Abstract
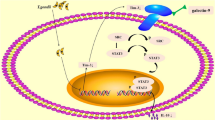
Soluble human leukocyte antigen G (sHLA-G) plays a key role in pregnancy through interaction with decidual natural killer (dNK) cell inhibitory receptors at the maternal-fetal interface. To demonstrate the possible role of sHLA-G during the pregnancy with Toxoplasma gondii infection, we compared the concentration of a murine functional homolog of sHLA-G, Qa-2, in T. gondii infected and non-infected pregnant C57BL/6 mice, and that of sHLA-G in BeWo culture supernatant. In addition, the levels of KIR2DL4 expressed on human dNK cells and NKG2A in pregnant mice were evaluated. We showed that T. gondii infection result in significant increase in the level of Qa-2 and NKG2A in pregnant mice. sHLA-G and KIR2DL4 in human samples were also significantly upregulated under the condition of T. gondii infection. The further treatment with sHLA-G antibody could reduce the expression level of KIR2DL4 which was upregulated by T. gondii infection. In summary, sHLA-G could upregulate the expression level of KIR2DL4 which lead to excessive immunological tolerance, and further contributed to T. gondii immunity escaping and affecting fetus via vertical transmission which may lead to adverse outcomes.






Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Mahalakshmi B., Therese K.L., Devipriya U., Pushpa-latha V., Margarita S., Madhavan H.N. 2010. Infectious aetiology of congenital cataract based on TORCHES screening in a tertiary eye hospital in Chennai, Tamil Nadu, India. Indian J. Med. Res. 131, 559–564.
Bessières M.H., Berrebi A., Rolland M., Bloom M.C., Roques C., Cassaing S., Courjault C., Séguéla J.P. 2001. Neonatal screening for congenital toxoplasmosis in a cohort of 165 women infected during pregnancy and influence of in utero treatment on the results of neonatal tests. Eur. J. Obstet. Gynecol. Reprod. Biol. 94, 37–45.
Abbasi M., Kowalewska-Grochowska K., Bahar M.A., Kilani R.T., Winkler-Lowen B., Guilbert L.J. 2003. Infection of placental trophoblasts by Toxoplasma gondii. J. Infect. Dis. 188, 608–616.
Tarrade A., Lai Kuen R., Malassine A. 2001. Characterization of human villous and extravillous trophoblasts isolated from first trimester placenta. Lab. Invest. 8l, 1199–1211.
Sipak-Szmigiel O., Ronin-Walknowska E., Cybulski C., Plonka T., Lubiński J. 2007. Antigens HLA-G, sHLA-G and sHLA-class I in reproductive failure. Folia Histochem. Cytobiol. 45, S137–141.
Pfeiffer K.A., Rebmann V., Pässler M., van der Ven K., van der Ven H., Krebs D., Grosse-Wilde H. 2000. Soluble HLA levels in early pregnancy after in vitro fertilization. Hum. Immunol. 61, 559–564.
Rebmann V., Switala M., Eue I., Grosse-Wilde H. 2010. Soluble HLA-G is an independent factor for the prediction of pregnancy outcome after ART: A German multi-centre study. Hum. Reprod. 25, 1691–1698.
Lee M., Choi B., Kwon H.J., Shim J.A., Park K.S., Lee E.S., Sohn S. 2010. The role of Qa-2, the functional homolog of HLA-G, in a Behcet’s disease-like mouse model induced by the herpes virus simplex. J. Inflamm. (Lond.). 7, 31–42.
Lindaman A., Dowden A., Zavazava N. 2006. Soluble HLA-G molecules induce apotosis in natural killer cells. Am. J. Peprod. Immunol. 56, 68–76.
Park G.M., Lee S., Park B., Kim E., Shin J., Cho K., Ahn K. 2004. Soluble HLA-G generated by proteolytic shedding inhibits NK-mediated cell lysis. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 3, 606–611.
Riley J.K., Yokoyama W.M. 2008. NK cell tolerance and the maternal–fetal interface. Am. J. Reprod. Immunol. 59, 371–387.
Morandi F., Ferretti E., Castriconi R., Dondero A., Petretto A., Bottino C., Pistoia V. 2011. Soluble HLA-G dampens CD94/NKG2A expression and function and differentially modulates chemotaxis and cytokine and chemokine secretion in CD56bright and CD56dim NK cells. Blood. 118, 5840–5850.
Zhao M., Zhang R., Xu X., Liu Y., Zhang H., Zhai X., Hu X. 2013. IL-10 reduces levels of apoptosis in Toxoplasma gondii-infected trophoblasts. PLoS One. 8, e56455.
Barbosa B.F., Silva D.A., Costa I.N., Mineo J.R., Ferro E.A. 2008. BeWo trophoblast cell susceptibility to Toxoplasma gondii is increased by interferon-gamma, interleukin-10 and transforming growth factor-beta1. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 151, 536–545.
Cowen D., Wolf A. 1950. Experimental congenital toxoplasmosis: 2. Transmission of toxoplasmosis to the placenta and fetus following vaginal infection in the pregnant mouse. J. Exp. Med. 92, 403–416.
Weng P.J., Fu Y.M., Ding S.X., Xu D.P., Lin A., Yan W.H. 2011. Elevation of plasma soluble human leukocyte antigen-G in patients with chronic hepatitis C virus infection. Hum. Immunol. 72, 406–411.
Celsi F., Catamo E., Kleiner G., Tricarico P.M., Vuch J., Crovella S. 2013. HLA-G/C, miRNAs, and their role in HIV infection and replication. Biomed. Res. Int. 2013, 693646.
Thibodeau V., Lajoie J., Labbé A.-C., Zannou M.D., Fowke K.R., Alary M., Poudrier J., Roger M. 2011. High level of soluble HLA-G in the female genital tract of Beninese commercial sex workers is associated with HIV-1 infection. PLoS One. 6, e25185.
d’Almeida T.C., Sadissou I., Milet J., Cottrell G., Mondière A., Avokpaho E., Gineau L., Sabbagh A., Massougbodji A., Moutairou K., Donadi E.A., Favier B., Carosella E., Moreau P., Rouas-Freiss N., et al. 2017. Soluble human leukocyte antigen-G during pregnancy and infancy in Benin: Mother/child resemblance and association with the risk of malaria infection and low birth weight. PLoS One. 12, e0171117.
Sadissou I., d’Almeida T., Cottrell G., Luty A., Krawice-Radanne I., Massougbodji A., Moreau P., Moutairou K., Malar J. 2014. High plasma levels of HLA-G are associated with low birth weight and with an increased risk of malaria in infancy. Malar. J. 13, 312–319.
Robert-Gangneux F., Gangneux J.P., Vu N., Jaillard S., Guiguen C., Amiot L. 2011. High level of soluble HLA-G in amniotic fluid is correlated with congenital transmission of Toxoplasma gondii. Clin. Immunol. 138, 129–134.
Kusanovic J.P., Romero R., Jodicke C., Mazaki-Tovi S., Vaisbuch E., Erez O., Mittal P., Gotsch F., Chaiworapongsa T., Edwin S.S., Pacora P., Hassan S.S. 2009. Amniotic fluid soluble human leukocyte antigen-G in term and preterm parturition, and intra-amniotic infection/inflammation. J. Matern. Fetal. Neonatal. Med. 22, 1151–1166.
Salcedo M., Bousso P., Ljunggren H.G., Kourilsky P., Abastado J.P. 1998. The Qa-1b molecule binds to a large subpopulation of murine NK cells. Eur. J. Immunol. 28, 4356–4361.
Xu X., Fu Q., Zhang Q., Zhao M., Gao Z., Liu X., Liu Y., Hu X. 2013. Changes of human decidual natural killer cells cocultured with YFP-Toxoplasma gondii: Implications for abnormal pregnancy. Fertil. Steril. 99, 427–432.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The text was submitted by the author(s) in English.
These authors contributed equally to the work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, H.F., Jiang, Y.Z., Ren, L.Q. et al. The Role of Soluble HLA-G in the Vertical Transmission of Toxoplasma gondii. Mol Biol 53, 267–273 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1134/S002689331902016X
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S002689331902016X