Abstract
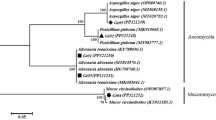
Based on special colony morphology, 340 endophytic fungi were isolated from the stems, leaves, and roots of Phlegmariurus phlegmaria. Among the 340 strains, eight, representative species (MY298, MJ216, MY237, MJ422, MY311, MY183, MJ484, and MY252) could produce HupA analyzed by UPLC-MS/MS (Ultra performance liquid chromatography), which compared with standard HupA under the same chromatographic conditions. And through the standard curve generated, among these HupA-producing fungi, the MY311 had highest content which was 40.53 µg/L. The extract of eight strains was examined by AChE inhibition activity assay in vitro and ELISA (enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay). These eight strains were found to have positive results for HupA production and MY311 extract obviously exhibited the highest inhibition activity. Furthermore, the genera of the eight fungi were identified based on the internal transcribed spacer sequence analysis. All eight distinctive genotypes were grouped into four fungal genera and six fungal species, however, MY311 and MY183 were Ceriporia lacerata and Hypoxylon investiens, which had never been reported as HupA-producing endophytic fungi.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bai, D.L., Tang, X.C., and He, X.C., Huperzine A, a potential therapeutic agent for treatment of Alzheimers disease, Curr. Med. Chem., 2000, vol. 7, no. 3, pp. 355–374.
Chowdhary, K., Kaushik, N., Coloma, A.G., and Raimundo, C.M., Endophytic fungi and their metabolites isolated from Indian medicinal plant, Phytochem. Rev., 2012, vol. 11, no. 4, pp. 467–485.
Dong, L.H., Fan, S.W., Ling, Q.Z., Huang, B.B., and Wei, Z.J., Indentification of huperzine A–producing endophytic fungi isolated from Huperzia serrata, World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol., 2014, vol. 30, no. 3, pp. 1011–1017.
Freitas–Silva, O., De Lourdes Mendes De Souza, M., and Venancio, A., Tracing fungi secondary metabolites in Brazil nuts using LC–MS/MS, Drug. Metab. Lett., 2011, vol. 5, no. 3, pp. 150–155.
Gu, Y.H. and Wu, Q.Q., HPLC method for the determination of huperzine A in Huperzia serrata, Zhongguo Yaolixue Tong bao, 2005, vol. 21, no. 8, pp. 1017–1018.
Gutierrez, J., Mendoza, J., Fernandez, F., Linares–Palomino, J., Soto, M.J., and Maroto, M.C., ELISA test to detect Chlamydophila pneumoniae IgG, J. Basic Microbiol., 2002, vol. 42, no. 1, pp. 13–18.
Li, J., Zhao, J.L., Xu, L.J., Zhou, L.G., Li, X.L. and Wang, J.G., Endophytic fungi from rhizomes of Paris polyphylla var. yunnanensis, World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol., 2008, vol. 24, no. 5, pp. 733–737.
Li, W.K., Zhou, J.Y., Lin, Z.W., and Hu, Z.B., Study on fermentation condition for production of huperzine A from endophytic fungus 2F09P03B of Huperzia serrata, Zhong guo yi yao Sheng wu ji shu, 2007, vol. 4, no. 4, pp. 254–259.
Ma, X., Tan, C., Zhu, D., Gang, D.R., and Xiao, P., Huperzine A from Huperzia species—an ethnopharmacolgical review, J. Ethnopharmacol., 2007, vol. 113, no. 1, pp. 15–34.
Ma, X.Q. and Gang, D.R., The lycopodium alkaloids, Nat. Prod. Rep., 2004, vol. 21, no. 6, pp. 752–772.
Ma, X.Q., Jiang, Sh.., and Zhu, D.Y., Alkaloid patterns in Huperzia and some related genera of Lycopodiaceae sensu lato occurring in China and their contribution to classification, Biochem. Syst. Ecol., 1998, vol. 26, no. 7, pp. 723–728.
Ma, X.Q., Tan, C.H., Zhu, D.Y., and Gang, D.R., Is there a better source of huperzine A than Huperzia serrata? Huperzine A content of Huperziaceae species in China, J. Agric. Food Chem., 2005, vol. 53, no. 5, pp. 1393–1398.
Ma, X.Q., Tan, C.H., Zhu, D.Y., and Gang, D.R., A survey of potential huperzine A natural resources in China: the Huperziaceae, J. Ethnopharmacol., 2006, vol. 104, nos. 1–2, pp. 54–67.
Perrig, D., Boiero, M.L., Masciarelli, O.A., Penna, C., Ruiz, O.A., Cassan, F.D., and Luna, M.V., Plant-growthpromoting compounds produced by two agronomically important strains of Azospirillum brasilense, and implications for inoculant formulation, Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol., 2007, vol. 75, no. 5, pp. 1143–1150.
Sloane, P.D., Zimmerman, S., Suchindran, C., Reed, P., Wang, L., Boustani, M., and Sudha, S., The public health impact of Alzheimer’s disease, 2000–2050: potential implication of treatment advances, Annu. Rev. Public Health, 2002, vol. 23, no. 1, pp. 213–231.
Strobel, G. and Daisy, B., Bioprospecting for microbial endophytes and their natural products, Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev., 2003, vol. 67, no. 4, pp. 491–502.
Strobel, G., Yang, X., Sears, J., Kramer, R., Sidhu, R.S., and Hess, W.M., Taxol from Pestalotiopsis microspora, an endophytic fungus of Taxus wallachiana, Microbiology (UK), 1996, vol. 142, no. 2, pp. 435–440.
Szypuła, W., Pietrosiuk, A., Suchocki, P., Olszowska, O., Furmanowa, M., and Kazimierska, O., Somatic embryogenesis and in vitro culture of Huperzia selago shoots as a potential source of huperzine A., Plant Sci. (Amsterdam), 2005, vol. 168, no. 6, pp. 1443–1452.
Tang, X.C., Huperzine A (shuangyiping): a promising drug for Alzheimer’s disease, Zhongguo Yao Li Xue Bao, 1996, vol. 17, no. 6, pp. 481–484.
Wang, R. and Yan, H., Progress in studies of huperzine A, a natural cholinesterase inhibitor from Chinese herbal medicine1, Acta Pharmacol. Sin., 2006, vol. 27, no. 1, pp. 1–26.
Wang, Y., Zeng, Q.G., Zhang, Z.B., Yan, R.M., Wang, L.Y., and Zhu, D., Isolation and characterization of endophytic huperzine A–producing fungi from Huperzia serrata, J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol., 2011, vol. 38, no. 9, pp. 1267–1278.
White, T.J., Bruns, T., Lee, S., and Taylor, J., Amplification and direct sequencing of fungal ribosomal RNA genes for phylogenetics, PCR Protoc.: Guide Methods Appl., 1990, vol. 18, no. pp. 315–322.
Wimo, A., Winblad, B., and Jönsson, L., An estimate of the total worldwide societal costs of dementia in 2005, Alzheimer’s Dementia, 2007, vol. 3, no. 2, pp. 81–91.
Yu, Y.Y., Teng, H.Y., Zhang, Y.H., Lin, S., and Zhou, Y.H., Preparation and establishment of ELISA method of huperzine A polyclonal antibody, Lishizhen Medicine and. Materia Medica Res., 2012, vol. 23, no. 10, pp. 2440–2442.
Zhang, D., Yang, Y., Castlebury, L.A., and Cerniglia, C.E., A method for the large scale isolation of high transformation efficiency fungal genomic DNA, FEMS Microbiol. Lett., 1996, vol. 145, no. 2, pp. 261–265.
Zhang, H.Y., Zheng, C.Y., Yan, H., Wang, Z.F., Tang, L.L., Gao, X., and Tang, X.C., Potential therapeutic targets of huperzine A for Alzheimer’s disease and vascular dementia, Chem.–Biol. Interact., 2008, vol. 175, no. 1, pp. 396–402.
Zhang, Z.B., Zeng, Q.G., Yan, R.M., Wang, Y., Zou, Z.R., and Zhu, D., Endophytic fungus Cladosporium cladosporioides LF70 from Huperzia serrata produces huperzine A, World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol., 2011, vol. 27, no. 3, pp. 479–486.
Zhao, Q. and Tang, X.C., Effects of huperzine A on acetylcholinesterase isoforms in vitro: comparison with tacrine, donepezil, rivastigmine and physostigmine, Eur. J. Pharmacol., 2002, vol. 455, no. 2, pp. 101–107.
Zhao, R.X., Yang, H.X., Zhao, J., and Zhang, J., Using native plants to evaluate the effect of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi on revegetation of iron tailings in grasslands, Biol Fertil. Soils, 2013, vol. 49, no. 6, pp. 617–626.
Zhu, D., Wang, J., Zeng, Q., Zhang, Z., and Yan, R., A novel endophytic huperzine A–producing fungus, Shiraia sp. Slf14, isolated from Huperzia serrata, J. Appl. Microbiol., 2010, vol. 109, no. 4, pp. 1469–1478.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The article is published in the original.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, F.F., Wang, M.Z., Zheng, Y.X. et al. Isolation and characterzation of endophytic Huperzine A-producing fungi from Phlegmariurus phlegmaria . Microbiology 84, 701–709 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0026261715050185
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0026261715050185