Abstract
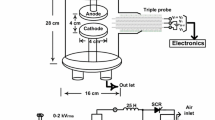
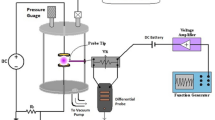
This study investigated the temporal profiles of electron temperature and number density in rectified DC air discharge generated with a 50 Hz step-up transformer. An in-house built triple Langmuir probe and circuitry were used to diagnose the plasma parameters as a function of input voltage and filling gas pressure. A tungsten metal wire capable of withstanding the high temperatures was used as probe tip material. The temporal profiles revealed an increase in electron temperature with input voltage in the range of 380 to 450 V, whereas, an inverse relation between number density and input voltage was evident in the given work. The observed trend in the plasma parameters was absolutely reversed in case of the filling gas pressure. The electron temperature linearly decreased with an increase in pressure from 1 to 4 mbar, whereas a linear increase in number density with pressure was seen in the temporal profiles. Finally, it was concluded that the results for the tested plasma parameters were consistent and the in-house built probe functioned well in DC discharge for the used range of voltage and filling pressure.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Donnelly, V.M., J. Appl. Phys., 2004, vol. 37, p. 217.
Naz, M.Y., Shukrullah, S., Ghaffar, A., and Rehman, N.U., Sci. World J., 2014, vol. 2014, p. 279868.
Kravchenko, A.V., Berlizova, S.A., Nesterenko, A.F., and Kublanovskii, V.S., High Energy Chem., 2004, vol. 38, p. 333.
Rehman, N.U., Murtaza, G., Naz, M.Y., Shafiq, M., and Zakaullah, M., Phys. Scripta, 2013, vol. 88, p. 045503.
Chen, F.F. and Chang, J.P., Plenum Kluwer Publishers, 2002, vol. 79, p. 5730.
Hutchinson, I.H., Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2002, p. 90.
Gatsonis, N.A., Byrne, L.T., Zwahlen, J.C., Pencil, E.J., and Kamhawi, H., IEEE Trans. Plasma Sci., 2004, vol. 32, p. 2118.
Gatsonis, N.A., Zwahlen, J.C., Wheelock, A., Pencil, E.J., and Kamhawi, H., J. Propul. Power, 2004, vol. 20, p. 243.
Eckman, R.F., Byrne, L., Gatsonis, N.A., and Pencil, E.J., J. Propul. Power, 2001, vol. 17, p. 762.
Chen, F.F., Introduction to Plasma Physics and Controlled Fusion, 2nd Ed., N.Y.: Plenum Press,, 1984.
Naz, M.Y., Shukrullah, S., Ghaffar, A., Shakir, I., Ullah, S., and Sagir, M., Surf. Rew. Lett., 2014, vol. 21, p. 1450056.
Naz, M.Y., Ghaffar, A., Rehman, N.U., Naseer, S., and Zakaullah, M., Prog. Electromagn. Res., 2011, vol. 114, p. 113.
Yong, S.I., Lim, H.B., and Houk, R.S., J. Anal. At. Spectrom., 2002, vol. 17, p. 565.
Skorodumov, A.E., Sitanov, D.V., and Svettsov, V.I., High Energy Chem., 2000, vol. 34, p. 331.
Pu, Y.K., Guo, Z.G., Rehman, A.U., and Yu, Z.D., J. Plasma Phys. Control. Fusion, 2006, vol. 48, p. 61.
Qayyum, A., Ahmad, N., Ahmad, S., Deeba, F., Ali, R., and Hussain, S., Rev. Sci. Instrum., 2013, vol. 84, p. 123502.
Hwang, K.T., Oh, S.J., Choi, I.J., and Chung, C.W., Phys. Plasmas, 2010, vol. 17, p. 063501.
Schwabedissen, A., Benck, E.C., and Roberts, J.R., Phys. Rev., 1997, vol. 56, p. 5866.
Lee, M.H., Jang, S.H., and Chung, C.W., J. Appl. Phys., 2007, vol. 101, p. 033305.
Yong, K.S., Lim, H.B., and Houk, R.S., J. Anal. At. Spectrom., 2002, vol. 17, p. 565.
Masashi, S., George, R.T., and Robert, C., Plasma Sources Sci. Technol., 2007, vol. 16, p. 193.
Oh, S.J., Choi, I.J., Kim, J.Y., and Chung, C.W., Meas. Sci. Technol., 2012, vol. 23, p. 085001.
Rudenko, K.V., High Energy Chem., 2009, vol. 43, p. 196.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The article is published in the original.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Farooq, M.U., Ali, A., Qayyum, A. et al. Time function triple Langmuir probe measurements in low frequency pulsed DC discharge plasma. High Energy Chem 49, 286–293 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0018143915040086
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0018143915040086