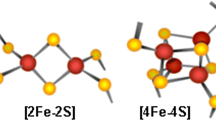
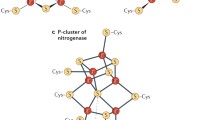
Abstract
Iron-sulfur metabolism is essential for cellular function and is a key process in mitochondria. In this review, we focus on the structure and assembly of mitochondrial iron-sulfur clusters and their roles in various metabolic processes that occur in mitochondria. Iron-sulfur clusters are crucial in mitochondrial respiration, in which they are required for the assembly, stability, and function of respiratory complexes I, II, and III. They also serve important functions in the citric acid cycle, DNA metabolism, and apoptosis. Whereas the identification of iron-sulfur containing proteins and their roles in numerous aspects of cellular function has been a long-standing research area, that in mitochondria is comparatively recent, and it is likely that their roles within mitochondria have been only partially revealed. We review the status of the field and provide examples of other cellular iron-sulfur proteins to highlight their multifarious roles.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- BN-PAGE:
-
blue native polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis
- cI-III:
-
respiratory complexes I-III
- CIA:
-
cytosolic iron-sulfur protein assembly
- ETC:
-
electron transport chain
- Fe-S:
-
iron-sulfur
- IRE:
-
iron-responsive elements
- IRP:
-
ironregulatory protein
- ISCs:
-
iron-sulfur clusters
- ISP:
-
iron-sulfur protein
- mtDNA:
-
mitochondrial DNA
- Q:
-
ubiquinone
References
Baker, H. M., Anderson, B. F., and Baker, E. N. (2003) Dealing with iron: common structural principles in proteins that transport iron and heme, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 100, 3579–3583.
Beinert, H., Holm, R. H., and Munck, E. (1997) Iron-sulfur clusters: nature’s modular, multipurpose structures, Science, 277, 653–659.
Beinert, H. (2000) Iron-sulfur proteins: ancient structures, still full of surprises, J. Biol. Inorg. Chem., 5, 2–15.
Kiley, P. J., and Beinert, H. (2003) The role of Fe-S proteins in sensing and regulation in bacteria, Curr. Opin. Microbiol., 6, 181–185.
Johnson, D. C., Dean, D. R., Smith, A. D., and Johnson, M. K. (2005) Structure, function, and formation of biological iron-sulfur clusters, Annu. Rev. Biochem., 74, 247–281.
Brzoska, K., Meczynska, S., and Kruszewski, M. (2006) Iron-sulfur cluster proteins: electron transfer and beyond, Acta Biochim. Pol., 53, 685–691.
Wiedemann, N., Urzica, E., Guiard, B., Muller, H., Lohaus, C., Meyer, H. E., Ryan, M. T., Meisinger, C., Muhlenhoff, U., Lill, R., and Pfanner, N. (2006) Essential role of Isd11 in mitochondrial iron-sulfur cluster synthesis on Isu scaffold proteins, EMBO J., 25, 184–195.
Shi, Y., Ghosh, M. C., Tong, W. H., and Rouault, T. A. (2009) Human ISD11 is essential for both iron-sulfur cluster assembly and maintenance of normal cellular iron homeostasis, Hum. Mol. Genet., 18, 3014–3025.
Tong, W. H., and Rouault, T. (2000) Distinct iron-sulfur cluster assembly complexes exist in the cytosol and mitochondria of human cells, EMBO J., 19, 5692–5700.
Tong, W. H., and Rouault, T. A. (2006) Functions of mitochondrial ISCU and cytosolic ISCU in mammalian ironsulfur cluster biogenesis and iron homeostasis, Cell Metab., 3, 199–210.
Tamir, S., Paddock, M. L., Darash- Yahana-Baram, M., Holt, S. H., Sohn, Y. S., Agranat, L., Michaeli, D., Stofleth, J. T., Lipper, C. H., Morcos, F., Cabantchik, I. Z., Onuchic, J. N., Jennings, P. A., Mittler, R., and Nechushtai, R. (2015) Structure-function analysis of NEET proteins uncovers their role as key regulators of iron and ROS homeostasis in health and disease, Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 1853, 1294–1315.
Fuss, J. O., Tsai, C. L., Ishida, J. P., and Tainer, J. A. (2015) Emerging critical roles of Fe-S clusters in DNA replication and repair, Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 1853, 1253–1271.
Stemmler, T. L., Lesuisse, E., Pain, D., and Dancis, A. (2010) Frataxin and mitochondrial Fe-S cluster biogenesis, J. Biol. Chem., 285, 26737–26743.
Bridwell-Rabb, J., Fox, N. G., Tsai, C. L., Winn, A. M., and Barondeau, D. P. (2014) Human frataxin activates FeS cluster biosynthesis by facilitating sulfur transfer chemistry, Biochemistry, 53, 4904–4913.
Rouault, T. A., and Tong, W. H. (2005) Iron-sulphur cluster biogenesis and mitochondrial iron homeostasis, Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol., 6, 345–351.
Lill, R., and Muhlenhoff, U. (2006) Iron-sulfur protein biogenesis in eukaryotes: components and mechanisms, Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol., 22, 457–486.
Lill, R., Dutkiewicz, R., Elsasser, H. P., Hausmann, A., Netz, D. J., Pierik, A. J., Stehling, O., Urzica, E., and Muhlenhoff, U. (2006) Mechanisms of iron-sulfur protein maturation in mitochondria, cytosol and nucleus of eukaryotes, Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 1763, 652–667.
Napier, I., Ponka, P., and Richardson, D. R. (2005) Iron trafficking in the mitochondrion: novel pathways revealed by disease, Blood, 105, 1867–1874.
Rouault, T. A. (2012) Biogenesis of iron-sulfur clusters in mammalian cells: new insights and relevance to human disease, Dis. Models Mech., 5, 155–164.
Beilschmidt, L. K., and Puccio, H. M. (2014) Mammalian Fe-S cluster biogenesis and its implication in disease, Biochimie, 100, 48–60.
Maio, N., Ghezzi, D., Verrigni, D., Rizza, T., Bertini, E., Martinelli, D., Zeviani, M., Singh, A., Carrozzo, R., and Rouault, T. A. (2015) Disease-causing SDHAF1 mutations impair transfer of Fe-S clusters to SDHB, Cell Metab., 23, 292–302.
Lill, R. (2009) Function and biogenesis of iron-sulphur proteins, Nature, 460, 831–838.
Paul, V. D., and Lill, R. (2015) Biogenesis of cytosolic and nuclear iron-sulfur proteins and their role in genome stability, Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 1853, 1528–1539.
Wiley, S. E., Paddock, M. L., Abresch, E. C., Gross, L., Van der Geer, P., Nechushtai, R., Murphy, A. N., Jennings, P. A., and Dixon, J. E. (2007) The outer mitochondrial membrane protein mitoNEET contains a novel redoxactive 2Fe-2S cluster, J. Biol. Chem., 282, 23745–23749.
Leggate, E. J., Bill, E., Essigke, T., Ullmann, G. M., and Hirst, J. (2004) Formation and characterization of an allferrous Rieske cluster and stabilization of the [2Fe-2S](0) core by protonation, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 101, 10913–10918.
Meyer, J. (2008) Iron-sulfur protein folds, iron-sulfur chemistry, and evolution, J. Biol. Inorg. Chem., 13, 157–170.
Johnson, M. K., and Smith, A. D. (2005) Iron-sulfur proteins, in Encyclopedia of Inorganic Chemistry (King, R. B., ed.) 2nd Edn., John Wiley & Sons, Chichester, pp. 2589–2619.
Ren, B., Duan, X., and Ding, H. (2009) Redox control of the DNA damage-inducible protein DinG helicase activity via its iron-sulfur cluster, J. Biol. Chem., 284, 4829–4835.
Ding, H., Hidalgo, E., and Demple, B. (1996) The redox state of the [2Fe-2S] clusters in SoxR protein regulates its activity as a transcription factor, J. Biol. Chem., 271, 33173–33175.
Ramon-Garcia, S., Ng, C., Jensen, P. R., Dosanjh, M., Burian, J., Morris, R. P., Folcher, M., Eltis, L. D., Grzesiek, S., Nguyen, L., and Thompson, C. J. (2013) WhiB7, an Fe-S-dependent transcription factor that activates species-specific repertoires of drug resistance determinants in actinobacteria, J. Biol. Chem., 288, 34514–34528.
Jain, R., Vanamee, E. S., Dzikovski, B. G., Buku, A., Johnson, R. E., Prakash, L., Prakash, S., and Aggarwal, A. K. (2014) An iron-sulfur cluster in the polymerase domain of yeast DNA polymerase epsilon, J. Mol. Biol., 426, 301–308.
Netz, D. J., Stith, C. M., Stumpfig, M., Kopf, G., Vogel, D., Genau, H. M., Stodola, J. L., Lill, R., Burgers, P. M., and Pierik, A. J. (2012) Eukaryotic DNA polymerases require an iron-sulfur cluster for the formation of active complexes, Nat. Chem. Biol., 8, 125–132.
Zhang, C. (2014) Essential functions of iron-requiring proteins in DNA replication, repair and cell cycle control, Protein Cell, 5, 750–760.
Stiban, J., Farnum, G. A., Hovde, S. L., and Kaguni, L. S. (2014) The N-terminal domain of the Drosophila mitochondrial replicative DNA helicase contains an iron-sulfur cluster and binds DNA, J. Biol. Chem., 289, 24032–24042.
Pokharel, S., and Campbell, J. L. (2012) Cross talk between the nuclease and helicase activities of Dna2: role of an essential iron-sulfur cluster domain, Nucleic Acids Res., 40, 7821–7830.
Frazzon, J., and Dean, D. R. (2003) Formation of ironsulfur clusters in bacteria: an emerging field in bioinorganic chemistry, Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol., 7, 166–173.
Biederbick, A., Stehling, O., Rosser, R., Niggemeyer, B., Nakai, Y., Elsasser, H. P., and Lill, R. (2006) Role of human mitochondrial Nfs1 in cytosolic iron-sulfur protein biogenesis and iron regulation, Mol. Cell. Biol., 26, 5675–5687.
Shi, R., Proteau, A., Villarroya, M., Moukadiri, I., Zhang, L., Trempe, J. F., Matte, A., Armengod, M. E., and Cygler, M. (2010) Structural basis for Fe-S cluster assembly and tRNA thiolation mediated by IscS protein–protein interactions, PLoS Biol., 8, e1000354.
Adam, A. C., Bornhovd, C., Prokisch, H., Neupert, W., and Hell, K. (2006) The Nfs1 interacting protein Isd11 has an essential role in Fe/S cluster biogenesis in mitochondria, EMBO J., 25, 174–183.
Bandyopadhyay, S., Chandramouli, K., and Johnson, M. K. (2008) Iron-sulfur cluster biosynthesis, Biochem. Soc. Trans., 36, 1112–1119.
Raulfs, E. C., O’Carroll, I. P., Dos Santos, P. C., Unciuleac, M. C., and Dean, D. R. (2008) In vivo iron-sulfur cluster formation, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 105, 8591–8596.
Fox, N. G., Das, D., Chakrabarti, M., Lindahl, P. A., and Barondeau, D. P. (2015) Frataxin accelerates [2Fe-2S] cluster formation on the human Fe–S assembly complex, Biochemistry, 54, 3880–3889.
Fox, N. G., Chakrabarti, M., McCormick, S. P., Lindahl, P. A., and Barondeau, D. P. (2015) The human iron–sulfur assembly complex catalyzes the synthesis of [2Fe-2S] clusters on ISCU2 that can be transferred to acceptor molecules, Biochemistry, 54, 3871–3879.
Schmucker, S., Martelli, A., Colin, F., Page, A., Wattenhofer-Donze, M., Reutenauer, L., and Puccio, H. (2011) Mammalian frataxin: an essential function for cellular viability through an interaction with a preformed ISCU/NFS1/ISD11 iron–sulfur assembly complex, PLoS One, 6, e16199.
Tsai, C. L., and Barondeau, D. P. (2010) Human frataxin is an allosteric switch that activates the Fe-S cluster biosynthetic complex, Biochemistry, 49, 9132–9139.
Bridwell-Rabb, J., Winn, A. M., and Barondeau, D. P. (2011) Structure-function analysis of Friedreich’s ataxia mutants reveals determinants of frataxin binding and activation of the Fe–S assembly complex, Biochemistry, 50, 7265–7274.
Shi, Y., Ghosh, M., Kovtunovych, G., Crooks, D. R., and Rouault, T. A. (2012) Both human ferredoxins 1 and 2 and ferredoxin reductase are important for iron-sulfur cluster biogenesis, Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 1823, 484–492.
Chandramouli, K., Unciuleac, M. C., Naik, S., Dean, D. R., Huynh, B. H., and Johnson, M. K. (2007) Formation and properties of [4Fe-4S] clusters on the IscU scaffold protein, Biochemistry, 46, 6804–6811.
Al-Hassnan, Z. N., Al-Dosary, M., Alfadhel, M., Faqeih, E. A., Alsagob, M., Kenana, R., Almass, R., Al-Harazi, O. S., Al-Hindi, H., Malibari, O. I., Almutari, F. B., Tulbah, S., Alhadeq, F., Al-Sheddi, T., Alamro, R., AlAsmari, A., Almuntashri, M., Alshaalan, H., Al-Mohanna, F. A., Colak, D., and Kaya, N. (2015) ISCA2 mutation causes infantile neurodegenerative mitochondrial disorder, J. Med. Genet., 52, 186–194.
Uhrigshardt, H., Singh, A., Kovtunovych, G., Ghosh, M., and Rouault, T. A. (2010) Characterization of the human HSC20, an unusual DnaJ type III protein, involved in ironsulfur cluster biogenesis, Hum. Mol. Genet., 19, 3816–3834.
Vickery, L. E., and Cupp-Vickery, J. R. (2007) Molecular chaperones HscA/Ssq1 and HscB/Jac1 and their roles in iron-sulfur protein maturation, Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. Biol., 42, 95–111.
Maio, N., Singh, A., Uhrigshardt, H., Saxena, N., Tong, W. H., and Rouault, T. A. (2014) Cochaperone binding to LYR motifs confers specificity of iron sulfur cluster delivery, Cell Metab., 19, 445–457.
Maio, N., and Rouault, T. A. (2015) Iron-sulfur cluster biogenesis in mammalian cells: new insights into the molecular mechanisms of cluster delivery, Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 1853, 1493–1512.
Bych, K., Kerscher, S., Netz, D. J., Pierik, A. J., Zwicker, K., Huynen, M. A., Lill, R., Brandt, U., and Balk, J. (2008) The iron-sulphur protein Ind1 is required for effective complex I assembly, EMBO J., 27, 1736–1746.
Sheftel, A. D., Stehling, O., Pierik, A. J., Netz, D. J., Kerscher, S., Elsasser, H. P., Wittig, I., Balk, J., Brandt, U., and Lill, R. (2009) Human ind1, an iron-sulfur cluster assembly factor for respiratory complex I, Mol. Cell. Biol., 29, 6059–6073.
Lill, R., Hoffmann, B., Molik, S., Pierik, A. J., Rietzschel, N., Stehling, O., Uzarska, M. A., Webert, H., Wilbrecht, C., and Muhlenhoff, U. (2012) The role of mitochondria in cellular iron-sulfur protein biogenesis and iron metabolism, Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 1823, 1491–1508.
Stehling, O., Wilbrecht, C., and Lill, R. (2014) Mitochondrial iron-sulfur protein biogenesis and human disease, Biochimie, 100, 61–77.
Guruharsha, K. G., Rual, J. F., Zhai, B., Mintseris, J., Vaidya, P., Vaidya, N., Beekman, C., Wong, C., Rhee, D. Y., Cenaj, O., McKillip, E., Shah, S., Stapleton, M., Wan, K. H., Yu, C., Parsa, B., Carlson, J. W., Chen, X., Kapadia, B., VijayRaghavan, K., Gygi, S. P., Celniker, S. E., Obar, R. A., and Artavanis-Tsakonas, S. (2011) A protein complex network of Drosophila melanogaster, Cell, 147, 690–703.
Lim, S. C., Friemel, M., Marum, J. E., Tucker, E. J., Bruno, D. L., Riley, L. G., Christodoulou, J., Kirk, E. P., Boneh, A., DeGennaro, C. M., Springer, M., Mootha, V. K., Rouault, T. A., Leimkuhler, S., Thorburn, D. R., and Compton, A. G. (2013) Mutations in LYRM4, encoding iron-sulfur cluster biogenesis factor ISD11, cause deficiency of multiple respiratory chain complexes, Hum. Mol. Genet., 22, 4460–4473.
Saha, P. P., Srivastava, S., Kumar, S. K. P., Sinha, D., and D’Silva, P. (2015) Mapping key residues of ISD11 critical for NFS1-ISD11 subcomplex stability: implications in the development of mitochondrial disorder, COXPD19, J. Biol. Chem., 290, 25876–25890.
Page, C. C., Moser, C. C., Chen, X., and Dutton, P. L. (1999) Natural engineering principles of electron tunnelling in biological oxidation-reduction, Nature, 402, 47–52.
Ohnishi, T. (1975) Thermodynamic and EPR characterization of iron-sulfur centers in the NADH-ubiquinone segment of the mitochondrial respiratory chain in pigeon heart, Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 387, 475–490.
Nakamaru-Ogiso, E. (2012) Iron-sulfur clusters in complex I, in A Structural Perspective on Respiratory Complex I (Sazanov, L., ed.) Springer, The Netherlands, pp. 61–79.
Pohl, T., Bauer, T., Dorner, K., Stolpe, S., Sell, P., Zocher, G., and Friedrich, T. (2007) Iron-sulfur cluster N7 of the NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase (complex I) is essential for stability but not involved in electron transfer, Biochemistry, 46, 6588–6596.
Tocilescu, M. A., Fendel, U., Zwicker, K., Drose, S., Kerscher, S., and Brandt, U. (2010) The role of a conserved tyrosine in the 49-kDa subunit of complex I for ubiquinone binding and reduction, Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 1797, 625–632.
Tocilescu, M. A., Zickermann, V., Zwicker, K., and Brandt, U. (2010) Quinone binding and reduction by respiratory complex I, Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 1797, 1883–1890.
Friedrich, T., Hellwig, P., and Einsle, O. (2012) On the mechanism of the respiratory complex I, in A Structural Perspective on Respiratory Complex I (Sazanov, L., ed.) Springer, The Netherlands, pp. 23–59.
Hinchliffe, P., Carroll, J., and Sazanov, L. A. (2006) Identification of a novel subunit of respiratory complex I from Thermus thermophilus, Biochemistry, 45, 4413–4420.
Sazanov, L. A., and Hinchliffe, P. (2006) Structure of the hydrophilic domain of respiratory complex I from Thermus thermophilus, Science, 311, 1430–1436.
Ohnishi, T. (1998) Iron-sulfur clusters/semiquinones in complex I, Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 1364, 186–206.
Hayashi, T., and Stuchebrukhov, A. A. (2010) Electron tunneling in respiratory complex I, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 107, 19157–19162.
Kmita, K., Wirth, C., Warnau, J., Guerrero-Castillo, S., Hunte, C., Hummer, G., Kaila, V. R., Zwicker, K., Brandt, U., and Zickermann, V. (2015) Accessory NUMM (NDUFS6) subunit harbors a Zn-binding site and is essential for biogenesis of mitochondrial complex I, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 112, 5685–5690.
Ohnishi, T., and Salerno, J. C. (2005) Conformation-driven and semiquinone-gated proton-pump mechanism in the NADH-ubiquinone oxidoreductase (complex I), FEBS Lett., 579, 4555–4561.
Zwicker, K., Galkin, A., Drose, S., Grgic, L., Kerscher, S., and Brandt, U. (2006) The Redox-Bohr group associated with iron-sulfur cluster N2 of complex I, J.Biol. Chem., 281, 23013–23017.
Yano, T., Dunham, W. R., and Ohnishi, T. (2005) Characterization of the delta muH+-sensitive ubisemiquinone species (SQ(Nf)) and the interaction with cluster N2: new insight into the energy-coupled electron transfer in complex I, Biochemistry, 44, 1744–1754.
Nakamaru-Ogiso, E., Narayanan, M., and Sakyiama, J. A. (2014) Roles of semiquinone species in proton pumping mechanism by complex I, J.Bioenerg. Biomembr., 46, 269–277.
Sazanov, L. A. (2007) Respiratory complex I: mechanistic and structural insights provided by the crystal structure of the hydrophilic domain, Biochemistry, 46, 2275–2288.
Sun, F., Huo, X., Zhai, Y., Wang, A., Xu, J., Su, D., Bartlam, M., and Rao, Z. (2005) Crystal structure of mitochondrial respiratory membrane protein complex II, Cell, 121, 1043–1057.
Iverson, T. M. (2013) Catalytic mechanisms of complex IIenzymes: a structural perspective, Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 1827, 648–657.
Van Vranken, J. G., Na, U., Winge, D. R., and Rutter, J. (2015) Protein-mediated assembly of succinate dehydrogenase and its cofactors, Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. Biol., 50, 168–180.
Iwata, S., Lee, J. W., Okada, K., Lee, J. K., Iwata, M., Rasmussen, B., Link, T. A., Ramaswamy, S., and Jap, B. K. (1998) Complete structure of the 11-subunit bovine mitochondrial cytochrome bc1 complex, Science, 281, 64–71.
Zhang, Z., Huang, L., Shulmeister, V. M., Chi, Y. I., Kim, K. K., Hung, L. W., Crofts, A. R., Berry, E. A., and Kim, S. H. (1998) Electron transfer by domain movement in cytochrome bc1, Nature, 392, 677–684.
Akiba, T., Toyoshima, C., Matsunaga, T., Kawamoto, M., Kubota, T., Fukuyama, K., Namba, K., and Matsubara, H. (1996) Three-dimensional structure of bovine cytochrome bc1 complex by electron cryomicroscopy and helical image reconstruction, Nat. Struct. Biol., 3, 553–561.
Xia, D., Esser, L., Tang, W. K., Zhou, F., Zhou, Y., Yu, L., and Yu, C. A. (2013) Structural analysis of cytochrome bc1 complexes: implications to the mechanism of function, Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 1827, 1278–1294.
Cooley, J. W. (2013) Protein conformational changes involved in the cytochrome bc1 complex catalytic cycle, Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 1827, 1340–1345.
Gurung, B., Yu, L., Xia, D., and Yu, C. A. (2005) The ironsulfur cluster of the Rieske iron-sulfur protein functions as a proton-exiting gate in the cytochrome bc(1) complex, J. Biol. Chem., 280, 24895–24902.
Iwata, S., Saynovits, M., Link, T. A., and Michel, H. (1996) Structure of a water soluble fragment of the “Rieske” iron-sulfur protein of the bovine heart mitochondrial cytochrome bc1 complex determined by MAD phasing at 1.5 Å resolution, Structure, 4, 567–579.
Link, T. A., and Iwata, S. (1996) Functional implications of the structure of the “Rieske” iron-sulfur protein of bovine heart mitochondrial cytochrome bc1 complex, Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 1275, 54–60.
Smith, J. L., Zhang, H., Yan, J., Kurisu, G., and Cramer, W. A. (2004) Cytochrome bc complexes: a common core of structure and function surrounded by diversity in the outlying provinces, Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol., 14, 432–439.
Esser, L., Gong, X., Yang, S., Yu, L., Yu, C. A., and Xia, D. (2006) Surface-modulated motion switch: capture and release of iron-sulfur protein in the cytochrome bc1 complex, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 103, 13045–13050.
Berry, E. A., De Bari, H., and Huang, L. S. (2013) Unanswered questions about the structure of cytochrome bc1 complexes, Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 1827, 1258–1277.
Borek, A., Kuleta, P., Ekiert, R., Pietras, R., Sarewicz, M., and Osyczka, A. (2015) Mitochondrial disease-related mutation G167P in cytochrome b of rhodobacter capsulatus cytochrome bc1 (S151P in human) affects the equilibrium distribution of [2Fe-2S] cluster and generation of superoxide, J. Biol. Chem., 290, 23781–23792.
Sanchez, E., Lobo, T., Fox, J. L., Zeviani, M., Winge, D. R., and Fernandez-Vizarra, E. (2013) LYRM7/MZM1L is a UQCRFS1 chaperone involved in the last steps of mitochondrial Complex III assembly in human cells, Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 1827, 285–293.
Lehninger, A. L., Nelson, D. L., and Cox, M. M. (2013) Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry, 6th Edn., W.H. Freeman, New York.
Robbins, A. H., and Stout, C. D. (1989) The structure of aconitase, Proteins, 5, 289–312.
Robbins, A. H., and Stout, C. D. (1989) Structure of activated aconitase: formation of the [4Fe-4S] cluster in the crystal, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 86, 3639–3643.
Lauble, H., Kennedy, M. C., Beinert, H., and Stout, C. D. (1992) Crystal structures of aconitase with isocitrate and nitroisocitrate bound, Biochemistry, 31, 2735–2748.
Talib, J., and Davies, M. J. (2016) Exposure of aconitase to smoking-related oxidants results in iron loss and increased iron response protein-1 activity: potential mechanisms for iron accumulation in human arterial cells, J. Biol. Inorg. Chem., 21, 305–317.
Myers, C. R., Antholine, W. E., and Myers, J. M. (2010) The pro-oxidant chromium(VI) inhibits mitochondrial complex I, complex II,and aconitase in the bronchial epithelium: EPR markers for Fe-S proteins, Free Radic. Biol. Med., 49, 1903–1915.
Han, D., Canali, R., Garcia, J., Aguilera, R., Gallaher, T. K., and Cadenas, E. (2005) Sites and mechanisms of aconitase inactivation by peroxynitrite: modulation by citrate and glutathione, Biochemistry, 44, 11986–11996.
Beinert, H., and Kennedy, M. C. (1993) Aconitase, a twofaced protein: enzyme and iron regulatory factor, FASEB J., 7, 1442–1449.
Eisenstein, R. S. (2000) Iron regulatory proteins and the molecular control of mammalian iron metabolism, Annu. Rev. Nutr., 20, 627–662.
Hentze, M. W., and Kuhn, L. C. (1996) Molecular control of vertebrate iron metabolism: mRNA-based regulatory circuits operated by iron, nitric oxide, and oxidative stress, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 93, 8175–8182.
Cairo, G., Recalcati, S., Pietrangelo, A., and Minotti, G. (2002) The iron regulatory proteins: targets and modulators of free radical reactions and oxidative damage, Free Radic. Biol. Med., 32, 1237–1243.
Chen, X. J., Wang, X., Kaufman, B. A., and Butow, R. A. (2005) Aconitase couples metabolic regulation to mitochondrial DNA maintenance, Science, 307, 714–717.
Ferrer, M., Golyshina, O. V., Beloqui, A., Golyshin, P. N., and Timmis, K. N. (2007) The cellular machinery of Ferroplasma acidiphilum is iron-protein-dominated, Nature, 445, 91–94.
White, M. F., and Dillingham, M. S. (2012) Iron-sulphur clusters in nucleic acid processing enzymes, Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol., 22, 94–100.
Boal, A. K., Yavin, E., and Barton, J. K. (2007) DNA repair glycosylases with a [4Fe-4S] cluster: a redox cofactor for DNA-mediated charge transport? J. Inorg. Biochem., 101, 1913–1921.
Genereux, J. C., Boal, A. K., and Barton, J. K. (2010) DNA-mediated charge transport in redox sensing and signaling, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 132, 891–905.
Atta, M., Mulliez, E., Arragain, S., Forouhar, F., Hunt, J. F., and Fontecave, M. (2010) S-adenosylmethioninedependent radical-based modification of biological macromolecules, Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol., 20, 684–692.
Liu, H., Rudolf, J., Johnson, K. A., McMahon, S. A., Oke, M., Carter, L., McRobbie, A. M., Brown, S. E., Naismith, J. H., and White, M. F. (2008) Structure of the DNA repair helicase XPD, Cell, 133, 801–812.
Wu, Y., Sommers, J. A., Suhasini, A. N., Leonard, T., Deakyne, J. S., Mazin, A. V., Shin-Ya, K., Kitao, H., and Brosh, R. M., Jr. (2010) Fanconi anemia group J mutation abolishes its DNA repair function by uncoupling DNA translocation from helicase activity or disruption of protein–DNA complexes, Blood, 116, 3780–3791.
Landry, A. P., and Ding, H. (2014) The N-terminal domain of human DNA helicase Rtel1 contains a redox active iron-sulfur cluster, Biomed Res. Int., 285791.
Capo-Chichi, J. M., Bharti, S. K., Sommers, J. A., Yammine, T., Chouery, E., Patry, L., Rouleau, G. A., Samuels, M. E., Hamdan, F. F., Michaud, J. L., Brosh, R. M., Jr., Megarbane, A., and Kibar, Z. (2013) Identification and biochemical characterization of a novel mutation in DDX11 causing Warsaw breakage syndrome, Hum. Mutat., 34, 103–107.
Yeeles, J. T., Cammack, R., and Dillingham, M. S. (2009) An iron-sulfur cluster is essential for the binding of broken DNA by AddAB-type helicase-nucleases, J. Biol. Chem., 284, 7746–7755.
Budd, M. E., Reis, C. C., Smith, S., Myung, K., and Campbell, J. L. (2006) Evidence suggesting that Pif1 helicase functions in DNA replication with the Dna2 helicase/nuclease and DNA polymerase delta, Mol. Cell. Biol., 26, 2490–2500.
Burgers, P. M., Stith, C. M., Yoder, B. L., and Sparks, J. L. (2010) Yeast exonuclease 5 is essential for mitochondrial genome maintenance, Mol. Cell. Biol., 30, 1457–1466.
Sparks, J. L., Kumar, R., Singh, M., Wold, M. S., Pandita, T. K., and Burgers, P. M. (2012) Human exonuclease 5 is a novel sliding exonuclease required for genome stability, J. Biol. Chem., 287, 42773–42783.
Zhang, J., Kasciukovic, T., and White, M. F. (2012) The CRISPR associated protein Cas4 is a 5' to 3' DNA exonuclease with an iron-sulfur cluster, PLoS One, 7, e47232.
Lemak, S., Beloglazova, N., Nocek, B., Skarina, T., Flick, R., Brown, G., Popovic, A., Joachimiak, A., Savchenko, A., and Yakunin, A. F. (2013) Toroidal structure and DNA cleavage by the CRISPR-associated [4Fe-4S] cluster containing Cas4 nuclease SSO0001 from Sulfolobus solfataricus, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 135, 17476–17487.
Lemak, S., Nocek, B., Beloglazova, N., Skarina, T., Flick, R., Brown, G., Joachimiak, A., Savchenko, A., and Yakunin, A. F. (2014) The CRISPR-associated Cas4 protein Pcal_0546 from Pyrobaculum calidifontis contains a [2Fe-2S] cluster: crystal structure and nuclease activity, Nucleic Acids Res., 42, 11144–11155.
Tuteja, N., and Tuteja, R. (2004) Prokaryotic and eukaryotic DNA helicases. Essential molecular motor proteins for cellular machinery, Eur. J. Biochem., 271, 1835–1848.
White, M. F. (2009) Structure, function and evolution of the XPD family of iron-sulfur-containing 5'→3' DNA helicases, Biochem. Soc. Trans., 37, 547–551.
Wu, Y., and Brosh, R. M., Jr. (2012) DNA helicase and helicase-nuclease enzymes with a conserved iron-sulfur cluster, Nucleic Acids Res., 40, 4247–4260.
Suhasini, A. N., and Brosh, R. M., Jr. (2013) DNA helicases associated with genetic instability, cancer, and aging, Adv. Exp. Med. Biol., 767, 123–144.
Rudolf, J., Makrantoni, V., Ingledew, W. J., Stark, M. J., and White, M. F. (2006) The DNA repair helicases XPD and FancJ have essential iron-sulfur domains, Mol. Cell, 23, 801–808.
Fan, L., Fuss, J. O., Cheng, Q. J., Arvai, A. S., Hammel, M., Roberts, V. A., Cooper, P. K., and Tainer, J. A. (2008) XPD helicase structures and activities: insights into the cancer and aging phenotypes from XPD mutations, Cell, 133, 789–800.
Wolski, S. C., Kuper, J., Hanzelmann, P., Truglio, J. J., Croteau, D. L., Van Houten, B., and Kisker, C. (2008) Crystal structure of the Fe-S cluster-containing nucleotide excision repair helicase XPD, PLoS Biol., 6, e149.
Pugh, R. A., Honda, M., Leesley, H., Thomas, A., Lin, Y., Nilges, M. J., Cann, I. K., and Spies, M. (2008) The ironcontaining domain is essential in Rad3 helicases for coupling of ATP hydrolysis to DNA translocation and for targeting the helicase to the single-stranded DNA–doublestranded DNA junction, J. Biol. Chem., 283, 1732–1743.
Sommers, J. A., Banerjee, T., Hinds, T., Wan, B., Wold, M. S., Lei, M., and Brosh, R. M., Jr. (2014) Novel function of the Fanconi anemia group J or RECQ1 helicase to disrupt protein–DNA complexes in a replication protein A-stimulated manner, J. Biol. Chem., 289, 19928–19941.
Mishra, N. C. (1995) Molecular Biology of Nucleases, CRC Press, Boca Raton.
Sisakova, E., Weiserova, M., Dekker, C., Seidel, R., and Szczelkun, M. D. (2008) The interrelationship of helicase and nuclease domains during DNA translocation by the molecular motor EcoR124I, J. Mol. Biol., 384, 1273–1286.
Wigley, D. B. (2013) Bacterial DNA repair: recent insights into the mechanism of RecBCD, AddAB and AdnAB, Nat. Rev. Microbiol., 11, 9–13.
Zheng, L., Zhou, M., Guo, Z., Lu, H., Qian, L., Dai, H., Qiu, J., Yakubovskaya, E., Bogenhagen, D. F., Demple, B., and Shen, B. (2008) Human DNA2 is a mitochondrial nuclease/helicase for efficient processing of DNA replication and repair intermediates, Mol. Cell, 32, 325–336.
Duxin, J. P., Dao, B., Martinsson, P., Rajala, N., Guittat, L., Campbell, J. L., Spelbrink, J. N., and Stewart, S. A. (2009) Human Dna2 is a nuclear and mitochondrial DNA maintenance protein, Mol. Cell. Biol., 29, 4274–4282.
Kang, Y. H., Lee, C. H., and Seo, Y. S. (2010) Dna2 on the road to Okazaki fragment processing and genome stability in eukaryotes, Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. Biol., 45, 71–96.
Taha, T. A., Kitatani, K., El-Alwani, M., Bielawski, J., Hannun, Y. A., and Obeid, L. M. (2006) Loss of sphingosine kinase-1 activates the intrinsic pathway of programmed cell death: modulation of sphingolipid levels and the induction of apoptosis, FASEB J., 20, 482–484.
Abou-Ghali, M., and Stiban, J. (2015) Regulation of ceramide channel formation and disassembly: insights on the initiation of apoptosis, Saudi J. Biol. Sci., 22, 760–772.
Stiban, J., and Perera, M. (2015) Very long chain ceramides interfere with C16-ceramide-induced channel formation: a plausible mechanism for regulating the initiation of intrinsic apoptosis, Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 1848, 561–567.
Wiley, S. E., Murphy, A. N., Ross, S. A., Van der Geer, P., and Dixon, J. E. (2007) MitoNEET is an iron-containing outer mitochondrial membrane protein that regulates oxidative capacity, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 104, 5318–5323.
Kusminski, C. M., Holland, W. L., Sun, K., Park, J., Spurgin, S. B., Lin, Y., Askew, G. R., Simcox, J. A., McClain, D. A., Li, C., and Scherer, P. E. (2012) MitoNEET-driven alterations in adipocyte mitochondrial activity reveal a crucial adaptive process that preserves insulin sensitivity in obesity, Nat. Med., 18, 1539–1549.
Landry, A. P., and Ding, H. (2014) Redox control of human mitochondrial outer membrane protein MitoNEET [2Fe-2S] clusters by biological thiols and hydrogen peroxide, J. Biol. Chem., 289, 4307–4315.
Via, A., Ferre, F., Brannetti, B., Valencia, A., and HelmerCitterich, M. (2000) Three-dimensional view of the surface motif associated with the P-loop structure: cis and trans cases of convergent evolution, J. Mol. Biol., 303, 455–465.
Lipper, C. H., Paddock, M. L., Onuchic, J. N., Mittler, R., Nechushtai, R., and Jennings, P. A. (2015) Cancerrelated NEET proteins transfer 2Fe-2S clusters to anamorsin, a protein required for cytosolic iron-sulfur cluster biogenesis, PLoS One, 10, e0139699.
Golinelli-Cohen, M. P., Lescop, E., Mons, C., Goncalves, S., Clemancey, M., Santolini, J., Guittet, E., Blondin, G., Latour, J. M., and Bouton, C. (2016) Redox control of the human iron-sulfur repair protein MitoNEET activity via its iron-sulfur cluster, J. Biol. Chem., 291, 7583–7593.
Ferecatu, I., Goncalves, S., Golinelli-Cohen, M. P., Clemancey, M., Martelli, A., Riquier, S., Guittet, E., Latour, J. M., Puccio, H., Drapier, J. C., Lescop, E., and Bouton, C. (2014) The diabetes drug target MitoNEET governs a novel trafficking pathway to rebuild an Fe-S cluster into cytosolic aconitase/iron regulatory protein 1, J. Biol. Chem., 289, 28070–28086.
Shulga, N., and Pastorino, J. G. (2014) Mitoneet mediates TNFalpha-induced necroptosis promoted by exposure to fructose and ethanol, J. Cell Sci., 127, 896–907.
Sohn, Y. S., Tamir, S., Song, L., Michaeli, D., Matouk, I., Conlan, A. R., Harir, Y., Holt, S. H., Shulaev, V., Paddock, M. L., Hochberg, A., Cabanchick, I. Z., Onuchic, J. N., Jennings, P. A., Nechushtai, R., and Mittler, R. (2013) NAF-1 and mitoNEET are central to human breast cancer proliferation by maintaining mitochondrial homeostasis and promoting tumor growth, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 110, 14676–14681.
Shimizu, R., Lan, N. N., Tai, T. T., Adachi, Y., Kawazoe, A., Mu, A., and Taketani, S. (2014) p53 directly regulates the transcription of the human frataxin gene and its lack of regulation in tumor cells decreases the utilization of mitochondrial iron, Gene, 551, 79–85.
Shakoury-Elizeh, M., Protchenko, O., Berger, A., Cox, J., Gable, K., Dunn, T. M., Prinz, W. A., Bard, M., and Philpott, C. C. (2010) Metabolic response to iron deficiency in Saccharomyces cerevisiae, J. Biol. Chem., 285, 14823–14833.
Yang, Z., Wang, W. E., and Zhang, Q. (2013) CIAPIN1 siRNA inhibits proliferation, migration and promotes apoptosis of VSMCs by regulating Bcl-2 and Bax, Curr. Neurovasc. Res., 10, 4–10.
Banci, L., Ciofi-Baffoni, S., Mikolajczyk, M., Winkelmann, J., Bill, E., and Pandelia, M. E. (2013) Human anamorsin binds [2Fe-2S] clusters with unique electronic properties, J. Biol. Inorg. Chem., 18, 883–893.
Netz, D. J., Stumpfig, M., Dore, C., Muhlenhoff, U., Pierik, A. J., and Lill, R. (2010) Tah18 transfers electrons to Dre2 in cytosolic iron-sulfur protein biogenesis, Nat. Chem. Biol., 6, 758–765.
Vernis, L., Facca, C., Delagoutte, E., Soler, N., Chanet, R., Guiard, B., Faye, G., and Baldacci, G. (2009) A newly identified essential complex, Dre2-Tah18, controls mitochondria integrity and cell death after oxidative stress in yeast, PLoS One, 4, e4376.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Published in Russian in Biokhimiya, 2016, Vol. 81, No. 10, pp. 1332–1348.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stiban, J., So, M. & Kaguni, L.S. Iron-sulfur clusters in mitochondrial metabolism: Multifaceted roles of a simple cofactor. Biochemistry Moscow 81, 1066–1080 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0006297916100059
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0006297916100059