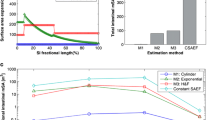
Abstract
The present study was performed to determine the relative contribution of both passive and nonpassive transport processes in jejunal absorption of gabapentin. The oral absorption of gabapentin was studied using in situ single pass intestinal perfusion technique in fasted rats. Unbiased intrinsic membrane absorption parameters such as maximal flux, Michaelis constant, carrier permeability, and membrane permeability were calculated using a modified boundary layer model. Gabapentin intestinal perfusion results indicate that its jejunal absorption in rats occurs via a nonpassive process, with no significant passive absorption kinetics and its concentration-dependent permeability. A good correlation (r 2=0.88) between observed human absorption fraction and calculated (from in situ rat intestine) human absorption fraction was obtained.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Satzinger G. Antiepileptics from gamma-aminobutyric acid.Arzenim Forsch Drug Res. 1994;44:261–266.
McLean MJ. Gabapentin: Chemistry, absorption, distribution and excretion. In: Levy R, Mattson R, Meldrum B.Antiepileptic Drugs. New York, NY: Raven Press Ltd; 1995;843–849.
Turck DVK, Bockbrader H, Sedman A. Dose linearity of the anticonvulsant gabapentin after multiple oral doses.Eur J Clin Pharmcol. 1989;36:A310.
Vollmer KO, Anhut H, Thomann P, Wagner F, Jahnchen D. Pharmacokinetics model and absolute bioavailability of new anticonvulsant gabapentin.Adv Epileptology. 1987;17:209–211.
Maurer HH, Rump AF. Intestinal absorptions of gabapentin in rats.Arzneim Forsch Drug Res. 1991;41:104–106.
Stewart BH, Kugler AR, Thompson PR, Bockbrader HN. A saturable transport mechanism in the intestinal absorption of gabapentin is the underlying cause of the lack of proportionality between increasing dose and drug levels in plasma.Pharm Res. 1993;10:276–281.
Su TZ, Lunney E, Campbell G, Oxender DL. Transport of gabapentin, a gamma amino acid drug, by system L-alpha-amino acid transporters, a comparative study in astrocytes, synaptosomes and CHO cells.J Neurochem. 1995;64:2125–2131.
Zhao YH, Abraham MH, Le J, et al. Rate-limited steps of human oral absorption and QSAR studies.Pharm Res. 2002;19:1446–1457.
Oh D-M, Sinko PJ, Amidon GL. Characterization of the oral absorption of several aminopenicillins: determination of intrinsic membrane absorption parameters in the rat intestine in situ.Int J Pharm. 1992;85:181–187.
Sinko PJ, Amidon GL. Characterization of the oral absorption of β-lactam antibiotics. I. Cephalosporins: determination of intrinsic membrane absorption parameters in the rat intestine in situ.Pharm Res. 1988;5:645–650.
Johnson DA, Amidon GL. Determination of intrinsic membrane transport parameters from perfused intestine experiments: a boundary layer approach to estimating the aqueous and unbiased membrane permeabilities.J Theor Biol. 1988;131:93–106.
Sinko PJ, Leesman GD, Amidon GL. Predicting fraction dose absorbed in humans using a macroscopic mass balance approach.Pharm Res. 1991;8:979–988.
Sutton SC, Rinaldi MT, Vukovinsky KE. Comparison of gravimetric, phenol red and 14C-PEG-3350 methods to determine water absorption in the rat single pass intestinal perfusion model.AAPS PharmSci. 2001;3:E25.
Hu M, Sinko PJ, DeMeere LJ, Johnson DA, Amidon GL. Membrane permeability parameters for some amino acids and betalactam antibiotics: application of the boundary layer approach.J Theor Biol. 1988;131:107–114.
Reid RC, Prausnnitz JM, Sherwood TK.The Properties of Gases and Liquids. New York, NY: McGraw Hill Book Co; 1997.
Amidson GL, Sinko PJ, Fleisher D. Estimating human oral fraction dose absorbed: a correlation using rat intestinal membrane permeability for passive and carrier-mediated compounds.Pharm Res. 1988;5:651–654.
Kitazawa S, Ito H, Johno I, Takahashi T, Takenaka H. Generality in effects of transmucosal fluid movement and glucose on drug absorption from the rat small intestine.Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo). 1978;26:915–924.
Karino A, Hayashi M, Horie T, Awazu S, Minami H, Hanano M. Solvent drag effect in drug intestinal absorption. I. Studies on drug and D2O absorption clearances.J Pharmacobiodyn. 1982;5:410–417.
Vollmer KO, Hodenberg AV, Kolle EU. Pharmacokinetics and metabolism of gabapentin in rat, dog and man.Arzenim Forsch Drug Res. 1986;36:830–839.
Amidon GL, Lennemas H, Shah VP, Crison JR. A theoretical basis for a biopharmaceutic drug classification: the correlation of in vitro, drug product dissolution and in vivo bioavailability.Pharm Res. 1995;12:413–420.
Crank J.The Mathematics of Diffusion. London, UK. Oxford University Press; 1975.
Oh DM, Curl RL, Amidon GL. Estimating the fraction dose absorbed from suspensions of poorly soluble compounds in humans: a mathematical model.Pharm Res. 1993;10:264–270.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Published: September 2, 2005
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Madan, J., Chawla, G., Arora, V. et al. Unbiased membrane permeability parameters for gabapentin using boundary layer approach. AAPS J 7, 21 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1208/aapsj070121
Received:
Accepted:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1208/aapsj070121