Abstract
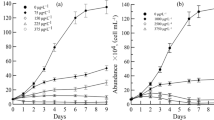
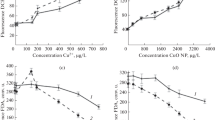
Effect of colloidal silver nanoparticles on growth and structure of laboratory populations was investigated in chlorococcal algae Scenedesmus quadricauda (Turp.) Bréb. and Monoraphidium arcuatum (Korsch.) Hind. in the range of concentrations from 0.0001 to 1 mg/L. The toxicity of colloidal silver was manifested at a concentration of 0.1 mg/L and higher and was associated with an algostatic effect, which duration directly depended on silver concentration in the medium. After a period of growth suppression at a concentration of 0.1 mg/L, in both species cell population in the culture was gradually recovered and the structure of population (ratio between the fractions of dividing, quiescent, and dead cells) became the same as in control material. The effect of adaptation of S. quadricauda to colloidal silver was detected upon successive passages to the media with toxic concentrations (0.1 and 0.5 mg/L), which depended on the concentration and duration of initial intoxication of the culture. The toxicity of cell-free filtrates from the culture of S. quadricauda, which was in contact with colloidal silver for different time periods, was estimated using intact culture of the same species, whose population on cell-free filtrates was close to control level. Transfer of the cells that were exposed to silver to a pure medium led to a long lag phase in all the cases. It is assumed that the main mechanism of algal population adaptation to higher concentrations (0.1 and 0.5 mg/L) of this toxicant depends on the selection of resistant cells present in the initial heterogeneous population in the course of primary exposure to colloidal silver. These resistant cells accidentally emerge in the population by means of rare spontaneous mutations occurring in the course of replication even before the contact with silver and have more perfect mechanisms of its detoxification.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AgNP:
-
silver nanoparticles
References
Wise, J.P., Sr., Goodale, B.C., Wise, S.S., Craig, G.A., Pongan, A.F., Walter, R.B., Thompson, W.D., Ng, A.K., Aboueissa, A.M., Mitani, H., Spalding, M.J., and Mason, M.D., Silver nanospheres are cytotoxic and genotoxic to fish cells, Aquat. Toxicol., 2010, vol. 97, pp. 34–41.
Piccapietra, F., Allué, C.G., Sigg, L., and Behra, R., Intracellular silver accumulation in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii upon exposure to carbonate coated silver nanoparticles and silver nitrate, Environ. Sci. Technol., 2012, vol. 46, p. 7390.
Navarro, E., Piccapietra, F., Wagner, B., Marconi, F., Kaegi, R., and Odzak, N., Toxicity of silver nanoparticles to Chlamydomonas reinhardtii, Environ. Sci. Technol., 2008, vol. 42, pp. 8959–8964.
Miao, A.J., Schwehr, K.A., Xu, C., Zhang, S.J., Luo, Z.P., Quigg, A., and Santschi, P.H., The algal toxicity of silver engineered nanoparticles and detoxification by exopolymeric substances, Environ. Pollut., 2009, vol. 157, pp. 3034–3041.
Miao, A.J., Luo, Z.P., Chen, C.S., Chin, W.C., Santschi, P.H., and Quigg, A., Intracellular uptake: a possible mechanism for silver engineered nanoparticle toxicity to a freshwater alga Ochromonas danica, Plos One, 2010, vol. 5: e15196.
Oukarroum, A., Barhoumi, L., Pirastru, L., and Dewez, D., Silver nanoparticle toxicity effect on growth and cellular viability of the aquatic plant Lemna gibba, Environ. Toxicol. Chem., 2013, vol. 32, pp. 902–907.
Oukarroum, A., Bras, S., Perreault, F., and Popovic, R., Inhibitory effects of silver nanoparticles in two green algae, Chlorella vulgaris and Dunaliella tertiolecta, Ecotox. Environ. Safe., 2012, vol. 78, pp. 80–85.
Navarro, E., Baun, A., Behra, R., Hartmann, N.B., Filser, J., Miao, A.J., Quigg, A., Santschi, P.H., and Sig, L., Environmental behavior and ecotoxicity of engineered nanoparticles to algae, plants, and fungi, Ecotoxicology, 2008, vol. 17, pp. 372–386.
Moore, M.N., Do nanoparticles present ecotoxicological risks for the health of the aquatic environment? Environ. Int., 2006, vol. 32, pp. 967–976.
Klaine, S.J., Alvarez, P.J.J., Batley, G.E., Fernandes, T.F., Handy, R.D., Lyon, D.Y., Mahendra, S., McLaughlin, M.J., and Lead, J.R., Nanomaterials in the environment: behavior, fate, bioavailability, and effects, Environ. Toxicol. Chem., 2008, vol. 27, pp. 1825–1851.
Hu, X., Cook, S., Wang, P., and Hwang, H.M., In vitro evaluation of cytotoxicity of engineered metal oxide nanoparticles, Sci. Total Environ., 2009, vol. 407, pp. 3070–3072.
Szivák, I., Behra, R., and Sigg, L., Metal-induced reactive oxygen species production in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii (Chlorophyceae), J. Phycol., 2009, vol. 45, pp. 427–435.
De Lima, R., Seabra, A.B., and Durán, N., Silver nanoparticles: a brief review of cytotoxicity and genotoxicity of chemically and biogenically synthesized nanoparticles, J. Appl. Toxicol., 2012, vol. 32, pp. 867–879.
Ratte, H.T., Bioaccumulation and toxicity of silver compounds: a review, Environ. Sci. Technol., 1999, vol. 18, pp. 89–108.
Fortin, C. and Campbell, P.G.C., Silver uptake by the green alga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii in relation to chemical speciation: influence of chloride, Environ. Toxicol. Chem., 2000, vol. 19, pp. 2769–2778.
Tsarenko, P.M., Kratkii opredelitel’ Khlorokokkovykh vodoroslei Ukrainskoi SSR (A Short Guide to Chlorococcales Algae), Kiev: Nauk. dumka, 1990.
Spirkina, N.E., Ipatova, V.I., Dmitrieva, A.G., and Filenko, O.F., Comparative dynamics of the growth of microalgae cultures Monoraphidium arcuatum (Korsch.) Hind. and Scenedesmus quadricauda (Turp.) Bréb., Byull. Mosk. Ob-va Ispytat. Prirody, 2014, vol. 119, no. 2, pp. 64–69.
Filenko, O.F., Dmitrieva, A.G., and Marushkina, E.V., Evaluation of the effect of copper on the model algal population Scenedesmus quadricauda (Turp.) Bréb. using the microculture method, Gidrobiol. Zh., 2007, vol. 42, no. 6, pp. 53–61.
Hoffmann, A.A. and Parsons, P.A., Evolutionary Genetics and Environmental Stress, Oxford: Oxford University Press, 1993.
Ipatova, V.I., Prokhotskaya, V.Yu., and Dmitrieva, A.G., Structural changes and adaptation of algal population under different regimens of toxic exposure, Unifying Themes in Complex Systems. VII. Proc. 7th Int. Conf. Complex Systems, Minai, A.A., Braha, D., and Bar-Yam, Y., Eds., Springer, 2012, pp. 149–156.
Ipatova, V.I., Adaptation of aquatic plant organisms to chemical pollution, Ekologicheskie Sistemy i Pribory, 2013, no. 3, pp. 47–53.
López-Rodas, V., Agrelo, M., Carrillo, E., Ferrero, L.M., Larrauri, A., Martín-Otero, L., and Costas, E., Resistance of microalgae to modern water contaminants as the result of rare spontaneous mutations, Eur. J. Phycol., 2001, vol. 36, pp. 179–190.
Flores-Moya, A., Costas, E., Bañares-España, E., García-Villada, L., Altamirano, M., and López-Rodas, V., Adaptation of Spirogyra insignis (Chlorophyta) to an extreme natural environment (sulphureous waters) through preselective mutations, New Phytol., 2005, vol. 165, pp. 655–661.
Sanita di Toppi, L., Pawlik-Skowrońska, B., Vurro, E., Vattuone, Z., Kalinowska, R., Restivo, F.M., Musetti, R., and Skowroński, T., First and second line mechanisms of cadmium detoxification in the lichen photobiont Trebouxia impressa (Chlorophyta), Environ. Pollut., 2008, vol. 151, pp. 280–286.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © V.I. Ipatova, N.E. Spirkina, A.G. Dmitrieva, 2015, published in Fiziologiya Rastenii, 2015, Vol. 62, No. 2, pp. 273–282.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ipatova, V.I., Spirkina, N.E. & Dmitrieva, A.G. Resistance of microalgae to colloidal silver nanoparticles. Russ J Plant Physiol 62, 253–261 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1021443715010082
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1021443715010082