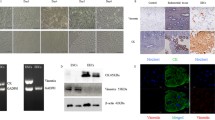
Abstract
Successful mouse embryo implantation requires a receptive uterus and an activated blastocyst. A large number of genes, cytokines, and other factors are involved in the process. MicroRNAs (miRNAs) regulate the expression of many genes, and previous studies have investigated the relationship between miRNA expression and embryo implantation. In this study, we show that mmu-microRNA-200a (mmu-miR-200a) is expressed in a spatiatemporal manner during implantation in mouse uterus and found that phosphatase and tensin homolog (PTEN), SON, and programmed cell death 4 (Pdcd4) are the target genes of mmu-miR-200a by bioinformatics analysis. In vitro gain and loss of function experiments confirm that PTEN, a critical gene for cell proliferation and apoptosis, is the target gene of mmu-miR-200a. Our experiments also show that injection of the uterine horn with mmu-miR-200a lentivirus leads to a decreased implantation rate. Collectively, our results suggest that mmu-miR-200a affects embryo implantation by regulating PTEN protein expression. Thus, clarifying the physiological functions of uterine miRNAs will help to elucidate the embryo implantation process and may even contribute to curing infertility and inventing new contraceptives.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brown JR, Sanseau P. A computational view of microRNAs and their targets. Drug Discov Today. 2005;10(8):595–601.
Nilsen TW. Mechanisms of microRNA-mediated gene regulation in animal cells. Trends Genet. 2007;23(5):243–249.
Du T, Zamore PD. microPrimer: the biogenesis and function of microRNA. Development. 2005;132(21):4645–4652.
Ouellet DL, Perron MP, Gobeil LA, Plante P, Provost P. MicroRNAs in gene regulation: when the smallest governs it all. J Biomed Biotechnol. 2006;2006(4):69616.
Bartel DP. MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 2004;116(2):281–297.
Rodriguez A, Vigorito E, Clare S, et al. Requirement of bic/ microRNA-155 for normal immune function. Science. 2007; 316(5824):608–611.
Zhao Y, Ransom JF, Li A, et al. Dysregulation of cardiogenesis, cardiac conduction, and cell cycle in mice lacking miRNA-1–2. Cell. 2007;129(2):303–317.
Wang H, Dey SK. Roadmap to embryo implantation: clues from mouse models. Nat Rev Genet. 2006;7(3):185–199.
Dey SK, Lim H, Das SK, et al. Molecular cues to implantation. Endocr Rev. 2004;25(3):341–373.
Lee K, Jeong J, Kwak I, et al. Indian hedgehog is a major mediator of progesterone signaling in the mouse uterus. Nat Genet. 2006; 38(10): 1204–1209.
Lee KY, Jeong JW, Wang J, et al. Bmp2 is critical for the murine uterine decidual response. Mol Cell Biol. 2007;27(15):5468–5478.
Stewart CL, Kaspar P, Brunet LJ, et al. Blastocyst implantation depends on maternal expression of leukaemia inhibitory factor. Nature. 1992;359(6390):76–79.
Daikoku T, Cha J, Sun X, et al. Conditional deletion of Msx homeobox genes in the uterus inhibits blastocyst implantation by altering uterine receptivity. Dev Cell. 2011;21(6):1014–1025.
Surveyor GA, Gendler SJ, Pemberton L, et al. Expression and steroid hormonal control of Muc-1 in the mouse uterus. Endocrinology. 1995;136(8):3639–3647.
Paria BC, Huet-Hudson YM, Dey SK. Blastocyst’s state of activity determines the “window” of implantation in the receptive mouse uterus. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1993;90(21): 10159–10162.
Cha J, Sun X, Dey SK. Mechanisms of implantation: strategies for successful pregnancy. Nat Med. 2012;18(12):1754–1767.
Song H, Lim H, Paria BC, et al. Cytosolic phospholipase A2alpha is crucial [correction of A2alpha deficiency is crucial] for ‘on-time’ embryo implantation that directs subsequent development. Development. 2002;129(12):2879–2889.
Ye X, Hama K, Contos JJ, et al. LPA3-mediated lysophosphatidic acid signalling in embryo implantation and spacing. Nature. 2005; 435(7038): 104–108.
Dey SK. Reproductive biology: fatty link to fertility. Nature. 2005;435(7038):34–35.
Liu JL, Su RW, Yang ZM. Differential expression profiles of mRNAs, miRNAs and proteins during embryo implantation. Front Biosci (Schol Ed). 2011;3:1511–1519.
Su RW, Lei W, Liu JL, et al. The integrative analysis of microRNA and mRNA expression in mouse uterus under delayed implantation and activation. PLoS One. 2010;5(11):e15513.
Chakrabarty A, Tranguch S, Daikoku T, Jensen K, Furneaux H, Dey SK. MicroRNA regulation of cyclooxygenase-2 during embryo implantation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2007;104(38):15144–15149.
Hu SJ, Ren G, Liu JL, et al. MicroRNA expression and regulation in mouse uterus during embryo implantation. J Biol Chem. 2008; 283(34):23473–23484.
Pan Q, Chegini N. MicroRNA signature and regulatory functions in the endometrium during normal and disease states. Semin Reprod Med. 2008;26(6):479–493.
Hiroki E, Akahira J, Suzuki F, et al. Changes in microRNA expression levels correlate with clinicopathological features and prognoses in endometrial serous adenocarcinomas. Cancer Sci. 2010;101(1):241–249.
Ohlsson Teague EM, Van der Hoek KH, Van der Hoek MB, et al. MicroRNA-regulated pathways associated with endometriosis. Mol Endocrinol. 2009;23(2):265–275.
Gibbons DL, Lin W, Creighton CJ, et al. Contextual extracellular cues promote tumor cell EMT and metastasis by regulating miR-200 family expression. Genes Dev. 2009;23(18):2140–2151.
Park NJ, Zhou H, Elashoff D, et al. Salivary microRNA: discovery, characterization, and clinical utility for oral cancer detection. Clin Cancer Res. 2009;15(17):5473–5477.
Xia H, Ng SS, Jiang S, et al. miR-200a-mediated downregulation of ZEB2 and CTNNB1 differentially inhibits nasopharyngeal carcinoma cell growth, migration and invasion. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2010;391(1):535–541.
Dykxhoorn DM, Wu Y, Xie H, et al. miR-200 enhances mouse breast cancer cell colonization to form distant metastases. PLoS One. 2009;4(9):e7181.
Taylor DD, Gercel-Taylor C. MicroRNA signatures of tumor-derived exosomes as diagnostic biomarkers of ovarian cancer. Gynecol Oncol. 2008;110(1):13–21.
Nam EJ, Yoon H, Kim SW, et al. MicroRNA expression profiles in serous ovarian carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 2008;14(9):2690–2695.
Roy BC, Kohno T, Iwakawa R, et al. Involvement of LKB1 in epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) of human lung cancer cells. Lung Cancer. 2010;70(2):136–145.
Wang G, Kwan BC, Lai FM, et al. Intrarenal expression of miRNAs in patients with hypertensive nephrosclerosis. Am J Hypertens. 2010;23(1):78–84.
Wang G, Kwan BC, Lai FM, Chow KM, Kam-Tao Li P, Szeto CC. Expression of microRNAs in the urinary sediment of patients with IgA nephropathy. Dis Markers. 2010;28(2):79–86.
Hu X, Macdonald DM, Huettner PC, et al. A miR-200 microRNA cluster as prognostic marker in advanced ovarian cancer. Gynecol Oncol. 2009;114(3):457–464.
Qin X, Yan L, Zhao X, Li C, Fu Y. microRNA-21 overexpression contributes to cell proliferation by targeting PTEN in endometrioid endometrial cancer. Oncol Lett. 2012;4(6):1290–1296.
Meng F, Henson R, Lang M, et al. Involvement of human microRNA in growth and response to chemotherapy in human cholangiocarcinoma cell lines. Gastroenterology. 2006;130(7):2113–2129.
Zaman MS, Thamminana S, Shahryari V, et al. Inhibition of PTEN gene expression by oncogenic miR-23b-3p in renal cancer. PLoS One. 2012;7(11):e50203.
Chen C, Ridzon DA, Broomer AJ, et al. Real-time quantification of microRNAs by stem-loop RT-PCR. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005; 33(20):e179.
Megraw M, Sethupathy P, Corda B, Hatzigeorgiou AG. miRGen: a database for the study of animal microRNA genomic organization and function. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007;35(Database issue): D149–D155.
Lewis BP, Burge CB, Bartel DP. Conserved seed pairing, often flanked by adenosines, indicates that thousands of human genes are microRNA targets. Cell. 2005;120(1):15–20.
Krek A, Grun D, Poy MN, et al. Combinatorial microRNA target predictions. Nat Genet. 2005;37(5):495–500.
Illera MJ, Cullinan E, Gui Y, Yuan L, Beyler SA, Lessey BA. Blockade of the alpha(v)beta(3) integrin adversely affects implantation in the mouse. Biol Reprod. 2000;62(5):1285–1290.
Tsai NP, Bi J, Loh HH, Wei LN. Netrin-1 signaling regulates de novo protein synthesis of kappa opioid receptor by facilitating polysomal partition of its mRNA. J Neurosci. 2006;26(38):9743–9749.
Song L, Tuan RS. MicroRNAs and cell differentiation in mammalian development. Birth Defects Res C Embryo Today. 2006; 78(2):140–149.
Bentwich I, Avniel A, Karov Y, et al. Identification of hundreds of conserved and nonconserved human microRNAs. Nat Genet. 2005;37(7):766–770.
Berezikov E, Guryev V, van de Belt J, Wienholds E, Plasterk RH, Cuppen E. Phylogenetic shadowing and computational identification of human microRNA genes. Cell. 2005;120(1):21–24.
Xie X, Lu J, Kulbokas EJ, et al. Systematic discovery of regulatory motifs in human promoters and 3’ UTRs by comparison of several mammals. Nature. 2005;434(7031):338–345.
Zhang N, Li X, Wu CW, et al. microRNA-7 is a novel inhibitor of YY1 contributing to colorectal tumorigenesis [published on December 3, 2012]. Oncogene. 2012.
van Rooij E, Sutherland LB, Qi X, Richardson JA, Hill J, Olson EN. Control of stress-dependent cardiac growth and gene expression by a microRNA. Science. 2007;316(5824):575–579.
Tan J, Raja S, Davis MK, Tawfik O, Dey SK, Das SK. Evidence for coordinated interaction of cyclin D3 with p21 and cdk6 in directing the development of uterine stromal cell decidualization and polyploidy during implantation. Mech Dev. 2002;111(1–2): 99–113.
Sun X, Zhang L, Xie H, et al. Kruppel-like factor 5 (KLF5) is critical for conferring uterine receptivity to implantation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2012;109(4):1145–1150.
Lim H, Paria BC, Das SK, et al. Multiple female reproductive failures in cyclooxygenase 2-deficient mice. Cell. 1997;91(2):197–208.
Garcia-Cao I, Song MS, Hobbs RM, et al. Systemic elevation of PTEN induces a tumor-suppressive metabolic state. Cell. 2012;149(1):49–62.
Tashiro H, Blazes MS, Wu R, et al. Mutations in PTEN are frequent in endometrial carcinoma but rare in other common gynecological malignancies. Cancer Res. 1997;57(18):3935–3940.
Chen XL, Ma HL, Xie Y, Yang R, Wei SL. Expression of phosphatase and tensin homolog deleted on chromosome ten in mouse endometrium and its effect during blastocyst implantation. Sheng Li Xue Bao. 2008;60(1):119–124.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shen, LJ., He, JL., Yang, DH. et al. Mmu-microRNA-200a Overexpression Leads to Implantation Defect by Targeting Phosphatase and Tensin Homolog in Mouse Uterus. Reprod. Sci. 20, 1518–1528 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1177/1933719113488453
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1177/1933719113488453