

ISSN 1004-5759 CN 62-1105/S


草业学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (1): 229-237.DOI: 10.11686/cyxb2020514
• 研究简报 • 上一篇
张永超( ), 梁国玲, 秦燕, 刘文辉(
), 梁国玲, 秦燕, 刘文辉( ), 贾志锋, 刘勇, 马祥
), 贾志锋, 刘勇, 马祥
收稿日期:2020-11-18
修回日期:2021-02-02
出版日期:2021-12-01
发布日期:2021-12-01
通讯作者:
刘文辉
作者简介:Corresponding author. E-mail: qhliuwenhui@163.com基金资助:
Yong-chao ZHANG( ), Guo-ling LIANG, Yan QIN, Wen-hui LIU(
), Guo-ling LIANG, Yan QIN, Wen-hui LIU( ), Zhi-feng JIA, Yong LIU, Xiang MA
), Zhi-feng JIA, Yong LIU, Xiang MA
Received:2020-11-18
Revised:2021-02-02
Online:2021-12-01
Published:2021-12-01
Contact:
Wen-hui LIU
摘要:
试验以青藏高原青海省高寒草地中广泛分布和退化草地补播改良中的常用牧草品种-青牧1号老芒麦为研究对象,分析老芒麦衰老过程中叶片叶绿素和光合作用变化特征及对养分的响应。在青藏高原东北部,青海湖湖东地区设置1~6龄老芒麦自然生长田,6龄老芒麦施肥田和老芒麦连续施肥田(6年)3个处理。从2015年开始,每年5月进行老芒麦种植,播量2.25 g·m-2,行距30 cm,小区面积15 m2 (3 m×5 m)。采用KONICA MINOLTA, INC公司的SPAD分析仪,每个处理随机选取10株健康植株,从旗叶开始从上往下依次测定3片叶子的叶绿素相对含量。采用LI-COR公司的LI-6400XT便携式光合作用测量系统,在老芒麦开花期(7月底-8月初),选择天气晴朗早上10:30-11:30,随机选取5株健康植株对其旗叶进行测量。结果表明:3龄时老芒麦叶片叶绿素相对含量出现降低趋势,6龄时老芒麦叶片出现了逆向衰老现象;随着老芒麦年龄增加,旗叶净光合速率持续降低,而胞间二氧化碳浓度呈上升趋势,气孔导度和蒸腾速率从3龄开始显著降低,且3~6龄间无显著差异;青牧1号老芒麦6龄田,氮肥和磷肥施入普遍提高老芒麦叶片叶绿素相对含量,且不同部位叶片叶绿素相对含量(33.30%~48.23%)均显著高于对照组(27.05%~30.72%),叶片逆向衰老现象在高氮处理下得到缓解,氮肥和磷肥施入普遍提高老芒麦叶片净光合速率,N(60 kg·hm-2)处理下叶片净光合速率最高(10.77 μmol·m-2·s-1);青牧1号老芒麦在连续施肥6年处理下,低氮(45 kg·hm-2)施肥下叶片叶绿素相对含量较高,磷肥对保持老芒麦叶片叶绿素相对含量效果不显著;中度氮肥(60 kg·hm-2),同时配合磷肥添加长期施入,可有效维持高龄老芒麦叶片的光合效率。
张永超, 梁国玲, 秦燕, 刘文辉, 贾志锋, 刘勇, 马祥. 老芒麦衰老过程中叶片叶绿素和光合作用变化特征及对养分的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2022, 31(1): 229-237.
Yong-chao ZHANG, Guo-ling LIANG, Yan QIN, Wen-hui LIU, Zhi-feng JIA, Yong LIU, Xiang MA. Characteristics of chlorophyll and photosynthesis in leaves and their response to nutrients during aging of Elymus sibiricus[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2022, 31(1): 229-237.
| 编号Number | 氮肥N | 磷肥P2O5 |
|---|---|---|
| N0P0 | 0 | 0 |
| N0P60 | 0 | 60 |
| N0P75 | 0 | 75 |
| N0P90 | 0 | 90 |
| N45P0 | 45 | 0 |
| N45P60 | 45 | 60 |
| N45P75 | 45 | 75 |
| N45P90 | 45 | 90 |
| N60P0 | 60 | 0 |
| N60P60 | 60 | 60 |
| N60P75 | 60 | 75 |
| N60P90 | 60 | 90 |
| N75P0 | 75 | 0 |
| N75P60 | 75 | 60 |
| N75P75 | 75 | 75 |
| N75P90 | 75 | 90 |
表1 青牧1号老芒麦田长期施肥处理
Table 1 The longer fertilizer treatments of E. sibiricus (kg·hm-2)
| 编号Number | 氮肥N | 磷肥P2O5 |
|---|---|---|
| N0P0 | 0 | 0 |
| N0P60 | 0 | 60 |
| N0P75 | 0 | 75 |
| N0P90 | 0 | 90 |
| N45P0 | 45 | 0 |
| N45P60 | 45 | 60 |
| N45P75 | 45 | 75 |
| N45P90 | 45 | 90 |
| N60P0 | 60 | 0 |
| N60P60 | 60 | 60 |
| N60P75 | 60 | 75 |
| N60P90 | 60 | 90 |
| N75P0 | 75 | 0 |
| N75P60 | 75 | 60 |
| N75P75 | 75 | 75 |
| N75P90 | 75 | 90 |

图1 青牧1号老芒麦1~6龄田(A),6龄田(B)和连续施肥6龄田(C)的不同部位叶片叶绿素相对含量不同小写字母表示同一部位叶片间差异显著(P<0.05),不同大写字母表示不同部位叶片间差异显著(P<0.05)。Different small letters indicate significant difference among the leaves in the same part of different plant (P<0.05), and different capital letters indicate significant difference among the leaves in the same plant of different part (P<0.05).
Fig.1 The leaf chlorophyll content in different part leaf of plant from one years old to six field (A), six years old field (B) and six years old in continuous fertilizer field (C) of E. sibiricus

图2 老芒麦田2龄到6龄叶片净光合速率,叶片胞间二氧化碳浓度,叶片气孔导度和叶片蒸腾速率不同小写字母表示差异显著(P<0.05),下同。Different small letters indicate significant differences (P<0.05), the same below.
Fig.2 The leaf net photosynthesis rate, the leaf intercellular CO2 concentration, the leaf stomatal conductance and the leaf transpiration rate from two to six years old of E. sibiricus

图3 青牧1号老芒麦6龄田施肥处理对叶片净光合速率、叶片胞间二氧化碳浓度、叶片气孔导度和蒸腾速率的影响
Fig.3 The leaf net photosynthesis rate, the leaf stomatal conductance, the leaf intercellular CO2 concentration and the leaf transpiration rate of E. sibiricus cv. Qinghai No.1 in six years old under different fertilizer treatments
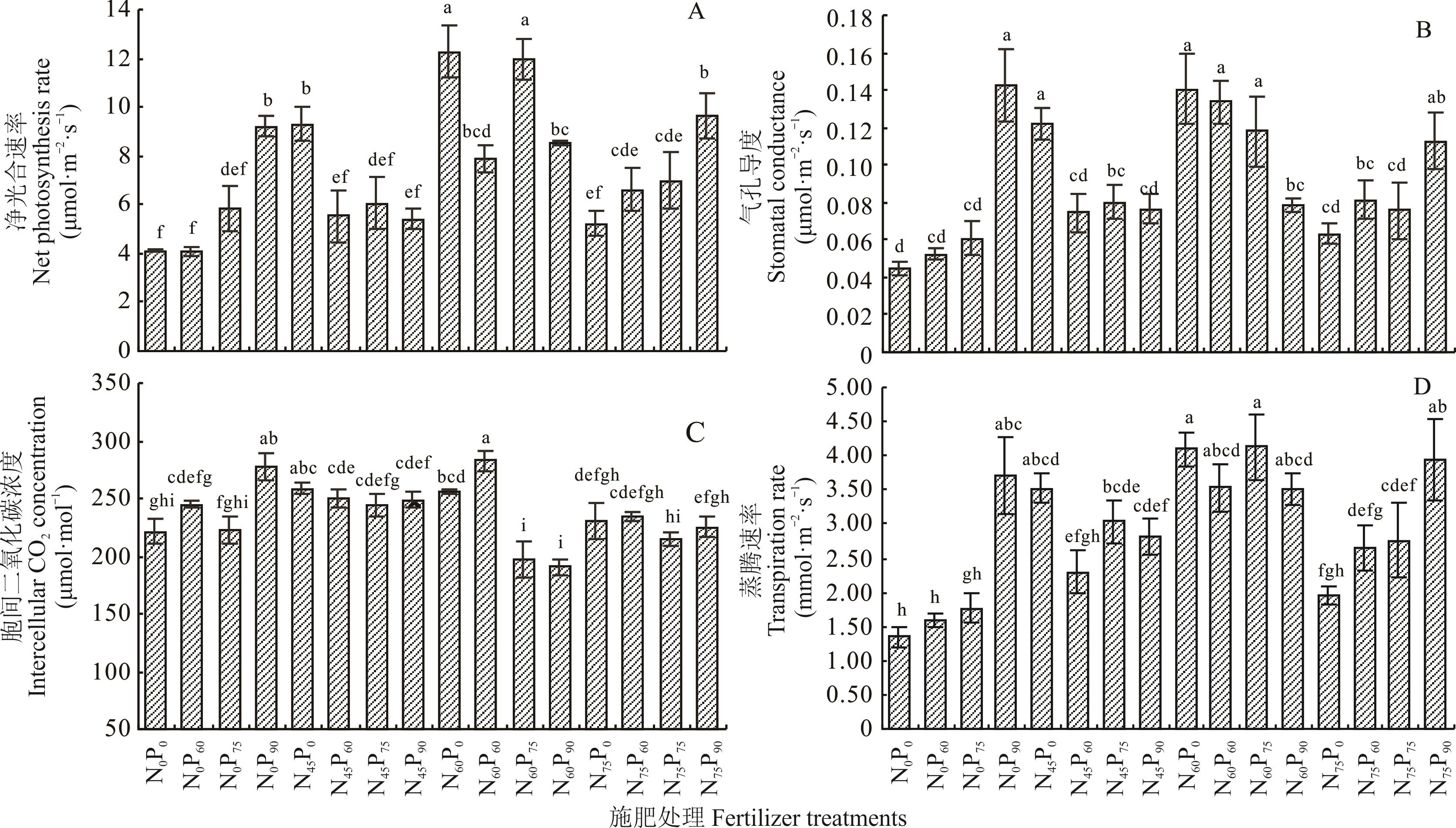
图4 青牧1号老芒麦连续施肥6龄田中施肥处理对叶片净光合速率,气孔导度,胞间二氧化碳浓度和蒸腾速率的影响
Fig.4 The leaf net photosynthesis rate, the leaf stomatal conductance, the leaf intercellular CO2 concentration and the leaf transpiration rate of E. sibiricus cv. Qinghai No.1 in six years old in continuous fertilizer field
| 1 | Jia S X, Shi D K. Flora of forage plants in China. Beijing: China Agriculture Press, 1997: 91-97. |
| 贾慎修, 史德宽. 中国饲用植物志. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 1997: 91-97. | |
| 2 | Zhou Y H, Zheng Y L, Yang J L, et al. Phylogenetic relationships among ten Elymus species based on random amplified polymorphic DNA. Acta Phytotaxonomica Sinica, 1999, 37(5): 425-432. |
| 周永红, 郑有良, 杨俊良, 等. 10种披碱草属植物的RAPD分析及其系统学意义. 植物分类学报, 1999, 37(5): 425-432. | |
| 3 | Howard T. Aging in the plant and animal kingdoms-the role of cell death. Reviews in Clinical Gerontology, 1994, 4(1): 5-20. |
| 4 | Alban V A, Didier C A, Abraham J, et al. A study of ryegrass architecture as a self-regulated system, using functional-structural plant modelling. Functional Plant Biology, 2008(35): 911-924. |
| 5 | Howard T. Senescence, ageing and death of the whole plant. New Phytologist, 2013, 197(3): 696-711. |
| 6 | Roca M, James C, Pruzinska A. Analysis of the chlorophyll catabolism pathway in leaves of an introgression senescence mutant of Lolium temulentum. Phytochemistry, 2004, 65: 1231-1238. |
| 7 | Feng B L, Gao X L, Wang C F, et al. Leaf senescence and active oxygen metabolism of different type wheats under drought. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2005, 13(4): 74-76. |
| 冯佰利, 高小丽, 王长发, 等. 干旱条件下不同温型小麦叶片衰老与活性氧代谢特性的研究. 中国生态农业学报, 2005, 13(4): 74-76. | |
| 8 | Ye H, Liu W, Chen Q L, et al. Chlorophyll breakdown in senescent leaves. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica, 2002(2): 437-443. |
| 叶蕙, 刘伟, 陈巧玲, 等. 衰老叶片中叶绿素的降解. 西北植物学报, 2002(2): 437-443. | |
| 9 | Yang W P, Wang C H, Wang Y S. Comparison of chlorophyll content and senescence physiology of flag leaves between two gluten-type winter wheat varieties. Guangdong Agriculture Sciences, 2011(24): 9-11. |
| 杨文平, 王春虎, 王玉帅. 两种筋型冬小麦旗叶叶绿素含量和衰老生理性状比较. 广东农业科学, 2011(24): 9-11. | |
| 10 | Sun J W, Fu X S, Xi H, et al. Gas exchange and chlorophyll fluorescence research on different position leaves of rich plant. Journal of Zhejiang University (Agriculture & Life Science), 2007, 33(3): 277-283. |
| 孙骏威, 付贤树, 奚辉, 等. 水稻不同叶位气体交换和叶绿素荧光研究. 浙江大学学报(农业与生命科学版), 2007, 33(3): 277-283. | |
| 11 | Dong B J, Huang R, Miao F, et al. Chlorophyll and photosynthetic characteristic variations in the inverted senescing process of wheat leaves. Journal of Northwest A & F University (Nature Science Edition), 2013, 41(6): 44-48. |
| 董宝婧, 黄蓉, 苗芳, 等. 小麦叶片逆向衰老过程中叶绿素含量及光合特性的变化. 西北农林科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2013, 41(6): 44-48. | |
| 12 | Zhang Y X, Zhu A M, Guo Y, et al. Effects of applying nitrogen fertilizer on leaf senescence characteristics of oat in sandy land during grain filling stage. Acta Agriculturae Boreali Sinica, 2019, 34(1): 124-130. |
| 张玉霞, 朱爱民, 郭园, 等. 追施氮肥对灌浆期沙地饲用燕麦叶片衰老特性的影响. 华北农学报, 2019, 34(1): 124-130. | |
| 13 | Zhao D H, Yang H M, Shi J G, et al. Study on the adaptability of the wheat leaf reverse aging to dry climate. Shannxi Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2019, 65(12): 61-64. |
| 赵德豪, 杨怀茂, 史建国, 等. 叶片逆向衰老小麦对旱区气候的适应性研究. 陕西农业科学, 2019, 65(12): 61-64. | |
| 14 | Liu Y, Liu Z X, He M J, et al. Effects of tillage modes in winter fallow period on leaf senescence and pod yield in continuous cropping peanut. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2019, 45(1): 135-147. |
| 刘妍, 刘兆新, 何美娟, 等. 冬闲期耕作方式对连作花生叶片衰老和产量的影响. 作物学报, 2019, 45(1): 135-147. | |
| 15 | Wang Q. Senescence mechanisms and vigor evaluation of old Pinus tabuliformis Carr. in Mountain Tai. Taian: Shandong Agricultural University, 2016. |
| 王巧. 泰山油松古树衰老机理与树势评价. 泰安: 山东农业大学, 2016. | |
| 16 | Xu Y M, Zhang Z, Chen Y Z, et al. Physiological characteristics of anti-aging leaves of Camellia oleifera. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences, 2019, 47(22): 188-191. |
| 许彦明, 张震, 陈永忠, 等. 油茶古树抗衰老叶片生理特性. 江苏农业科学, 2019, 47(22): 188-191. | |
| 17 | Sun H M. Research on the features of DNA methylation in Bamboo during aging and rejuvenation. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Forestry, 2013. |
| 孙慧敏. 竹类植物衰老与复壮过程中的DNA甲基化研究. 北京: 中国林业科学研究院, 2013. | |
| 18 | Wang Y T. Studies on senescence characteristics and regularity of nitrogen metabolic variation in perennial grass-take Kalimeris integrifolia as model plant. Beijng: China Agricultural University, 2014. |
| 王宇通. 多年生牧草衰老特征及氮代谢变化规律的研究. 北京: 中国农业大学, 2014. | |
| 19 | Zhao S H. Detection of physiology and biochemistry and transcriptome analysis in senescence leaves from red clover. Beijing: Beijing Forestry University, 2019. |
| 赵思涵. 红三叶叶片衰老生理生化及转录组分析. 北京: 北京林业大学, 2019. | |
| 20 | Ren Y J, Yang S W, Wu D X, et al. Leaf senescence characteristics and the screen and identification of leaf senescence associated genes in moso bamboo. Journal of Fujian Agriculture and Forestry University (Natural Science Edition), 2017, 46(6): 630-640. |
| 任育军, 杨树伟, 吴栋雄, 等. 毛竹叶片衰老特性及衰老相关基因的筛选和鉴定. 福建农林大学学报(自然科学版), 2017, 46(6): 630-640. | |
| 21 | Li S S, Ai X, Long W, et al. Morphological and physiological characteristics of Miscanthus lutarioriparius during leaf senescence in Autumn. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2015, 23(1): 215-218. |
| 李莎莎, 艾辛, 龙卫, 等. 南荻衰老的形态和生理生化特征的研究. 草地学报, 2015, 23(1): 215-218. | |
| 22 | Zhu A M, Zhang Y X, Wang X G, et al. Effects of applying nitrogen fertilizer on leaf senescence characeristics of Leymus chinensis in sandy land. Grassland and Turf, 2019, 39(2): 39-46. |
| 朱爱民, 张玉霞, 王显国, 等. 不同施氮水平对羊草抗衰老能力的影响. 草原与草坪, 2019, 39(2): 39-46. | |
| 23 | Liu Q B. Genome-wide association studies of traits related to senescence in upland cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.). Beijing: Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, 2018. |
| 刘其宝. 陆地棉衰老相关性状的全基因组关联分析. 北京: 中国农业科学院, 2018. | |
| 24 | Wu S J, Wang Y B, Wang W Q. Study on the nutrients retranslocation of mangroves during leaf senescence. Journal of Quanzhou Normal University, 2012, 30(6): 47-52. |
| 吴世军, 王赟博, 王文卿. 红树植物叶片衰老过程中养分的内吸收. 泉州师范学院学报, 2012, 30(6): 47-52. | |
| 25 | Guo T C, Song X, Ma D Y, et al. Effects of nitrogen application rates on photosynthetic characteristics of flag leaves in winter wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2007, 33(12): 1977-1981. |
| 郭天财, 宋晓, 马冬云, 等. 施氮水平对冬小麦旗叶光合特性的调控效应. 作物学报, 2007, 33(12): 1977-1981. | |
| 26 | Li J T, Jiang W, Zhang Y M, et al. Effects of long-term locating fertilization on decrepitude index of root system and yield of winter wheat at later growth stage. Acta Agriculturae Boreali Sinica, 2007, 22(5): 138-141. |
| 李京涛, 姜雯, 张玉梅, 等. 长期定位施肥对冬小麦后期根系衰老和产量的影响. 华北农学报, 2007, 22(5): 138-141. | |
| 27 | Zhou Q, Zhao C P, Cao C X, et al. Effects of N dressing ratio on carbon and nitrogen transport and on grain yield of Lolium multiflorum. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2010, 19(4): 47-53. |
| 周琴, 赵超鹏, 曹春信, 等. 不同氮肥基追比对多花黑麦草碳氮转运和种子产量的影响. 草业学报, 2010, 19(4): 47-53. | |
| 28 | Wang S. Study on leaf senescence physiology and anti-aging technology of grape cultured in protected and delayed cultivation. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, 2015. |
| 王帅. 设施葡萄延迟栽培叶片衰老生理及抗衰老技术研究. 北京: 中国农业科学院, 2015. | |
| 29 | Zhang Y. Active oxygen metabolism of leaves and regulation effect of nitrogen and phosphorus in grain filling stage. Xianyang: Northwest A & F University, 2008. |
| 张英. 小麦籽粒灌浆期叶片活性氧代谢与氮磷调控研究. 咸阳: 西北农林科技大学, 2008. |
| [1] | 吴路遥, 张建国, 常闻谦, 张少磊, 常青. 三种荒漠植物叶绿素荧光参数日变化特征[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(9): 203-213. |
| [2] | 赵利清, 彭向永, 刘俊祥, 毛金梅, 孙振元. GSH对铅胁迫下多年生黑麦草生长及光合生理的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(9): 97-104. |
| [3] | 王传旗, 刘文辉, 张永超, 周青平. 野生老芒麦苗期耐旱性研究[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(8): 127-136. |
| [4] | 吴瑞, 刘文辉, 张永超, 秦燕, 魏小星, 刘敏洁. 青藏高原老芒麦落粒性及农艺性状相关性研究[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(4): 130-139. |
| [5] | 汪辉, 田浩琦, 毛培胜, 刘文辉, 贾志锋, 魏露萍, 周青平. 植物非叶绿色器官光合特征研究进展[J]. 草业学报, 2021, 30(10): 191-200. |
| [6] | 单立文, 张强, 朱瑞芬, 孔晓蕾, 陈积山. 氮、磷添加下AMF对羊草和苜蓿生长与光合生理特性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(8): 46-57. |
| [7] | 王玉萍, 郜春晓, 王盛祥, 何晓童. 低温弱光胁迫下芸豆叶片光抑制与类囊体膜脂构成变化[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(8): 116-125. |
| [8] | 张利霞, 常青山, 薛娴, 刘伟, 张巧明, 陈苏丹, 郑轶琦, 李景林, 陈婉东, 李大钊. 酸胁迫对夏枯草叶绿素荧光特性和根系抗氧化酶活性的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(8): 134-142. |
| [9] | 王泳超, 张颖蕾, 闫东良, 何灵芝, 李卓, 燕博文, 邵瑞鑫, 郭家萌, 杨青华. 干旱胁迫下γ-氨基丁酸保护玉米幼苗光合系统的生理响应[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(6): 191-203. |
| [10] | 刘文文, 崔会婷, 尉春雪, 龙瑞才, 康俊梅, 杨青川, 王珍. 蒺藜苜蓿叶绿素酸酯a加氧酶(MtCAO)基因的克隆与功能分析[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(5): 171-181. |
| [11] | 黄曦叶, 何林江, 刘金平, 游明鸿, 刘航江. 葎草水分和光合特征及抗性物质含量响应冬季降温的性别差异[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(2): 103-113. |
| [12] | 赵小强, 陆晏天, 白明兴, 徐明霞, 彭云玲, 丁永福, 庄泽龙, 陈奋奇, 张大志. 不同株型玉米基因型对干旱胁迫的响应分析[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(2): 149-162. |
| [13] | 程守丰, 梁巧兰, 魏列新, 桑旭文, 姜玉玲. 苜蓿不同品种AMV和WCMV带毒检测及生理生化特性研究[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(12): 140-149. |
| [14] | 何海锋, 闫承宏, 吴娜, 刘吉利, 常雯雯. 施氮量对柳枝稷叶片叶绿素荧光特性及干物质积累的影响[J]. 草业学报, 2020, 29(11): 141-150. |
| [15] | 李文彬, 宁楚涵, 李伟, 李峰, 郭绍霞. 菲和芘胁迫下AMF和PGPR对高羊茅生理生态的响应[J]. 草业学报, 2019, 28(8): 84-94. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||