Abstract
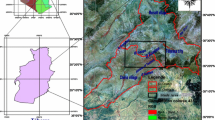
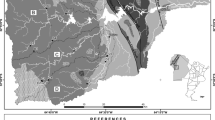
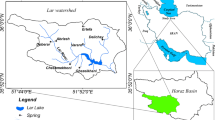
Syri i Kalter (“Blue Eye” in english) is the name of the largest spring of Albania, situated in the south of the country, not far from the town of Sarande. The spring is located near the tectonic contact between the Mesozoic-Paleogenic Mali i Gjiere carbonate sequence and the Terziary flysch units of the “Ionian Zone” of Albania. The discharge area is characterized by the presence of Triassic evaporites, mainly constituted by gypsum and anhydrite, associated with clay, limestones, dolomite and halite. The spring consists of several discharge points, yielding as a whole an average water flow of about 11 m3/s.
Analyses of water samples from the spring show relatively high concentrations of calcium, sulphate and alkalinity, with a minor magnesium content and low concentrations of alkali-ions and chloride. Analogous composition results in samples from the Bistrica river, which is fed by the groundwater discharging from the spring. From the geological features of the area, it can be expected that minerals within the aquifer are represented mainly by calcite, dolomite and, close to the discharge point, by gypsum and anhydrite. Calculation of minerals equilibria displays that all samples are undersaturated with respect to gypsum, and oversaturated with respect to calcite. In these conditions, incongruent dissolution of dolomite (dedolomitization) is likely to occur. According to this process, the analytical Mg/Ca ratios match to the oversaturation state with respect to calcite and to the equilibrium with dolomite.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Appelo, C.A.J., and Postma, D., Geochemistry, Groundwater and Pollution, Rotterdam: Balkema, 2005.
Back, W. and Hanshaw, B.B., Journal of Hydrology, 1970, no. 10, pp. 30–368.
Donald Langmuir. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1971, vol. 35, pp. 1023–1045.
Eftimiu R., Tafilaj J., Bisha G. Short notes on Hydrogeological Map of PSR of Albania, scale 1: 200000, Tirana: Albanian Hydrogeological Service, 1985, pp. 1–12.
Holland H.D., Kirsipu T.V., Huebner J.S., Oxburn U.M. Journal of Geology, 1964, no. 72, pp. 6–67.
Meco S., Aliaj S. Geology of Albania, Berlin; Stuttgart: Gebruder Borntraeger, 2000, P. 1–231.
Plummer L.N., Busby J.F., Lee R.W., Hanshaw B.B. Water Resources Research, 1990, vol. 26, no. 9, pp. 1981–2014.
Robertson A., Shallo M. Tecntonophysics, 2000, no. 316, pp. 197–254.
Sherman L.A., Barak P. Soil Science Society of America Journal, vol. 64, pp. 1959–1968.
Wigley T.M.L. Canadian Journal of Earth Science, 197, no. 10, pp. 306–315.
Wigley T.M.L. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 1973, vol. 37, pp. 1397–1402.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
The article is published in the original.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Baldassare, G., Pagliarulo, P. & Zuffianò, L.E. Water composition and minerals equilibria at the Syri i Kalter spring and in the Bistrica river (South Albania). Water Resour 38, 662–669 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0097807811050022
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0097807811050022