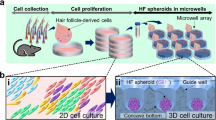
Abstract
In this study, modern techniques of laser microsurgery of cell spheroids have been used to develop a new simple, reproducible model for studying the mechanisms of repair and regeneration in vitro. Nanosecond laser pulses were applied to perform a microdissection of the outer and the inner zones of the spheroids from dermal fibroblasts. To achieve effective dissection and preservation of spheroid viability, the optimal parameters were chosen: 355 nm wavelength, 100 Hz frequency, 2 ns pulse duration, laser pulses in the range of 7–9 μJ. After microdissection, we observed injury of the spheroids: the edges of the wound surface opened and the angular opening reached a value of more than 180°. As early as during the first hour after spheroid microdissection with laser radiation, the surviving cells changed their shape: cells on the spheroid surface and directly in the damaged area became rounded. One day after microdissection, the structure of the spheroids began to partially recover, the cells in the surface layers began to take the original flattened shape; debris of dead damaged cells and their fragments was gradually cleared from the spheroid composition. In the proposed model, the first data on stimulation of structure recovery of injured spheroids from dermal fibroblasts with a P199 synthetic polypeptide, which is used in cosmetology for the initiation of antiaging and regenerative effects in the skin, were received. After microdissection, recovery of the spheroids structure with a few surface layers of flattened imbricated arranged cells and polygonal cells of the inner zone in the presence of P199 peptide was faster than in the control group, and was completed within 7 days, presumably due to the remodeling of the survived cells.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alvarado, A.S. and Tsonis, P.A., Bridging the regeneration gap: genetic insights from diverse animal models, Nat. Rev. Genet., 2006, vol. 7, no. 11, pp. 873–884.
Antoni, D., Burcke, H., Josset, E., et al., Three-dimensional cell culture: a breakthrough in vivo, Int. J. Mol. Sci., 2015, vol. 16, no. 3, pp. 5517–5527.
Baker, B.M. and Chen, C.S., Deconstructing the third dimension–how 3D culture microenvironments alter cellular cues, J. Cell Sci., 2012, vol. 125, no. 13, pp. 3015–3024.
Belousov, L.V., Ermakov, A.S., and Luchinskaia, N.N., Cytomechanical control of morphogenesis, Tsitologiia, 1999, vol. 42, no. 1, pp. 84–91.
Bely, A.E., Evolutionary loss of animal regeneration: pattern and process, Integr. Comp. Biol., 2010, vol. 50, no. 4, pp. 515–527.
Bruns, T., Schickinger, S., Wittig, R., et al., Preparation strategy and illumination of three-dimensional cell cultures in light sheet-based fluorescence microscopy, J. Biomed. Opt., 2012, vol. 17, pp. 1015181–1015185.
Clement-Sengewald, A., Schütze, K., Ashkin, A., et al., Fertilization of bovine oocytes induced solely with combined laser microbeam and optical tweezers, J. Assist. Reprod. Genet., 1996, vol. 13, pp. 259–265.
Colombelli, J., Reynaud, E.G., Rietdorf, J., et al., In vivo selective cytoskeleton dynamics quantification in interphase cells induced by pulsed ultraviolet laser nanosurgery, Traffic, 2005, vol. 6, pp. 1093–1102.
Fouchard, J., Bimbard, C., Bufi, N., et al., Three-dimensional cell body shape dictates the onset of traction force generation and growth of focal adhesions, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A., 2014, vol. 111, no. 36, pp. 13075–13080.
Genc, S.L., Ma, H., and Venugopalan, V., Low-density plasma formation in aqueous biological media using sub-nanosecond laser pulses, Appl. Phys. Lett., 2014, vol. 105, no. 6, p. 063701.
Haycock, J.W., 3D cell culture: a review of current approaches and techniques, Methods Mol. Biol., 2011, vol. 695, pp. 1–15.
Heisterkamp, A., Maxwell, I.Z., Mazur, E., et al., Pulse energy dependence of subcellular dissection by femtosecond laser pulses, Opt. Express., 2005, vol. 13, no. 10, pp. 3690–3696.
Il’ina, I.V., Ovchinnikov, A.V., Chefonov, O.V., et al., Noncontact microsurgery of cell membranes using femtosecond laser pulses for optoinjection of specified substances into cells, Quantum Electronics, 2013, vol. 43, no. 4, pp. 365–369.
Il’ina, I.V., Ovchinnikov, A.V., Sitnikov, D.S., et al., Noncontact microsurgery and delivery of substances into stem cells by means of femtosecond laser pulses, Quantum Electronics, 2014, vol. 44, no. 6, pp. 594–598.
Ilina, O., Bakker, G.-J., Vasaturo, A., et al., Two-photon laser-generated microtracks in 3D collagen lattices: principles of MMP-dependent and-independent collective cancer cell invasion, Phys. Biol., 2011, vol. 8, no. 1, p. 015010.
Ilina, I.V., Khramova, Yu.V., Filatov, M.A., et al., Application of femtosecond laser scalpel and optical tweezers for noncontact biopsy of late preimplantation embryos, High Temperature, 2015, vol. 53, no. 6, pp. 804–809.
Ilina, I.V., Khramova, Yu.V., Filatov, M.A., et al., Femtosecond laser assisted hatching: dependence of zona pellucida drilling efficiency and embryo development on laser wavelength and pulse energy, High Temperature, 2016, vol. 54, no. 1, pp. 46–51.
Jenkins, G., Molecular mechanisms of skin ageing, Mech. Ageing Dev., 2002, vol. 123, no. 7, pp. 801–810.
Khodjakov, A., La Terra, S., Chang, F., Laser microsurgery in fission yeast: role of the mitotic spindle midzone in anaphase B, Curr. Biol., 2004, vol. 14, no. 15, pp. 1330–1340.
Kolokol’tsova, T.D., Saburina, I.N., and Rybakov, A.S., Cell culture as a unique model for research in modern biology and medicine, Patogenez, 2014, vol. 11, no. 2, pp. 17–25.
König, K., Uchugonova, A., and Gorjup, E., Multiphoton fluorescence lifetime imaging of 3D-stem cell spheroids during differentiation, Microsc. Res. Tech., 2011, vol. 74, no. 1, pp. 9–17.
Kosheleva, N.V., Zurina, I.M., Saburina, I.N., et al., Effect of fetal calf serum on the formation of spheroids from eye limb stromal cells, Patogenez, 2015, vol. 13, no. 2, pp. 4–11.
Kosheleva, N.V., Ilina, I.V., Zurina, I.M., et al., Laserbased technique for controlled damage of mesenchymal cell spheroids: a first step in studying reparation in vitro, Biol. Open., 2016, vol. 5, no. 7, pp. 993–1000.
Kozhina, K.V., Saburina, I.N., Gorkun, A.A., et al., Comparative analysis of the effects of p199 on 2D and 3D culture of human dermal fibroblasts, Patogenez, 2015, no. 4, pp. 34–40.
Kozhina, K.V., Volkova, E.N., Saburina, I.N., et al., Study of the effect of peptide bioregulators on skin aging in a 3D culture model, Ross. Zh. Kozhn. Venerich. Bol., 2016, vol. 19, no. 1, pp. 58–63.
Kubatiev, A.A., Zurina, I.M., Kosheleva, N.V., et al., From 2D cell phenotypes to 3D live high-content imaging: new ways to windows, J. Cytol. Histol., 2015, vol. 6, no. 6, p. 378.
Lin, R.-Z. and Chang, H.-Y., Recent advances in threedimensional multicellular spheroid culture for biomedical research, Biotechnol. J., 2008, vol. 3, nos. 9–10, pp. 1172–1184.
Magidson, V., Loncarek, J., Hergert, P., et al., Laser microsurgery in the GFP era: a cell biologist’s perspective, Methods Cell Biol., 2007, vol. 82, pp. 239–266.
Makrantonaki, E. and Zouboulis, C.C., Molecular mechanisms of skin aging, Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci., 2007, vol. 1119, no. 1, pp. 40–50.
Pampaloni, F., Ansari, N., and Stelzer, E.H., High-resolution deep imaging of live cellular spheroids with lightsheet-based fluorescence microscopy, Cell Tissue Res., 2013, vol. 352, no. 1, pp. 161–177.
Petrikovskii, B., Skin cell renewal of as a result of peptide regulation of activity of own stem cells, Estet. Med., 2012, no. 2, pp. 283–293.
Rattan, S.I.S., Aging of skin cells in culture, in Textbook of Aging Skin, Berlin: Springer, 2010, pp. 487–492.
Rau, K.R., Quinto-Su, P.A., Hellman, A.N., et al., Pulsed laser microbeam-induced cell lysis: time-resolved imaging and analysis of hydrodynamic, Biophys. J., 2006, vol. 91, no. 1, pp. 317–329.
Repin, V.S., Saburina, I.N., Kosheleva, N.V., et al., 3D-technology of the formation and maintenance of single dormant microspheres from 2000 human somatic cells and their reactivation in vitro, Bull. Exp. Biol. Med., 2014, vol. 158, no. 1, pp. 137–144.
Saburina, I.N., Gorkun, A.A., Zurina, I.M., et al., The study of the angiogenic potential of human multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells, Patogenez, 2013, vol. 11, no. 1, pp. 65–68.
Sacconi, L., Tolic-Norrelykke, I.M., Antolini, R., et al., Combined intracellular three-dimensional imaging and selective nanosurgery by a nonlinear microscope, J. Biomed. Opt., 2005, vol. 10, no. 1, pp. 014002–014025.
Salmenperä, P., Kankuri, E., Bizik, J., et al., Formation and activation of fibroblast spheroids depend on fibronectin-integrin interaction, Exp. Cell Res., 2008, vol. 314, no. 19, pp. 3444–3452.
Shekhvatova, A.S., Durnova, A.O., Kvetnoi, I.M., et al., The expression of signaling molecules under the influence of P199 peptide in Meso-Wharton preparation, In”ekts. Metody Kosmetol., 2013, no. 4, pp. 38–46.
Shen, N., Datta, D., Schaffer, C.B., et al., Ablation of cytoskeletal filaments and mitochondria in live cells using a femtosecond laser nanoscissor, Mech. Chem. Biosyst., 2005, vol. 2, no. 1, pp. 17–25.
Stevenson, D., Agate, B., Tsampoula, X., et al., Femtosecond optical transfection of cells: viability and efficiency, Opt. Express., 2006, vol. 14, no. 16, pp. 7125–7133.
Uchugonova, A., Riemann, I., Stracke, F., et al., The influence of NIR femtosecond laser radiation on the viability of 3D stem cell clusters and tumor spheroids, in Biomedical Optics (BiOS), International Society for Optics and Photonics, 2007, p. 64421Z–64421Z–5.
Uchugonova, A., König, K., Bueckle, R., et al., Targeted transfection of stem cells with sub-20 femtosecond laser pulses, Opt. Express., 2008, vol. 16, no. 13, pp. 9357–9364.
Yegorov, E.E., Moldaver, M.V., Vishnyakova, Kh.S., et al., Enhanced control of proliferation in telomerized cells, Russ. J. Dev. Biol., 2007, vol. 38, no. 2, pp. 76–89.
Yutskovskaya, Ya.A. and Danilova, A.A., Therapy of skin with signs of chronological aging with the P199 Meso-Wharton drug: a clinical example, Plastich. Khirurg. Kosmetol., 2014, no. 3, pp. 337–496.
Zhang, L. and Falla, T.J., Cosmeceuticals and peptides, Clin. Dermatol., 2009, vol. 27, no. 5, pp. 485–494.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © N.V. Kosheleva, I.V. Ilina, K.V. Kozhina, I.M. Zurina, A.E. Roskova, A.A. Gorkun, A.V. Ovchinnikov, M.B. Agranat, S.G. Morozov, I.N. Saburina, 2017, published in Ontogenez, 2017, Vol. 48, No. 1, pp. 63–72.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kosheleva, N.V., Ilina, I.V., Kozhina, K.V. et al. Cellular model based on laser microsurgery of cell spheroids to study the repair process. Russ J Dev Biol 48, 56–64 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1062360417010076
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1062360417010076