang S H, et al. Toroidal‐assisted generalized Huygens' sources for highly transmissive plasmonic metasurfaces[J]. Laser Photonics Rev, 2022, 16(6): 2100525. doi: 10.1002/lpor.202100525
[130] Song W T, Liang X N, Li S Q, et al. Retinal projection near‐eye displays with Huygens' metasurfaces[J]. Adv Opt Mater, 2023, 11(5): 2202348. doi: 10.1002/adom.202202348
[131] Epstein A, Eleftheriades G V. Arbitrary power-conserving field transformations with passive lossless omega-type bianisotropic metasurfaces[J]. IEEE Trans Antennas Propagat, 2016, 64(9): 3880−3895. doi: 10.1109/TAP.2016.2588495
[132] Kerker M, Wang D S, Giles C L. Electromagnetic scattering by magnetic spheres[J]. J Opt Soc Am, 1983, 73(6): 765−767. doi: 10.1364/JOSA.73.000765
[133] Yang J Y, Gurung S, Bej S, et al. Active optical metasurfaces: comprehensive review on physics, mechanisms, and prospective applications[J]. Rep Prog Phys, 2022, 85(3): 036101. doi: 10.1088/1361-6633/ac2aaf
[134] Berreman D W. Optics in stratified and anisotropic media: 4×4-matrix formulation[J]. J Opt Soc Am, 1972, 62(4): 502−510. doi: 10.1364/JOSA.62.000502
[135] Luo J, Lu W X, Hang Z H, et al. Arbitrary control of electromagnetic flux in inhomogeneous anisotropic media with near-zero index[J]. Phys Rev Lett, 2014, 112(7): 073903. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.112.073903
[136] Luo J, Hang Z H, Chan C T, et al. Unusual percolation threshold of electromagnetic waves in double-zero medium embedded with random inclusions[J]. Laser Photonics Rev, 2015, 9(5): 523−529. doi: 10.1002/lpor.201500083
[137] Liberal I, Engheta N. Near-zero refractive index photonics[J]. Nat Photonics, 2017, 11(3): 149−158. doi: 10.1038/nphoton.2017.13
[138] Niu X X, Hu X Y, Chu S S, et al. Epsilon-near-zero photonics: a new platform for integrated devices[J]. Adv Opt Mater, 2018, 6(10): 1701292. doi: 10.1002/adom.201701292
[139] Kinsey N, Devault C, Boltasseva A, et al. Near-zero-index materials for photonics[J]. Nat Rev Mater, 2019, 4(12): 742−760. doi: 10.1038/s41578-019-0133-0
[140] Li Y, Chan C T, Mazur E. Dirac-like cone-based electromagnetic zero-index metamaterials[J]. Light Sci Appl, 2021, 10(1): 203. doi: 10.1038/S41377-021-00642-2
[141] Luo J, Lai Y. Hermitian and non-hermitian dirac-like cones in photonic and phononic structures[J]. Front Phys, 2022, 10: 845624. doi: 10.3389/FPHY.2022.845624
[142] Ji W J, Luo J, Chu H C, et al. Crosstalk prohibition at the deep-subwavelength scale by epsilon-near-zero claddings[J]. Nanophotonics, 2023, 12(11): 2007−2017. doi: 10.1515/nanoph-2023-0085
[143] Brewster D. IX. On the laws which regulate the polarisation of light by reflexion from transparent bodies. By David Brewster, LL. D. F. R. S. Edin. and F. S. A. Edin. In a letter addressed to Right Hon. Sir Joseph Banks, Bart. K. B. P. R. S[J]. Philos Trans Roy Soc London, 1815, 105: 125−159. doi: 10.1098/rstl.1815.0010
[144] Mahlein H F. Generalized Brewster-angle conditions for quarter-wave multilayers at non-normal incidence[J]. J Opt Soc Am, 1974, 64(5): 647−653. doi: 10.1364/JOSA.64.000647
[145] Lakhtakia A. Would Brewster recognize today's Brewster angle?[J]. Opt News, 1989, 15(6): 14−18. doi: 10.1364/ON.15.6.000014
[146] Wang C, Zhu Z B, Cui W Z, et al. All-angle Brewster effect observed on a terahertz metasurface[J]. Appl Phys Lett, 2019, 114(19): 191902. doi: 10.1063/1.5097742
[147] Hua J Y, Hua E K, Zhou F B, et al. Foveated glasses-free 3D display with ultrawide field of view via a large-scale 2D-metagrating complex[J]. Light Sci Appl, 2021, 10(1): 213. doi: 10.1038/S41377-021-00651-1
[148] Kim I, Martins R J, Jang J, et al. Nanophotonics for light detection and ranging technology[J]. Nat Nanotechnol, 2021, 16(5): 508−524. doi: 10.1038/s41565-021-00895-3
[149] Luo J, Yang Y T, Yao Z Q, et al. Ultratransparent media and transformation optics with shifted spatial dispersions[J]. Phys Rev Lett, 2016, 117(22): 223901. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.117.223901
[150] Liu Y C, Wang G P, Zhang S. A nonlocal effective medium description of topological weyl metamaterials[J]. Laser Photonics Rev, 2021, 15(10): 2100129. doi: 10.1002/lpor.202100129
[151] Song T T, Chu H C, Luo J, et al. Ultracompact photonic circuits without cladding layers[J]. Phys Rev X, 2022, 12(1): 011053. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevX.12.011053
[152] Lv Q H, Jin C, Zhang B C, et al. Ultrawide‐angle ultralow‐reflection phenomenon for transverse electric mode in anisotropic metasurface[J]. Adv Opt Mater, 2022, 10(12): 2102400. doi: 10.1002/adom.202102400
[153] Tamayama Y, Nakanishi T, Sugiyama K, et al. Observation of Brewster's effect for transverse-electric electromagnetic waves in metamaterials: experiment and theory[J]. Phys Rev B, 2006, 73(19): 193104. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.73.193104
[154] Yao Z Q, Luo J, Lai Y. Illusion optics via one-dimensional ultratransparent photonic crystals with shifted spatial dispersions[J]. Opt Express, 2017, 25(25): 30931−30938. doi: 10.1364/OE.25.030931
[155] Xu L, Chen H Y. Transformation metamaterials[J]. Adv Mater, 2021, 33(52): 2005489. doi: 10.1002/adma.202005489
[156] Chu Z T, Li T F, Wang J F, et al. Tailoring permittivity using metasurface: a facile way of enhancing extreme-angle transmissions for both TE- and TM-polarizations[J]. Opt Express, 2022, 30(16): 29365−29378. doi: 10.1364/OE.467426
[157] Dong D S, Yang J, Cheng Q, et al. Terahertz broadband low-reflection metasurface by controlling phase distributions[J]. Adv Opt Mater, 2015, 3(10): 1405−1410. doi: 10.1002/adom.201500156
[158] Zheng X Y, Lin J, Wang Z, et al. Manipulating light transmission and absorption via an achromatic reflectionless metasurface[J]. PhotoniX, 2023, 4(1): 3. doi: 10.1186/S43074-022-00078-W
[159] Ebbesen T W, Lezec H J, Ghaemi H F, et al. Extraordinary optical transmission through sub-wavelength hole arrays[J]. Nature, 1998, 391(6668): 667−669. doi: 10.1038/35570
[160] Genet C, Ebbesen T W. Light in tiny holes[J]. Nature, 2007, 445(7123): 39−46. doi: 10.1038/nature05350
[161] de Abajo F J G. Colloquium: light scattering by particle and hole arrays[J]. Rev Mod Phys, 2007, 79(4): 1267−1290. doi: 10.1103/RevModPhys.79.1267
[162] Garcia-Vidal F J, Martin-Moreno L, Ebbesen T W, et al. Light passing through subwavelength apertures[J]. Rev Mod Phys, 2010, 82(1): 729−787. doi: 10.1103/RevModPhys.82.729
[163] Coe J V, Rodriguez K R, Teeters-Kennedy S, et al. Metal films with arrays of tiny holes: spectroscopy with infrared plasmonic scaffolding[J]. J Phys Chem C, 2007, 111(47): 17459−17472. doi: 10.1021/jp072909a
[164] Chen Y Z, Zhou C X, Luo X G, et al. Structured lens formed by a 2D square hole array in a metallic film[J]. Opt Lett, 2008, 33(7): 753−755. doi: 10.1364/OL.33.000753
[165] Coe J V, Heer J M, Teeters-Kennedy S, et al. Extraordinary transmission of metal films with arrays of subwavelength holes[J]. Annu Rev Phys Chem, 2008, 59: 179−202. doi: 10.1146/annurev.physchem.59.032607.093703
[166] Gordon R, Brolo A G, Sinton D, et al. Resonant optical transmission through hole-arrays in metal films: physics and applications[J]. Laser Photonics Rev, 2010, 4(2): 311−335. doi: 10.1002/lpor.200810079
[167] Baida F I, Belkhir A, Arar O, et al. Enhanced optical transmission by light coaxing: mechanism of the TEM-mode excitation[J]. Micron, 2010, 41(7): 742−745. doi: 10.1016/j.micron.2010.06.009
[168] Hu C G, Pu M B, Li X, et al. Extraordinary optical transmission induced by electric resonance ring and its dynamic manipulation at far-infrared regime[J]. Opt Express, 2011, 19(19): 18109−18115. doi: 10.1364/OE.19.018109
[169] 张鑫, 刘海涛. 光学异常透射研究进展[J]. 物理学进展, 2016, 36(4): 118−127. doi: 10.13725/j.cnki.pip.2015.04.002
Zhang X, Liu H T. Progress in extraordinary optical transmission[J]. Prog Phys, 2016, 36(4): 118−127. doi: 10.13725/j.cnki.pip.2015.04.002
[170] Oh Y, Kim K, Hwang S, et al. Recent advances of nanostructure implemented spectroscopic sensors-A brief overview[J]. Appl Spectrosc Rev, 2016, 51(7-9): 656−668. doi: 10.1080/05704928.2016.1166437
[171] 杨泽华, 宋阳, 陈爽, 等. 同轴纳米柱对亚波长金属牛眼结构EOT的调控[J]. 光电工程, 2018, 45(11): 180207. doi: 10.12086/oee.2018.180207
Yang Z H, Song Y, Chen S, et al. Control of EOT of subwavelength metal bullseye structures by coaxial nano-columns[J]. Opto-Electron Eng, 2018, 45(11): 180207. doi: 10.12086/oee.2018.180207
[172] Zhang X H, Li X, Jin J J, et al. Polarization-independent broadband meta-holograms via polarization-dependent nanoholes[J]. Nanoscale, 2018, 10(19): 9304−9310. doi: 10.1039/C7NR08428E
[173] Wang Y Q, Ma X L, Li X, et al. Perfect electromagnetic and sound absorption via subwavelength holes array[J]. Opto-Electron Adv, 2018, 1(8): 180013. doi: 10.29026/oea.2018.180013
[174] 刘觉夫, 陈娇, 李康康, 等. 宽频十字缝隙分形纳米天线及其异常透射特性[J]. 光电工程, 2020, 47(6): 190422. doi: 10.12086/oee.2020.190422
Liu J F, Chen J, Li K K, et al. Broadband cross-slots fractal nano-antenna and its extraordinary optical transmission characteristics[J]. Opto-Electron Eng, 2020, 47(6): 190422. doi: 10.12086/oee.2020.190422
[175] Fleischhauer M, Imamoglu A, Marangos J P. Electromagnetically induced transparency: optics in coherent media[J]. Rev Mod Phys, 2005, 77(2): 633−673. doi: 10.1103/RevModPhys.77.633
[176] Xu Q F, Sandhu S, Povinelli M L, et al. Experimental realization of an on-chip all-optical analogue to electromagnetically induced transparency[J]. Phys Rev Lett, 2006, 96(12): 123901. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.96.123901
[177] Papasimakis N, Fedotov V A, Zheludev N I, et al. Metamaterial analog of electromagnetically induced transparency[J]. Phys Rev Lett, 2008, 101(25): 253903. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.101.253903
[178] Yang Y M, Kravchenko I I, Briggs D P, et al. All-dielectric metasurface analogue of electromagnetically induced transparency[J]. Nat Commun, 2014, 5(1): 5753. doi: 10.1038/ncomms6753
[179] Mørk J, Lunnemann P, Xue W, et al. Slow and fast light in semiconductor waveguides[J]. Semicond Sci Technol, 2010, 25(8): 083002. doi: 10.1088/0268-1242/25/8/083002
[180] Hadad Y, Sounas D L, Alu A. Space-time gradient metasurfaces[J]. Phys Rev B, 2015, 92(10): 100304. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.92.100304
[181] Zhang X Q, Xu N N, Qu K N, et al. Electromagnetically induced absorption in a three-resonator metasurface system[J]. Sci Rep, 2015, 5(1): 10737. doi: 10.1038/srep10737
[182] Yahiaoui R, Burrow J A, Mekonen S M, et al. Electromagnetically induced transparency control in terahertz metasurfaces based on bright-bright mode coupling[J]. Phys Rev B, 2018, 97(15): 155403. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.97.155403
[183] Liu Y C, Li B B, Xiao Y F. Electromagnetically induced transparency in optical microcavities[J]. Nanophotonics, 2017, 6(5): 789−811. doi: 10.1515/nanoph-2016-0168
[184] Ma L J, Slattery O, Tang X. Optical quantum memory based on electromagnetically induced transparency[J]. J Opt, 2017, 19(4): 043001. doi: 10.1088/2040-8986/19/4/043001
[185] Limonov M F, Rybin M V, Poddubny A N, et al. Fano resonances in photonics[J]. Nat Photonics, 2017, 11(9): 543−554. doi: 10.1038/nphoton.2017.142
[186] Liu H Z, Guo C, Vampa G, et al. Enhanced high-harmonic generation from an all-dielectric metasurface[J]. Nat Physics, 2018, 14(10): 1006−1010. doi: 10.1038/s41567-018-0233-6
[187] 马长伟, 马文英, 谭毅, 等. 高Q值THz类EIT超材料及传感特性研究[J]. 光电工程, 2018, 45(11): 180298. doi: 10.12086/oee.2018.180298
Ma C W, Ma W Y, Tan Y, et al. High Q-factor terahertz metamaterial based on analog of electromagnetically induced transparency and its sensing characteristics[J]. Opto-Electron Eng, 2018, 45(11): 180298. doi: 10.12086/oee.2018.180298
[188] 唐雨竹, 马文英, 魏耀华, 等. 一种旋转可调的太赫兹超材料及其传感特性[J]. 光电工程, 2017, 44(4): 453−457. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-501X.2017.04.010
Tang Y Z, Ma W Y, Wei Y H, et al. A tunable terahertz metamaterial and its sensing performance[J]. Opto-Electron Eng, 2017, 44(4): 453−457. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-501X.2017.04.010
[189] Kim T T, Kim H D, Zhao R K, et al. Electrically tunable slow light using graphene metamaterials[J]. ACS Photonics, 2018, 5(5): 1800−1807. doi: 10.1021/acsphotonics.7b01551
[190] You Y, Hu Y Q, Lin G W, et al. Quantum nonreciprocity based on electromagnetically induced transparency in chiral quantum-optical systems[J]. Phys Rev A, 2021, 103(6): 063706. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevA.103.063706
[191] Bayrakli I. Electromagnetically induced transparency in natural and artificial molecules[J]. Opt Laser Technol, 2021, 141: 107168. doi: 10.1016/J.OPTLASTEC.2021.107168
[192] Zhang J, Mu N, Liu L H, et al. Highly sensitive detection of malignant glioma cells using metamaterial-inspired THz biosensor based on electromagnetically induced transparency[J]. Biosens Bioelectron, 2021, 185: 113241. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2021.113241
[193] Liu S, Noor A, Du L L, et al. Anomalous refraction and nondiffractive bessel-beam generation of terahertz waves through transmission-type coding metasurfaces[J]. ACS Photonics, 2016, 3(10): 1968−1977. doi: 10.1021/acsphotonics.6b00515
[194] Lavigne G, Caloz C. Generalized Brewster effect using bianisotropic metasurfaces[J]. Opt Express, 2021, 29(7): 11361−11370. doi: 10.1364/OE.423078
[195] Zhang Z, Che Z Y, Liang X Y, et al. Realizing generalized Brewster effect by generalized Kerker effect[J]. Phys Rev Appl, 2021, 16(5): 054017. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevApplied.16.054017
[196] Sun J B, Liu L Y, Dong G Y, et al. An extremely broad band metamaterial absorber based on destructive interference[J]. Opt Express, 2011, 19(22): 21155−21162. doi: 10.1364/OE.19.021155
[197] Liu X L, Tyler T, Starr T, et al. Taming the blackbody with infrared metamaterials as selective thermal emitters[J]. Phys Rev Lett, 2011, 107(4): 045901. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.107.045901
[198] Tao H, Bingham C M, Pilon D, et al. A dual band terahertz metamaterial absorber[J]. J Phys D:Appl Phys, 2010, 43(22): 225101. doi: 10.1088/0022-3727/43/22/225102
[199] Xu H X, Wang G M, Qi M Q, et al. Triple-band polarization-insensitive wide-angle ultra-miniature metamaterial transmission line absorber[J]. Phys Rev B, 2012, 86(20): 205104. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.86.205104
[200] Wu P C, Papasimakis N, Tsai D P. Self-affine graphene metasurfaces for tunable broadband absorption[J]. Phys Rev Appl, 2016, 6(4): 044019. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevApplied.6.044019
[201] Zhou L, Tan Y L, Wang J Y, et al. 3D self-assembly of aluminium nanoparticles for plasmon-enhanced solar desalination[J]. Nat Photonics, 2016, 10(6): 393−398. doi: 10.1038/nphoton.2016.75
[202] Zhou L, Tan Y L, Ji D X, et al. Self-assembly of highly efficient, broadband plasmonic absorbers for solar steam generation[J]. Sci Adv, 2016, 2(4): e1501227. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.1501227
[203] Cui Y X, Fung K H, Xu J, et al. Ultrabroadband light absorption by a sawtooth anisotropic metamaterial slab[J]. Nano Lett, 2012, 12(3): 1443−1447. doi: 10.1021/nl204118h
[204] Ye D X, Wang Z Y, Xu K W, et al. Ultrawideband dispersion control of a metamaterial surface for perfectly-matched-layer-like absorption[J]. Phys Rev Lett, 2013, 111(18): 187402. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.111.187402
[205] Wetzstein G, Ozcan A, Gigan S, et al. Inference in artificial intelligence with deep optics and photonics[J]. Nature, 2020, 588(7836): 39−47. doi: 10.1038/s41586-020-2973-6
[206] Ma W, Liu Z C, Kudyshev Z A, et al. Deep learning for the design of photonic structures[J]. Nat Photonics, 2021, 15(2): 77−90. doi: 10.1038/s41566-020-0685-y
[207] Wiecha P R, Arbouet A, Girard C, et al. Deep learning in nano-photonics: inverse design and beyond[J]. Photonics Res, 2021, 9(5): B182−B200. doi: 10.1364/PRJ.415960
[208] Jia Y T, Qian C, Fan Z X, et al. In situ customized illusion enabled by global metasurface reconstruction[J]. Adv Funct Mater, 2022, 32(19): 2109331. doi: 10.1002/adfm.202109331
[209] An S S, Zheng B W, Julian M, et al. Deep neural network enabled active metasurface embedded design[J]. Nanophotonics, 2022, 11(17): 4149−4158. doi: 10.1515/nanoph-2022-0152
[210] Krasikov S, Tranter A, Bogdanov A, et al. Intelligent metaphotonics empowered by machine learning[J]. Opto-Electron Adv, 2022, 5(3): 210147. doi: 10.29026/oea.2022.210147
[211] Jin Y B, He L S, Wen Z H, et al. Intelligent on-demand design of phononic metamaterials[J]. Nanophotonics, 2022, 11(3): 439−460. doi: 10.1515/nanoph-2021-0639
[212] Chen J T, Qian C, Zhang J, et al. Correlating metasurface spectra with a generation-elimination framework[J]. Nat Commun, 2023, 14(1): 4872. doi: 10.1038/S41467-023-40619-W
[213] Guo J J, Zhang Y L, Huang M, et al. Electromagnetically large cylinders with duality symmetry by hybrid neural networks[J]. Opt Laser Technol, 2024, 168: 109935. doi: 10.1016/J.OPTLASTEC.2023.109935
-


 E-mail Alert
E-mail Alert RSS
RSS
 下载:
下载: