Abstract
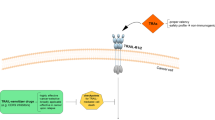
Tumor necrosis factor superfamily cytokine TRAIL (tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand) induces apoptosis in tumor cells by binding to death receptors DR4 and DR5 without affecting normal cells. However, the therapeutic use of TRAIL is limited, because many tumor cells are resistant to it. The resistance is partially related to interaction of TRAIL with the decoy receptors DcR1 and DcR2, which do not trigger the apoptotic signal and inhibit signaling of death receptors. Previously, we designed a unique DR5-specific TRAIL mutant variant DR5-B, which binds to DR5 receptor as effectively as the original cytokine, but has practically no interaction with DR4 and DcR1 receptors, and its affinity for DcR2 is reduced 400-fold. In the present work, the cytotoxity of TRAIL and DR5-B was analyzed on 12 different tumor cell lines and two types of normal cells. In nine of 12 tumor cell lines, DR5-B killed 1.5–5.0 times more tumor cells than TRAIL, and it did not exhibit toxicity towards normal cells. Chemotherapeutic drugs such as doxorubicin, paclitaxel, and bortezomib augmented the effect of both TRAIL variants, and the enhancing effect was more pronounced for DR5-B. Half-maximal effective concentrations (EC50) for DR5-B in combination with chemotherapeutic agents were 1.5–10.0 times lower than for wild-type TRAIL. Thus, DR5-B is a promising candidate both for monotherapy and in combination with chemotherapy for treatment of TRAIL-resistant tumors.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wiley, S. R., Schooley, K., Smolak, P. J., Din, W. S., Huang, C. P., Nicholl, J. K., Sutherland, G. R., Smith, T. D., Rauch, C., and Smith, C. A. (1995) Identification and characterization of a new member of the TNF family that induces apoptosis, Immunity, 3, 673–682.
Pitti, R. M., Marsters, S. A., Ruppert, S., Donahue, C. J., Moore, A., and Ashkenazi, A. (1996) Induction of apoptosis by Apo-2 ligand, a new member of the tumor necrosis factor cytokine family, J. Biol. Chem., 271, 12687–12690.
Ashkenazi, A., Pai, R. C., Fong, S., Leung, S., Lawrence, D. A., Marsters, S. A., Blackie, C., Chang, L., Mc Murtrey, A. E., Hebert, A., DeForge, L., Koumenis, I. L., Lewis, D., Harris, L., Bussiere, J., Koeppen, H., Shahrokh, Z., and Schwall, R. H. (1999). Safety and antitumor activity of recombinant soluble Apo2 ligand, J. Clin. Invest., 104, 155–162.
Wajant, H., Gerspach, J., and Pfizenmaier, K. (2013) Engineering death receptor ligands for cancer therapy, Cancer Lett., 332, 163–174.
Lemke, J., von Karstedt, S., Zinngrebe, J., and Walczak, H. (2014) Getting TRAIL back on track for cancer therapy, Cell Death Differ., 21, 1350–1364.
Wajant, H., Gerspach, J., and Pfizenmaier, K. (2005) Tumor therapeutics by design: targeting and activation of death receptors, Cytokine Growth Factor Rev., 16, 55–76.
Dimberg, L. Y., Anderson, C. K., Camidge, R., Behbakht, K., Thorburn, A., and Ford, H. L. (2013) On the TRAIL to successful cancer therapy? Predicting and counteracting resistance against TRAIL-based therapeutics, Oncogene, 32, 1341–1350.
Gonzalvez, F., and Ashkenazi, A. (2010) New insights into apoptosis signaling by Apo2L/TRAIL, Oncogene, 29, 4752–4765.
Merino, D., Lalaoui, N., Morizot, A., Schneider, P., Solary, E., and Micheau, O. (2006) Differential inhibition of TRAIL-mediated DR5-DISC formation by decoy receptors 1 and 2, Mol. Cell Biol., 26, 7046–7055.
Hymowitz, S. G., O’ Connell, M. P., Ultsch, M. H., Hurst, A., Totpal, K., Ashkenazi, A., de Vos, A. M., and Kelley, R. F. (2000) A unique zinc-binding site revealed by a high-resolution X-ray structure of homotrimeric Apo2L/TRAIL, Biochemistry, 39, 633–640.
Gasparian, M. E., Chernyak, B. V., Dolgikh, D. A., Yagolovich, A. V., Popova, E. N., Sycheva, A. M., Moshkovskii, S. A., and Kirpichnikov, M. P. (2009) Generation of new TRAIL mutants DR5-A and DR5-B with improved selectivity to death receptor 5, Apoptosis, 14, 778–787.
Georgakis, G. V., Li, Y., Humphreys, R., Andreeff, M., O’ Brien, S., Younes, M., Carbone, A., Albert, V., and Younes, A. (2005) Activity of selective fully human agonistic antibodies to the TRAIL death receptors TRAIL-R1 and TRAIL-R2 in primary and cultured lymphoma cells: induction of apoptosis and enhancement of doxorubicinand bortezomib-induced cell death, Br. J. Haematol., 130, 501–510.
Griffith, T. S., Rauch, C. T., Smolak, P. J., Waugh, J. Y., Boiani, N., Lynch, D. H., Smith, C. A., Goodwin, R. G., and Kubin, M. Z. (1999) Functional analysis of TRAIL receptors using monoclonal antibodies, J. Immunol., 162, 2597–2605.
Elrod, H. A., and Sun, S. Y. (2008) Modulation of death receptors by cancer therapeutic agents, Cancer Biol. Ther., 7, 163–173.
Mahalingam, D., Szegezdi, E., Keane, M., de Jong, S., and Samali, A. (2009) TRAIL receptor signaling and modulation: are we on the right TRAIL? Cancer Treat. Rev., 35, 280–288.
Li, F., and Ravetch, J. V. (2012) Apoptotic and antitumor activity of death receptor antibodies require inhibitory Fcγ receptor engagement, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 109, 10966–10971.
Kelley, R. F., Totpal, K., Lindstrom, S. H., Mathieu, M., Billeci, K., Deforge, L., Pai, R., Hymowitz, S. G., and Ashkenazi, A. (2005) Receptor-selective mutants of Apo2L/TRAIL reveal a greater contribution of DR5 than DR4 to apoptosis signaling, J. Biol. Chem., 28, 2205–2212.
Van der Sloot, A. M., Tur, V., Szegezdi, T. E., Mullally, M. M., Cool, R. H., Samali, A., Serrano, L., and Quax, W. J. (2006) Designed tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosisinducing ligand variants initiating apoptosis exclusively via the DR5 receptor, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 10, 8634–8639.
Gasparian, M. E., Ostapchenko, V. G., Schulga, A. A., Dolgikh, D. A., and Kirpichnikov, M. P. (2003) Expression, purification, and characterization of human enteropeptidase catalytic subunit in Escherichia coli, Protein Express. Purif., 31, 133–139.
Gasparian, M. E., Bychkov, M. L., Dolgikh, D. A., and Kirpichnikov, M. P. (2011) Strategy for improvement of enteropeptidase efficiency in tag removal processes, Protein Express. Purif., 79, 191–196.
Yagita, H., Takeda, K., Hayakawa, Y., Smyth, M. J., and Okumura, K. (2004) TRAIL and its receptors as targets for cancer therapy, Cancer Sci., 95, 777–783.
Ashkenazi, A., and Herbst, R. S. (2008) To kill a tumor cell: the potential of proapoptotic receptor agonists, J. Clin. Invest., 118, 1979–1990.
Prasad, S., Kim, J. H., Gupta, S. C., and Aggarwal, B. B. (2014) Targeting death receptors for TRAIL by agents designed by Mother Nature, Trends Pharmacol. Sci., 35, 520–536.
Van Roosmalen, I. A., Quax, W. J., and Kruyt, F. A. (2014) Two death-inducing human TRAIL receptors to target in cancer: similar or distinct regulation and function? Biochem. Pharmacol., 91, 447–456.
Lu, M., Lawrence, D. A., Marsters, S., Acosta-Alvear, D., Kimmig, P., Mendez, A. S., Paton, A. W., Paton, J. C., Walter, P., and Ashkenazi, A. (2014) Cell death. Opposing unfolded-protein-response signals converge on death receptor 5 to control apoptosis, Science, 345, 98–101.
Holland, P. M. (2014) Death receptor agonist therapies for cancer, which is the right TRAIL? Cytokine Growth Factor Rev., 25, 185–193.
MacFarlane, M., Inoue, S., Kohlhaas, S. L., Majid, A., Harper, N., Kennedy, B. D., Dyer, M. J., and Cohen, G. M. (2005) Chronic lymphocytic leukemic cells exhibit apoptotic signaling via TRAIL-R1, Cell Death Differ., 12, 773–782.
Kabore, A. F., Sun, J., Hu, X., Mc Crea, K., Johnston, J. B., and Gibson, S. B. (2006) The TRAIL apoptotic pathway mediates proteasome inhibitor induced apoptosis in primary chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells, Apoptosis, 11, 1175–1193.
Bychkov, M. L., Gasparian, M. E., Dolgikh, D. A., and Kirpichnikov, M. P. (2014) Combination of TRAIL with bortezomib shifted apoptotic signaling from DR4 to DR5 death receptor by selective internalization and degradation of DR4, PLoS One, 19, e109756.
Herbst, R. S., Eckhardt, S. G., Kurzrock, R., Ebbinghaus, S., O’Dwyer, P. J., Gordon, M. S., Novotny, W., Goldwasser, M. A., Tohnya, T. M., Lum, B. L., Ashkenazi, A., Jubb, A. M., and Mendelson, D. S. (2010) Phase I doseescalation study of recombinant human Apo2L/TRAIL, a dual proapoptotic receptor agonist, in patients with advanced cancer, J. Clin. Oncol., 28, 2839–2846.
Bosman, M. C., Reis, C. R., Schuringa, J. J., Vellenga, E., and Quax, W. J. (2014) Decreased affinity of recombinant human tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (rhTRAIL) D269H/E195R to osteoprotegerin (OPG) overcomes TRAIL resistance mediated by the bone microenvironment, J. Biol. Chem., 289, 1071–1078.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Published in Russian in Biokhimiya, 2015, Vol. 80, No. 8, pp. 1298–1311.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gasparian, M.E., Bychkov, M.L., Yagolovich, A.V. et al. Mutations enhancing selectivity of antitumor cytokine TRAIL to DR5 receptor increase its cytotoxicity against tumor cells. Biochemistry Moscow 80, 1080–1091 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0006297915080143
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0006297915080143