Abstract
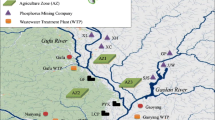
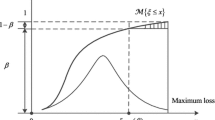
The possibility-probability risk calculated using the interior-outer set model is referred to as fuzzy risk. A fuzzy expected value of the possibility-probability distribution is a set with E α(x) and \(\bar E_\alpha \)(x) as its boundaries. The fuzzy expected values E α(x) and \(\bar E_\alpha \)(x) of a possibility-probability distribution represent the fuzzy risk values being calculated. Under such an α level, three risk values can be calculated: conservative risk value, venture risk value and maximum probability risk value. As α adopts all values throughout the set [0, 1], it is possible to obtain a series of risk values. Therefore, the fuzzy risk can be a multi-valued risk or set-valued risk. Calculation of the fuzzy expected value of Yiwu city’s water resource risk has been performed based on the interior-outer set model. We can get a conservative risk value (R C ) of 800 mm for Yiwu city’s water resource risk, a venture risk value (R V ) of 1020 mm, and a maximum probability risk value (R M ) of 988 mm for the α = 0.1 level cut set.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allahviranloo, T., Successive Over Relaxation Iterative Method for Fuzzy System of Linear Equations, Applied Mathematics and Computation, 2005, vol. 162, no. 1, pp. 189–196.
Alsharif, K., Feroz, E.H., Klemer, A., and Raab, R., Governance of Water Supply Systems in the Palestinian Territories: A Data Envelopment Analysis Approach To the Management of Water Resources, Journal of Environmental Management, 2008, vol. 87, no. 1, pp. 80–94.
Cazurra, T., Water Reuse of South Barcelona’s Wastewater Reclamation Plant, Desalination, 2008, vol. 218, nos. 1–3, pp. 43–51.
Delgado, M., Vgay, J.L., and Vila, M.A., A Model for Linguistic Partial Information in Decision-Making Problems, Intern. Journal of Intelligent System, 1994, vol. 9, pp. 365–378.
Dikmen, I., Birgonul, M.T., and Han, S., Using Fuzzy Risk Assessment to Rate Cost Overrun Risk in International Construction Projects, Intern. Journal of Project Management, 2007, vol. 25, no. 5, pp. 494–505.
Elsalamony, G., A Note on Fuzzy Neighbourhood Base Spaces, Fuzzy Sets and Systems, 2006, vol. 157, no. 20, pp. 2725–2738.
Feng, L.H. and Zhang, X.C., Quantitative Expression on Drought Magnitude and Disaster Intensity, Natural Hazards and Earth System Sciences, 2005, vol. 5, no. 4, pp. 495–498.
Hajkowicz, S. and Higgins, A., A Comparison of Multiple Criteria Analysis Techniques for Water Resource Management, European Journal of Operational Research, vol. 184, no. 1, pp. 255–265.
Huang, C.F., Concepts and Methods of Fuzzy Risk Analysis, Proc. of the First China-Japan Conference on Risk Assessment and Management, Beijing: Intern. Academic Publishers, 1998, pp. 12–23.
Huang, C.F., Moraga, C., and Chen, Z.F., A Simple Algorithm of Interior-Outer Set Model, Journal of Natural Disasters, 2004, vol. 13, no. 4, pp. 15–20.
Huang, C.F., and Shi, Y., Towards Efficient Fuzzy Information Processing—Using the Principle of Information Diffusion, Heidelberg: Physica-Verlag (Springer), 2002.
Joblonowski, M., Fuzzy Risk Analysis, Using AI Systems, AI Expert, 1994, vol. 9, no. 12, pp. 34–37.
Karimi, I. and Hullermeier, E., Risk Assessment System of Natural Hazards: A New Approach Based on Fuzzy Probability, Fuzzy Sets and Systems, 2007, vol. 158, no. 9, pp. 987–999.
Machias, A.V. and Skikos, G.D., Fuzzy Risk Index of Wind Sites, IEEE Transactions on Energy Conversion, 1992, vol. 7, no. 4.
Matos, M.A., Decision under Risk as a Multicriteria Problem, European Journal of Operational Research, 2007, vol. 181, no. 3, pp. 1516–1529.
Moraga, C., and Huang, C.F., Learning Subjective Probabilities from a Small Data Set, Proc. of 33rd Intern. Sympos. on Multiple-Value Logic, IEEE Computer Society, Los Alamitos, 2003, pp. 355–360.
Reyna, V.F., and Brainerd, C.J., Numeracy, Ratio Bias, and Denominator Neglect in Judgments of Risk and Probability, Learning and Individual Differences, 2008, vol. 18, no. 1, pp. 89–107.
Riecan, B., On the Dobrakov Submeasure on Fuzzy Sets, Fuzzy Sets and Systems, 2005, vol. 151, no. 3, pp. 635–641.
Schmucker, K.J., Fuzzy Sets, Natural Language Computations, and Risk Analysis, Rockvill: Computer Science Press, 1984.
Thavaneswaran, A., Thiagarajah, K., and Appadoo, S.S., Fuzzy Coefficient Volatility (FCV) Models with Applications, Mathematical and Computer Modeling, 2007, vol. 45, nos. 7–8, pp. 777–786.
Wu, H.C., Using Fuzzy Sets Theory and Black-Scholes Formula to Generate Pricing Boundaries of European Options, Applied Mathematics and Computation, 2007, vol. 185, no. 1, pp. 136–146.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
The article is published in the original.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Feng, L.H., Luo, G.Y. Application of possibility-probability distribution in assessing water resource risk in Yiwu city. Water Resour 38, 409–416 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1134/S009780781103002X
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S009780781103002X