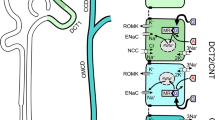
Abstract
The review focuses on the key sodium transporters involved in maintaining water–salt balance in the kidney. The topography of sodium transporters is discussed. Specifics of the hormone-dependent regulation, including phosphorylation, traffic, and expression, are considered for particular transporters. Special attention is paid to direct intracellular regulators of the transporter function. The role that dopamine plays as a natriuretic factor in modulating the function of various transporters is described.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Palmer, L.G. and Schnermann, J., Integrated control of Na transport along the Nephron, Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol., 2015, vol. 10, no. 4, p. 676.
Staruschenko, A., Regulation of transport in the connecting tubule and cortical collecting duct, Compr. Physiol., 2012, vol. 2, no. 2, p. 1541.
Taub, M., Springate, J.E., and Cutuli, F., Targeting of renal proximal tubule Na+/K+-ATPase by salt-inducible kinase, Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 2010, vol. 393, no. 3, p. 339.
Efendiev, R., Krmar, R.T., Ogimoto, G., et al., Hypertension-linked mutation in the adducin alpha-subunit leads to higher AP2-μ2 phosphorylation and impaired Na+/K+-ATPase trafficking in response to GPCR signals and intracellular sodium, Circ. Res., 2004, vol. 95, no. 11, p. 1100.
Procino, G., Romano, F., Torielli, L., et al., Altered expression of renal aquaporins and α-adducin polymorphisms may contribute to the establishment of saltsensitive hypertension, Am. J. Hypertens., 2011, vol. 24, no. 7, p. 822.
Mondini, A., Sassone, F., Civello, D.A., et al., Hypertension- linked mutation of α-adducin increases CFTR surface expression and activity in HEK and cultured rat distal convoluted tubule cells, PLoS One, 2012, vol. 7, no. 12, p. e52014.
Periyasamy, S.M., Liu, J., Tanta, F., et al., Salt loading induces redistribution of the plasmalemmal Na+/K+- ATPase in proximal tubule cells, Kidney Int., 2005, vol. 67, no. 5, p. 1868.
Lang, F. and Cohen, P., Regulation and physiological roles of serum- and glucocorticoid-induced protein kinase isoforms, Sci. Signaling, 2001, vol. 108, p. 1.
Lou, Y., Zhang, F., Luo, Y., et al., Serum and glucocorticoid regulated kinase 1 in sodium homeostasis, Int. J. Mol. Sci., 2016, vol. 17, no. 8, p. 1307.
Salyer, S.A., Parks, J., Barati, M.T., et al., Aldosterone regulates Na+/K+-ATPase activity in human renal proximal tubule cells through mineralocorticoid receptor, Biochim. Biophys. Acta, Mol. Cell Res., 2013, vol. 1833, no. 10, p. 2143.
Fuster, D.G., Bobulescu, I.A., Zhang, J., et al., Characterization of the regulation of renal Na+/H+ exchanger NHE3 by insulin, Am. J. Physiol.: Renal Physiol., 2007, vol. 292, no. 2, p. F577.
Pao, A.C., Bhargava, A., Di Sole, F., et al., Expression and role of serum and glucocorticoid-regulated kinase 2 in the regulation of Na+/H+ exchanger 3 in the mammalian kidney, Am. J. Physiol.: Renal Physiol., 2010, vol. 299, no. 6, p. F1496.
Hurley, J.H. and Stenmark, H., Molecular mechanisms of ubiquitin-dependent membrane, Annu. Rev. Biophys., 2012, vol. 40, p. 119.
Bazúa-Valenti, S., Castañeda-Bueno, M., and Gamba, G., Physiological role of SLC12 family members in the kidney, Am. J. Physiol.: Renal Physiol., 2016, vol. 311, no. 1, p. 131.
Zhuo, J.L. and Li, X.C., Proximal nephron, Compr. Physiol., 2013, vol. 3, no. 3, p. 1079.
Golembiewska, E. and Ciechanowski, K., Renal tubular acidosis–underrated problem?, Acta Biochim. Pol., 2012, vol. 59, no. 2, p. 213.
Wagner, C.A., Mohebbi, N., Capasso, G., and Geibel, J.P., The anion exchanger pendrin (SLC26A4) and renal acid-base homeostasis, Cell. Physiol. Biochem., 2011, vol. 28, no. 3, p. 497.
Aperia, A., To serve and protect: Classic and novel roles for Na+, K+-adenosine triphosphatase, J. Am. Soc. Nephrol., 2012, vol. 23, no. 8, p. 1283.
Aperia, A., Ibarra, F., Svensson, L.B., et al., Calcineurin mediates alpha-adrenergic stimulation of Na+/K+-ATPase activity in renal tubule cells, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A., 1992, vol. 89, no. 16, p. 7394.
Aperia, A., Holtbäck, U., Syrén, M.L., et al., Activation/ deactivation pathway of renal Na+/K+-ATPase: A final common pathway for regulation of natriuresis, Res. Commun., 1994, vol. 8, no. 6, p. 436.
Yu, M., Lopez, B., Dos Santos, E.A., et al., Effects of 20-HETE on Na+ transport and Na+/K+-ATPase in the thick ascending loop of Henle, Am. J. Physiol.: Regul., Integr. Comp. Physiol., 2007, vol. 292, no. 6, p. 2400.
Varela, M., Herrera, M., and Garvin, J.L., Inhibition of Na+/K+-ATPase in thick ascending limbs by NO depends on O2– and is diminished by a high-salt diet, Am. J. Physiol.: Renal Physiol., 2004, vol. 287, no. 2, p. 224.
Bełtowski, J., Wjcicka, G., Górny, D., and Marciniak, A., Human leptin administered intraperitoneally stimulates natriuresis and decreases renal medullary Na+/K+- ATPase activity in the rat–impaired effect in dietaryinduced obesity, Med. Sci. Monit. Basic Res., 2002, vol. 8, no. 6, p. 221.
Sampaio, L.S., Taveira, Da., Silva, R., Lima, D., et al., The endocannabinoid system in renal cells: Regulation of Na(+) transport by CB1 receptors through distinct cell signalling pathways, Br. J. Pharmacol., 2015, vol. 72, no. 19, p. 4615.
Ontomo, Y., Ono, S., Zettergren, E., and Sahlgren, B., Neuropeptide Y regulates rat renal tubular Na+/K+- ATPase through several signalling pathways, Acta Physiol. Scand., 1996, vol. 158, no. 1, p. 97.
Morla, L., Crambert, G., Mordasini, D., et al., Proteinase- activated receptor 2 stimulates Na+/K+- ATPase and sodium reabsorption in native kidney epithelium, J. Biol. Chem., 2008, vol. 283, no. 42, p. 28020.
Obradovic, M., Bjelogrlic, P., Rizzo, M., et al., Effects of obesity and estradiol on Na+/K+-ATPase and their relevance to cardiovascular diseases, J. Endocrinol., 2013, vol. 218, no. 3, p. R13.
Ciano, L.A.Di., Azurmendi, P.J., Toledo, J.E., et al., Ovariectomy causes overexpression of renal Na+/K+- ATPase and sodium-sensitive hypertension in adult Wistar rats, Clin. Exp. Hypertens., 2013, vol. 35, no. 7, p. 475.
Galuska, D., Pirkmajer, S., Barrès, R., et al., C-peptide increases Na+/K+-ATPase expression via PKC- and MAP kinase-dependent activation of transcription factor ZEB in human renal tubular cells, PLoS One, 2011, vol. 6, no. 12, p. e28294.
Summa, V., Camargo, S.M., Bauch, C., et al., Isoform specificity of human Na+/K+-ATPase localization and aldosterone regulation in mouse kidney cells, J. Physiol., 2003, vol. 555, no. 2, p. 355.
Khundmiri, S.J., Ameen, M., Delamere, N.A., and Lederer, E.D., PTH-mediated regulation of Na+/K+- ATPase requires Src kinase-dependent ERK phosphorylation, Am. J. Physiol.: Renal Physiol., 2008, vol. 40202, p. 426.
Khundmiri, S.J., Bertorello, A.M., Delamere, N.A., and Lederer, E.D., Clathrin-mediated endocytosis of Na+/K+-ATPase in response to parathyroid hormone requires ERK-dependent phosphorylation of Ser-11 within the α1-Subunit, J. Biol. Chem., 2004, vol. 279, no. 17, p. 17418.
Cui, J., Li, X., Duan, Z., et al., Analysis of Kif5b expression during mouse kidney development, PLoS One, 2015, vol. 10, no. 4, p. e0126002.
Ramseyer, V.D., Ortiz, P.A., Carretero, O.A., and Garvin, J.L., Angiotensin II-mediated hypertension impairs nitric oxide-induced NKCC2 inhibition in thick ascending limbs, Am. J. Physiol.: Renal Physiol., 2016, vol. 310, no. 8, p. F748.
Féraille, E. and Doucet, A., Sodium-potassium-adenosinetriphosphatase-dependent sodium transport in the kidney?: Hormonal control, Physiol. Rev., 2001, vol. 81, no. 1, p. 345.
Caceres, P.S., Mendez, M., Haque, M.Z., and Ortiz, P.A., Vesicle-associated membrane protein 3 (VAMP3) mediates constitutive trafficking of the renal co-transporter NKCC2 in thick ascending limbs: Role in renal function and blood pressure, J. Biol. Chem., 2016, vol. 3, no. 3, p. 22063.
Mount, D.B., Renal physiology thick ascending limb of the loop of Henle, Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol., 2014, vol. 9, no. 11, p. 1974.
Gerbino, A., Schena, G., Milano, S., et al., Spilanthol from Acmella Oleracea lowers the intracellular levels of cAMP impairing NKCC2 phosphorylation and water channel AQP2 membrane expression in mouse kidney, PLoS One, 2016, vol. 11, no. 5, p. e0156021.
Zhang, J., Rudemiller, N.P., Patel, M.B., et al., Interleukin- 1 receptor activation potentiates salt reabsorption in angiotensin II-induced hypertension via the NKCC2 Co-transporter in the nephron, Cell Metab., 2016, vol. 23, no. 2, p. 360.
Markadieu, N. and Delpire, E., Physiology and pathophysiology of SLC12A1/2 transporters, Pfluegers Arch., 2014, vol. 466, no. 1, p. 91.
Knepper, M., Kwon, T.-H., and Nielsen, S., Molecular physiology of water balance, N. Engl. J. Med., 2015, vol. 372, no. 14, p. 1349.
Ye, T., Liu, Z.Q., Sun, C.F., et al., Altered expression of renal bumetanide-sensitive sodium-potassium-2 chloride cotransporter and Cl- channel-K2 gene in angiotensin II-infused hypertensive rats, Chin. Med. J., 2005, vol. 118, no. 23, p. 1945.
Mutig, K., Saritas, T., Uchida, S., et al., Short-term stimulation of the thiazide-sensitive Na+-Cl- cotransporter by vasopressin involves phosphorylation and membrane translocation, Am. J. Physiol.: Renal Physiol., 2010, vol. 298, no. 3, p. F502.
Hoover, R.S., Tomilin, V., Hanson, L., et al., PTH modulation of NCC activity regulates TRPV5 Ca2+- reabsorption, Am. J. Physiol.: Renal Physiol., 2016, vol. 310, no. 2, p. F144.
Lin, C.-H., Hu, H.-J., and Hwang, P.-P., Cortisol regulates sodium homeostasis by stimulating the transcription of sodium-chloride transporter (NCC) in zebrafish (Danio rerio), Mol. Cell. Endocrinol., 2016, vol. 422, p. 93.
Gailly, P., Szutkowska, M., Olinger, E., et al., P2Y2 receptor activation inhibits the expression of the sodium-chloride cotransporter NCC in distal convoluted tubule cells, Pfluegers Arch., 2014, vol. 466, no. 11, p. 2035.
Roos, K.P., Bugaj, V., Mironova, E., et al., Adenylyl cyclase VI mediates vasopressin-stimulated ENaC activity, J. Am. Soc. Nephrol., 2013, vol. 24, no. 2, p. 218.
Hills, C., Bland, R., Bennett, J., et al., High glucose up-regulates ENaC and SGK1 expression in HCDcells, Cell. Physiol. Biochem., 2006, vol. 18, no. 6, p. 337.
Greenlee, M.M., Mitzelfelt, J.D., Duke, B.J., et al., Prolactin stimulates sodium and chloride ion channels in A6 renal epithelial cells, Am. J. Physiol.: Renal Physiol., 2015, vol. 308, no. 7, p. F697.
Lu, C., Pribanic, S., Debonneville, A., et al., The PY motif of ENaC, mutated in liddle syndrome, regulates channel internalization, sorting and mobilization from subapical pool, Traffic, 2007, vol. 8, no. 9, p. 1246.
Wen, D., Yuan, Y., Warner, P.C., et al., Increased epithelial sodium channel activity contributes to hypertension caused by Na+-HCO3-cotransporter electrogenic 2 deficiency, Hypertension, 2015, vol. 66, no. 1, p. 68.
McDonough, A., Mechanisms of proximal tubule sodium transport regulation that link extracellular fluid volume and blood pressure, Am. J. Physiol.: Regul., Integr. Comp. Physiol., 2010, vol. 298, no. 4, p. R851.
de Morais, C.P., Polidoro, J.Z., Ralph, D.L., et al., Proximal tubule NHE-3 activity is inhibited by betaarrestin-biased angiotensin II type 1 receptor signaling, Am. J. Physiol.: Cell Physiol., 2015, vol. 309, no. 33, p. 541.
Lee, Y.J. and Han, H.J., Regulatory mechanisms of Na+/glucose cotransporters in renal proximal tubule cells, Kidney Int., 2007, vol. 72, p. 27.
Amemiya, M., Kusano, E., Muto, S., et al., Glucagon acutely inhibits but chronically activates Na(+)/H(+) antiporter 3 activity in OKP cells, Exp. Nephrol., 2002, vol. 10, no. 1, p. 26.
Lee, J., Ha, J.H., Kim, S., et al., Caffeine decreases the expression of Na+/K+-ATPase and the type 3 Na +/H+-exchanger in rat kidney, Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol., 2002, vol. 29, p. 559.
Fenton, R.A., Poulsen, S.B., de la Mora, Chavez S., et al., Caffeine-induced diuresis and natriuresis is independent of renal tubular, Am. J. Physiol.: Ren. Physiol., 2015, vol. 308, no. 12, p. F1409.
Kurtz, I. and Zhu, Q., Proximal renal tubular acidosis mediated by mutations in NBCe1-A: Unraveling the transporter’s structure-functional properties, Front. Physiol., 2013, vol. 4, p. 350.
Ferlazzo, A., Carvalho, E.S., Gregorio, S.F., et al., Prolactin regulates luminal bicarbonate secretion in the intestine of the sea bream (Sparus aurata L.), J. Exp. Biol., 2012, vol. 215, no. 21, p. 3836.
Sonalker, P.A., Tofovic, S.P., Bastacky, S.I., and Jackson, E.K., Chronic noradrenaline increases renal expression of NHE-3, NBC-1, BSC-1 and aquaporin-2, Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol., 2008, vol. 35, p. 594.
Ali, R., Amlal, H., Burnham, C.E., and Soleimani, M., Glucocorticoids enhance the expression of the basolateral Na+/HCO3-cotransporter in renal proximal tubules, Kidney Int., 2000, vol. 57, no. 3, p. 1063.
Vrhovac, I., Balen, Eror D., Klessen, D., et al., Localizations of Na+-D-glucose cotransporters SGLT1 and SGLT2 in human kidney and of SGLT1 in human small intestine, liver, lung and heart, Eur. J. Physiol., 2014, vol. 467, no. 9, p. 1881.
Ghezzi, C. and Wright, E.M., Regulation of the human Na+-dependent glucose cotransporter hSGLT2, Am. J. Physiol.: Cell Physiol., 2012, vol. 303, no. 3, p. C348.
Andrianesis, V. and Doupis, J., The role of kidney in glucose inhibitors, a new approach in diabetes treatment, Expert Rev. Clin. Pharmacol., 2013, vol. 6, no. 5, p. 519.
Su, M., Mu, X., Gui, L., et al., Dopamine regulates renal osmoregulation during hyposaline stress via DRD1 in the spotted scat (Scatophagus argus), Sci. Rep., 2016, vol. 6, p. 37535.
Ibarra, F., Crambert, S., Eklof, A.C., et al., Prolactin, a natriuretic hormone, interacting with the renal dopamine system, Kidney Int., 2005, vol. 68, no. 4, p. 1700.
Crambert, S., Sjöberg, A., Eklöf, A.C., et al., Prolactin and dopamine 1-like receptor interaction in renal proximal tubular cells, Am. J. Physiol.: Renal Physiol., 2010, vol. 299, no. 1, p. F49.
Zhang, L.-N., Li, J.X., Hao, L., et al., Crosstalk between dopamine receptors and the Na+/K+-ATPase (Review), Mol. Med. Rep., 2013, vol. 8, no. 5, p. 1291.
Jiang, X., Chen, W., Liu, X., et al., The synergistic roles of cholecystokinin B and dopamine D5 receptors on the regulation of renal sodium excretion, PLoS One, 2016, vol. 11, no. 1, p. e0146641.
Zhang, M.-Z. and Harris, R.C., Current antihypertensive mechanisms of intra-renal dopamine, Curr. Opin. Nephrol. Hypertens., 2015, vol. 24, no. 2, p. 117.
Atkinson, K.F., Kathem, S.H., Jin, X., et al., Dopaminergic signaling within the primary cilia in the renovascular system, Front. Physiol., 2015, vol. 6, p. 103.
Brismar, H., Agren, M., and Holtback, U., β-adrenoceptor agonist sensitizes the dopamine-1 receptor in renal tubular cells, Acta Physiol. Scand., 2002, vol. 175, no. 4, p. 333.
Smirnova, O.V., Osmoregulatory function of prolactin in fish and its projection on mammals, Usp. Fiziol. Nauk, 2011, vol. 42, no. 4, p. 59.
Faron-Górecka, A., Kuśmider, M., Solich, J., et al., Involvement of prolactin and somatostatin in depression and the mechanism of action of antidepressant drugs, Pharmacol. Rep., 2013, vol. 65, no. 6, p. 1640.
Ben-Jonathan, N., LaPensee, C.R., and LaPensee, E.W., What can we learn from rodents about prolactin in humans?, Endocr. Rev., 2008, vol. 29, no. 1, p. 1.
Chen, Y., Asico, L.D., Zheng, S., et al., Gastrin and D1 dopamine receptor interact to induce natriuresis and diuresis, Hypertension, 2013, vol. 62, no. 5, p. 927.
Salomone, L.J., Howell, N.L., McGrath, H.E., et al., Intrarenal dopamine D1-like receptor stimulation induces natriuresis via an angiotensin type-2 receptor mechanism, Hypertension, 2007, vol. 49, no. 1, p. 155.
Bacic, D., Capuano, P., Baum, M., et al., Activation of dopamine D1-like receptors induces acute internalization of the renal Na+/phosphate cotransporter NaPi-IIa in mouse kidney and OK cells, Am. J. Physiol.: Renal Physiol., 2005, vol. 288, no. 4, p. F740.
Gildea, J.J., Shah, I.T., Van Sciver, R.E., et al., The cooperative roles of the dopamine receptors, D1R and D5R, on the regulation of renal sodium transport, Kidney Int., 2014, vol. 86, no. 1, p. 118.
Wang, X., Luo, Y., Escano, C.S., et al., Upregulation of renal sodium transporters in D5 dopamine receptordeficient mice, Hypertension, 2010, vol. 55, no. 6, p. 1431.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © P.A. Abramicheva, O.V. Smirnova, 2017, published in Fiziologiya Cheloveka, 2017, Vol. 43, No. 4, pp. 134–149.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abramicheva, P.A., Smirnova, O.V. Role of hormones in regulating sodium transporters in the kidney: Modulation of phosphorylation, traffic, and expression. Hum Physiol 43, 474–487 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0362119717040028
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0362119717040028