Abstract
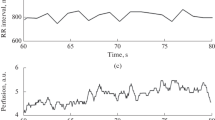
Laser Doppler flowmetry with wavelet analysis, spectrophotometry, computer-aided capillaroscopy, and thermometry were used to study cardiac and respiratory oscillations of the blood flow in the skin microvessels of 30 subjects. The amplitudes of the cardiac and respiratory rhythms (Ac and Ar, respectively) were found to be determined predominantly by the distribution of perfusion and pressure in larger vessels (arterioles and venules). The cardiorespiratory coupling is a regulatory factor in the microcirculatory system; at rest, the value of Ac/Ar reflects the capillary arteriovenous ratio. In the structure of the microcirculation index (MI) and Ac, the velocity-to-volume ratio depends on the perfusion of the corresponding skin region: at rest, the volume-related component is expressed only in the skin with arteriolovenular anastomoses, whereas, in the skin without these anastomoses, MI and Ac are predominantly correlated with the dynamic velocity-related component. Ac is inversely dependent on both stationary and oscillatory components of the microvascular tone. The nature of the respiratory wave depends not only on the respiratory modulation of the venous outflow, but also on the perfusion pressure in the microvessels and venular hematocrit. The correlation of Ar with the total blood flow in the skin microvessels and the individual contributions of velocity-and volume-related components to Ar were significant only in situations where the blood flow was above a certain threshold, below which the respiratory waves can penetrate into the microvessels but their correlation with the total perfusion is nonsignificant.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Stefanovska, A. and Bracic, M., Physics of Human Cardiovascular System, Contemp. Phys., 1999, vol. 40, no. 1, p. 31.
Caro, C.G., Pedley, T.J., Schroter, R.C., and Seed, W.A., The Mechanics of the Circulation, New York: Oxford Univ. Press, 1978, p. 606.
Folkow, B. and Neil, E., Circulation, New York: Oxford Univ. Press, 1971, p. 431.
Levtov, V.A. and Regirer, S.A., Pulse Oscillation in Arteries, in Tkachenko, B.I., Ed., Rukovodstvo po fiziologii. Fiziologiya krovoobrashcheniya: fiziologiya sosudistoi sistemy (Handbook of Physiology. Physiology of Circulation: Physiology of the Vascular System), Leningrad: Nauka, 1984, p. 104.
Krupatkin, A.I., Dynamic Oscillatory Circuit of Regulation of Capillary Hemodynamics, Fiziol. Chel., 2007, vol. 33, no. 5, p. 93 [Hum. Physiol. (Engl. Transl.), 2007, vol. 33, no. 5, p. 595].
Krupatkin, A.I. and Sidorov, V.V., Eds., Laser Doppler Flowmetry of the Blood Microcirculation. A Handbook for Phisicians, Moscow: Meditsina, 2005, p. 256.
Bollinger, A., Yanar, A., Hoffmann, U., and Franzeck, U.K., Is a High-Frequency Flux Motion Due to Respiration or to Vasomotion Activity? In Allegra, C., Intaglietta, M., and Messmer, K., Eds., Vasomotion and Flow Motion, Prog. Appl. Microcirc., Basel: Karger, 1993, vol. 20, p. 52.
Muck-Weymann, M.E., Albrecht, H.P., Hiller, D., et al., Breath-Dependent Laser Doppler Flux Motion in the Skin, Vasa, 1994, no. 4, p. 229.
Krupatkin, A.I., The Influence of the Sympathetic Innervation on the Skin Microvascular Tone and Blood Flow Oscillations, Fiziol. Chel., 2006, vol. 32, no. 5, p. 95 [Hum. Physiol. (Engl. Transl.), 2006, vol. 32, no. 5, p. 584].
Krupatkin, A.I., Influence of Sensory Peptidergic Innervation on Human Skin Blood Flow Oscillations in the Range 0.047–0.069 Hz, Fiziol. Chel., 2007, vol. 33, no. 3, p. 48 [Hum. Physiol. (Engl. Transl.), 2007, vol. 33, no. 3, p. 296].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Original Russian Text © A.I. Krupatkin, 2008, published in Fiziologiya Cheloveka, 2008, Vol. 34, No. 3, pp. 70–76.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Krupatkin, A.I. Cardiac and respiratory oscillations of the blood flow in microvessels of the human skin. Hum Physiol 34, 323–329 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0362119708030092
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0362119708030092