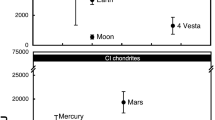
Abstract
A summary is given of the literature data on the content of volatiles in the lunar regolith, the characterization of the likely sources of the volatiles, and the possible processes of their migration and burial. The main sources of volatiles in the regolith are the solar wind, small Solar System bodies (comets and meteorites), and the lunar interior. Different sources are the leading ones for different volatiles. Water and other volatiles can accumulate on the surface and in the near-surface layers of the Moon only in the so-called cold traps in polar basins, where other volatiles, as well as water ice, including highly toxic elements such as mercury and cadmium must be accumulated. The content of volatiles in the lunar interior is comparable to that in terrestrial rocks. Water could have played an important role in the early stages of the Moon’s history, e.g., in the formation of mare basalts. The isotopic composition of the lunar juvenile water is similar to that on the Earth, which suggests a common origin of the terrestrial and lunar water.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akhmanova, M.V., Dement’ev, B.V., and Markov, M.N., Water in Mare Crisium regolith (Luna 24), Geokhimiya, 1978, no. 2, pp. 285–288.
Alter, D., The Kozyrev observations of Alphonsus, Publ. Astron. Soc. Pacific, 1959, vol. 71, no. 418, p. 46.
Anand, M., Lunar water: a brief review, Earth, Moon Planets, 2010, vol. 107, pp. 65–73.
Anand, M., Tartèse, R., Barnes, J.J., et al., Abundance, distribution, and isotopic composition of water in the Moon as revealed by basaltic lunar meteorites, Lunar Planet. Sci., 2013, vol. 44, Abstract no. 1957.
Arnold, J.R., Ice in the lunar polar region, J. Geophys. Res., 1979, vol. 84, pp. 5659–5668.
Artemieva, N.A. and Shuvalov V.V., Numerical simulation of high-velocity impact ejecta following falls of comets and asteroids onto the Moon, Solar Syst. Res., 2008, vol. 42, no. 4, pp. 329–334.
Barnes, J.J., Anand, M., Franchi, I.A., et al., The hydroxyl content and hydrogen isotope composition of lunar apatite, Lunar Planet. Sci., 2012, vol. 43, Abstract no. 1757.
Basilevsky, A.T., Abdrakhimov, A.M., and Dorofeeva, V.A., Water and other volatiles on the Moon: a review, Solar Syst. Res., 2012, vol. 46, no. 2, pp. 89–107.
Becker, R.H., Clayton, R.N., and Mayeda, T.K., Characterization of lunar nitrogen compounds, Proc. 7th Conf. Lunar Sci., Houston, 1976, pp. 441–458.
Becker, R.H., Light elements in lunar soils revisited: carbon, nitrogen, hydrogen, and helium, Proc. 11th Conf. Lunar Planet. Sci., Houston, 1980, pp. 1743–1761.
Bell, D.R. and Rossman, G.R., Water in Earth’s mantle: the role of nominally anhydrous minerals, Science, 1992, vol. 255, no. 5056, pp. 1391–1397.
Belyaev, Yu.I. and Koveshnikova, T.A., Mercury content in Mare Fecunditatis, Mare Tranquillitatis and Oceanus Procellarum regolith, in Lunnyi grunt iz Morya Izobiliya (Lunar Soil from Mare Fecunditatis), Moscow: Nauka, 1974, pp. 335–338.
Belyaev, Yu.I. and Koveshnikova, T.A., Mercury content in continental (Luna-20) and sea (Luna-16) regolith, in Grunt iz materikovogo raiona Luny (Soil from Lunar Continental Area), Moscow: Nauka, 1979, pp. 468–469.
Bogard, D.D. and Hirsch, W.C., Noble gas studied on grain size separated of Apollo 15 and 16 deep drill cores, Proc. 6th Conf. Lunar Sci., Houston, 1975, pp. 2057–2083.
Boyce, J.W., Liu, Y., Rossman, G.R., et al., Lunar apatite with terrestrial volatile abundances, Nature, 2010, vol. 466, no. 7305, pp. 466–469.
Butler, P., Jr. and Meyer, C., Sulfur prevails in coatings on glass droplets: Apollo 15 green and brown glasses and Apollo 17 orange and black (devitrified) glasses, Proc. 7th Conf. Lunar Sci., Houston, 1976, pp. 1561–1581.
Chou, C.-L., Boynton, W.V., Sundberg, L.L., and Wasson, J.T., Volatiles on the surface of Apollo 15 green glass and trace-element distributions among Apollo 15 soils, Proc. 6th Conf. Lunar Sci., Houston, 1975, pp. 1701–1727.
Cirlin, E.N., Housley, R.M., and Grant, R.W., Studied of volatiles in Apollo 17 samples and their implication to vapor transport processes, Proc. 9th Conf. Lunar Planet. Sci., 1978, pp. 2049–2063.
Colaprete, A. and Schultz, P.H., Heldmann, J., et al., Detection of water in the LCROSS ejecta plume, Science, 2010, vol. 330, pp. 463–468.
Crotts, A.P.S., Lunar outgassing, transient phenomena, and the return to the Moon. I. Existing data, Astrophys. J., 2008, vol. 687, pp. 692–705.
Crotts, A.P.S. and Hummels, C., Lunar outgassing, transient phenomena, and the return to the Moon. II. Predictions and tests for outgassing/regolith interactions, Astrophys. J., 2009, vol. 707, pp. 1506–1523.
Delano, J., Pristine lunar glasses: criteria, data, and implications, Proc. 16th Conf. Lunar Planet. Sci., 1986, pp. D201–D213.
Delano, J.W., Hanson, B.Z., and Watson, W.B., Abundance and diffusivity of sulfur in lunar picritic magmas, Lunar Planet. Sci., 1994, vol. 38, pp. 325–326.
Dikov, Yu.P., Bogatikov, O.A., Barsukov, V.L., et al., Chemical peculiarities of particles surface layers of some Apollo 17 regolith samples, Proc. 10th Conf. Lunar Planet. Sci., 1979, pp. 1491–1505.
Eberhardt, P., Geiss, J., Graf, H., et al., Trapped solar wind noble gases, exposure age and K/Ar-age in Apollo 11 lunar fine material, Proc. Apollo 11 Lunar Sci. Conf., Houston, 1970a, pp. 1037–1070.
Eberhardt, P., Geiss, J., Graf, H., et al., Trapped solar wind noble gases, Kr81/Kr exposure ages and K/Ar ages in Apollo 11 lunar material, Science, 1970b, vol. 167, pp. 558–560.
Eberhardt, P., Geiss, J., Grögler, N., et al., 40Ar-39Ar ages of lunar material, Meteoritics, 1973, vol. 8, pp. 360–361.
Epstain, S. and Taylor, H.P., Jr., 180/160, 30Si/28Si, D/H, and 13C/12C studies of lunar rocks and minerals, Science, 1970, vol. 167, pp. 533–535.
Eugster, O. and Niedermann, S., Trapped Xe isotopically different from modern solar wind Xe in lunar breccia 60018 and black glass 74001, Lunar Planet. Sci., 1987, vol. 18, pp. 275–276.
Fegley, B., Jr. and Swingle, T.D., Lunar volatiles: implications for lunar resource utilization, in Resources of Near-Earth Space, Lewis, J., Matthews, M.S., and Guerrieri, M.L., Eds., Univ. Arizona Press, 1993, pp. 367–426.
Florensky, K.P., Basilevsky, A.T., and Ivanov, A.V., Role of exogenous factors in Moon surface formation, in Kosmokhimiya Luny i planet (Lunar and Planets Cosmochemistry), Moscow: Nauka, 1975, pp. 439–452.
Florensky, K.P., Basilevsky, A.T., Burba, G.A., et al., Ocherki sravnitel’noi planetologii (Reviews of Comparative Planetary Science), Moscow: Nauka, 1981.
Fogel, R.A. and Rutherford, M.J., Magmatic volatiles in primitive lunar glasses: I. FTIR and EPMA analyses of Apollo 15 green and yellow glasses and revision of the volatile-assisted fire-fountain theory, Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta, 1995, vol. 59, no. 1, pp. 201–215.
Friedman, B., Saal, A.E., Hauri, E.H., et al., The volatile content of the Apollo 15 picritic glasses, Lunar Planet Sci. Conf., Houston, 2009, vol. 40, Abstract no. 2444.
Gaddis, L.R., Staid, M.I., Tyburczy, J.A., et al., Compositional analyses of lunar pyroclastic deposits, Icarus, 2003, vol. 161, pp. 262–280.
Galimov, E.M., On the Lunar matter origin, Geokhimiya, 2004, no. 7, pp. 691–706.
Gault, D.E., Hérz, F., Brownlee, D.W., and Hartung, J.B., Mixing of the lunar regolith, Proc. 5th Conf. Lunar Sci., 1974, pp. 2365–2386.
Gibson, E.K., Jr. and Bustin, R., Hydrogen abundances vs. depth in the lunar regolith: results from an Apollo double drive tube and deep drill core, Proc. 18th Conf. Lunar Planet. Sci., Houston, 1987, pp. 324–325.
Gladstone, G.R., Hurley, D.M., Retherford, K.D., et al., LRO-LAMP observations of the LCROSS impact plume, Science, 2010, vol. 330, pp. 472–476.
Greenwood, J.P., Itoh, S., Sakamoto, N., et al., Water in Apollo rock samples and the D/H of lunar apatite, Lunar Planet. Sci., 2010, vol. 41, Abstract no. 2439.
Greenwood, J.P., Itoh, S., Sakamoto, N., et al., Origin of lunar water and evidence for a wet Moon from D/H and water in lunar apatites, Lunar Planet. Sci., 2011a, vol. 42, Abstract no. 3753.
Greenwood, J.P., Itoh, S., Sakamoto, N., et al., Hydrogen isotope ratios in lunar rocks indicate delivery of cometary water to the Moon, Nature Geosci., 2011b, vol. 4, pp. 78–82.
Grieve, R.A.F. and Cintala, M.J., Planetary impacts, in Encyclopedia of the Solar System, Weissman, P.R., McFadden, L.-A., and Johnson, T.R., Eds., Acad. Press, 1999, pp. 845–876.
Hartmann, W., Relative crater production rates on planets, Icarus, 1977, vol. 31, pp. 260–276.
Hartogh, P., Lis, D.S., Bockelee-Morvan, D., et al., Ocean-like water in the Jupiter-family comet 103P/Hartley 2, Nature, 2011, vol. 478, pp. 218–220.
Haskin, L. and Warren, P., Lunar chemisry, in Lunar Sourcebook. A User’s Guide to the Moon, Heiken, G.H., Vaniman, D.T., and French, B.M., Eds., New York: Cambridge Univ. Press, 1991, pp. 357–474.
Hauri, E.H., Saal, A.E., Van Orman, J., et al., New estimates of the water content of the Moon from Apollo 15 picritic glasses, Lunar Planet. Sci., 2009, vol. 40, Abstract no. 2344.
Hauri, E.H., Weinreich, T., Saal, A.E., et al., High preeruptive water contents preserved in lunar melt inclusions, Science, 2011, vol. 333, pp. 213–215.
Hayne, P.O., Greenhagen, B.T., Foote, M.C., et al., Diviner lunar radiometer observations of the LCROSS impact, Science, 2010, vol. 330, pp. 477–479.
Head, J.W. III and Wilson, L., Alphonsus-type dark-halo craters: morphology, morphometry, and eruption conditions, Proc. 10th Conf. Lunar Planet. Sci., Houston, 1979, pp. 2861–2897.
Herschel, W. and Bank, J., A account of three volcanos in the Moon by William Herschel, L.L. D. F.R.S.; Communicated by Sir Joseph Banks, Bart, P.R.S., Phil. Trans. Roy. Soc. London, 1787, vol. 77, pp. 229–232.
Hess, P.C., Petrogenesis of lunar troctolites, J. Geophys. Res. Planets, 1994, vol. 99, no. E9, pp. 19083–19093.
Housley, R.M., Grant, R.W., and Paton, N.E., Origin and characteristics of excess Fe metal in lunar glass welded aggregates, Proc. 4th Conf. Lunar Sci., Houston, 1973, pp. 2737–2749.
Housley, R.M., Cirlin, E.H., Paton, N.E., and Goldberg, I.B., Solar wind and micrometeorite alteration of the lunar regolith, Proc. 5th Conf. Lunar Sci., Houston, 1974, pp. 2623–2642.
Hui, H., Peslier, A.H., Zhang, Y., and Neal, C.R., Water in lunar anorthosites and evidence for a wet early Moon, Nature Geosci., 2013, vol. 6, pp. 177–181.
Huneke, J.C., Jessberger, E.K., Podosek, F.A., and Wasserburg, G.J., 40Ar/39Ar measurements in Apollo 16 and Apollo 17 samples and the chronology of metamorphic and volcanic activity in the Taurus-Littrow region, Proc. 4th Conf. Lunar Sci., Houston, 1973, pp. 1725–1756.
Ingersoll, AP., Svitek, T., and Murray, B.C., Stability of polar frost in spherical bowl-shaped craters on the Moon, Mercury, and Mars, Icarus, 1992, vol. 100, pp. 40–47.
Jovanovich, S. and Reed, G.W., Jr., Regolith layering processes based on studies of low-temperature volatile elements in Apollo core samples, Proc. 10th Conf. Lunar Sci., 1979, pp. 1425–1435.
Kerridge, J.F., What has caused the secular increase in solar nitrogen-15?, Science, 1989, vol. 245, pp. 480–486.
Khisina, N.R., Wirth, R., and Nazarov, M., Lamellar spinel-pyroxene symplectites in lunar olivine: evidence for H2O traces in lunar magmas?, Meteorit. Planet. Sci., 2009, vol. 11,Suppl., p. A109.
Khisina, N.R., Wirth, R., Abart, R., et al., Oriented chromite-diopside symplectic inclusions in olivine from lunar regolith delivered by Luna-24 mission, Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta, 2013, vol. 104, pp. 84–98.
Kozyrev, N.A., Observation of a volcanic process on the Moon, Sky Telescope, 1959, vol. 18, p. 184.
Kozyrev, N.A., Spectroscopic proofs for existence of volcanic process on the Moon, in The Moon, Kopal, Z. and Mikhailov, Z., Eds., London-New York: Acad. Press, 1962, pp. 263–271.
Kozyrev, N., Volcanic phenomena on the Moon, Nature, 1963, vol. 198, no. 4884, pp. 979–980.
Kyte, F.T. and Wasson, J.T., Accretion rate of extraterrestrial matter-iridium deposited 33 to 67 million years ago, Science, 1986, vol. 232, pp. 1225–1229.
Liu, Y., Boyce, J.W., Rossman, G.R., et al., Water in lunar mare basalt: confirmation from apatite in lunar basalt 14053, Lunar Planet. Sci., 2010, vol. 41, Abstract no. 2647.
Liu, Y., Guan, Y., Zhang, Y., et al., Lunar surface water in agglutinates: origin and abundances, Lunar Planet. Sci., 2012a, vol. 43, Abstract no. 1864.
Liu, Y., Guan, Y., Zhang, Y., et al., Direct measurement of hydroxyl in the lunar regolith and the origin of lunar surface water, Nature Geosci., 2012b, vol. 5, pp. 779–782.
Liu, Y., Mosenfelder, J.L., Guan, Y., et al., SIMS analysis of water abundances in nominally anhydrous minerals in lunar basalts, Lunar Planet. Sci., 2012c, vol. 43, Abstract no. 1866.
Lloyd, A.S., Plank, T., Ruprecht, P., et al., Volatile loss from melt inclusions in pyroclasts of differind sizes, Contrib. Mineral. Petrol., 2013, vol. 165, pp. 129–153.
Love, S.G. and Brownlee, D.E., A direct measurement of terrestrial mass accretion rate of cosmic dust, Science, 1993, vol. 262, no. 5133, pp. 550–553.
LSPET (Lunar Science Preliminary Examination Team), Apollo 17 lunar samples: chemical and petrographic description, Science, 1973, vol. 182, no. 4113, pp. 659–672.
Lucey, P.G., Hawke, B.R., Pieters, C.M., et al., A compositional study of the Aristarchus region of the Moon using near-infrared reflectance spectroscopy, Proc. 16th Conf. Lunar and Planet. Sci., J. Geophys. Res., 1986, vol. 91, pp. D344–D354.
Lucey, P., The poles of the Moon, Elements, 2009, vol. 5, no. 1, pp. 41–46.
McCord, T.B., Taylor, L.A., Orlando, T.M., et al., Origin of OH/water on the lunar surface detected by the Moon Mineralogy Mapper, Lunar Planet. Sci., 2010, vol. 41, Abstract no. 1860.
McCord, T.B. and Combe, J.-Ph., Relationships of wide-spread OH presence in the lunar surface materials with lunar physical properties, Lunar Planet. Sci., 2011, vol. 42, Abstract no. 1483.
McCubbin, F.M., Steele, A., Nekvasil, H., et al., Detection of structurally bound hydroxyl in fluorapatite from Apollo mare basalt 15058.128 using TOF-SIMS, Amer. Mineral., 2010, vol. 95, pp. 1141–1150.
McCubbin, F.M., Jolliff, B.L., Nekvasil, H., et al., Fluorine and chlorine abundances in lunar apatite: implications for heterogeneous distributions of magmatic volatiles in the lunar interior, Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta, 2011, vol. 75, pp. 5073–5093.
McKay, D.S., Heiken, G., Basu, A., et al., The lunar regolith, in Lunar Sourcebook. A User’s Guide to the Moon, Heiken, G.H., Vaniman, D.T., and French, B.M., Eds., New York: Cambridge Univ. Press, 1991, pp. 283–356.
Meyer, C., Jr., McKay, D.S., Anderson, D.H., and Butler, P., Jr., The source of sublimates on the Apollo 15 green and Apollo 17 orange glass samples, Proc. 6th Conf. Lunar Sci., 1975, pp. 1673–1699.
Middlehurst, B.M., Lunar transient phenomena, Icarus, 1967a, vol. 6, pp. 140–142.
Middlehurst, B.M. and Moore, P.A., Lunar transient phenomena: topographical distribution, Science, 1967b, vol. 155, pp. 449–451.
Middlehurst, B.M., A survey of lunar transient phenomena, Phys. Earth Planet. Interiors, 1977, vol. 14, pp. 185–193.
Mironov, N.L. and Portnyagin, M.V., H2O and CO2 content in initial magmas of Klyuchevskoi volcano according to melted and fluidic inclusions in olivine, Geol. Geofiz., 2011, vol. 52, no. 11, pp. 1718–1735.
Morgan, T.H. and Shemansky, D.E., Limits to the lunar atmosphere, J. Geophys. Res., 1991, vol. 96, pp. 1351–1367.
Morris, R.V., Surface exposure indices of lunar rocks: a comparative FMR study, Proc. 7th Conf. Lunar Sci., 1976, pp. 315–335.
Ozima, M. and Podosek, F.A., Noble Gas Geochemistry, New York: Cambridge Univ., 1983.
Palme, H. and Beer, H., Abundances of the elements in the solar system, in Landolt-Børnstein, Group VI: Astronomy and Astrophysics: Instruments; Methods; Solar System, Voigt, H.H., Ed., Berlin: Springer, 1993, vol. 3(a), pp. 196–221.
Papike, J., Taylor, L., and Simon, S., Lunar minerals, in Lunar Sourcebook. A User’s Guide to the Moon, Heiken, G.H., Vaniman, D.T., and French, B.M., Eds., Cambridge: Univ. Press, 1991, pp. 121–182.
Pierazzo, E. and Melosh, H.J., Hydrocode modeling of oblique impacts: the fate of projectile, Meteorit. Planet. Sci., 2000, vol. 35, pp. 117–130.
Pieters, C.M., Goswami, J.N., Clark, R.N., et al., Character and spatial distribution of OH/H2O on the surface of the moon seen by M3 on Chandrayaan-1, Science, 2009, vol. 326, no. 5952, pp. 568–572.
Podosek, F.A. and Huneke, J.C., Argon in Apollo 15 green glass spherules (15426): 40Ar-39Ar age and trapped argon, Earth Planet. Sci. Lett., 1973, vol. 19, pp. 413–421.
Portnyagin, M., Almeev, R., Matveev, S., and Holtz, F., Experimental evidence for rapid water exchange between melt inclusions in olivine and host magma, Earth Planet. Sci. Lett., 2008, vol. 2008, pp. 541–552.
Rhodes, J.M., Rodgers, K.V., Shih, C., et al., The relationships between geology and soil chemistry at the Apollo 17 landing site, Proc. 5th Conf. Lunar Sci., Houston, 1974, pp. 1097–1117.
Rychagov, S.N., Nuzhdaev, A.A., and Stepanov, I.I., Hydrargyrum behavior in hypergenezis area of geothermal depositions (Southern Kamchatka), Geokhimiya, 2009, no. 5, pp. 533–542.
Saal, A.E., Hauri, E.H., Cascio, M.L., et al., Volatile content of lunar volcanic glasses and the presence of water in the Moon’s interior, Nature, 2008, vol. 454, no. 7201, pp. 192–195.
Saal, A.E., Hauri, E.H., Van Orman, J.A., and Rutherford, M.J., The volatile contents of the Apollo 15 lunar volcanic glasses, Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta Suppl., 2009, vol. 73, p. A1139.
Saal, A.E., Hauri, E.H., Van Orman, J.A., and Rutherford, M.J., D/H ratios of the lunar volcanic glasses, Lunar Planet. Sci., 2012, vol. 43, Abstract no. 1327.
Saal, A.E., Hauri, E.H., Van Orman, J.A., and Rutherford, M.J., Hydrogen isotopes in lunar volcanic glasses and melt inclusions reveal a carbonaceous chondrite heritage, Science, 2013, vol. 340, pp. 1317–1320. doi: 10.1126/science.1235142
Schultz, P.H., Hermalyn, B., Colaprete, A., et al., The LCROSS cratering experiment, Science, 2010, vol. 330, pp. 468–472.
Sharp, Z.D., McCubbin, F.M., and Shearer, C.K., A unifying theory for H-bearing volatiles on the Moon, Lunar Planet. Sci., 2012, vol. 43, Abstract no. 2751.
Shearer, C.K., Weidenbeck, M.G., Fowler, G.W., and Papike, J.J., S and other volatiles in lunar picritic magmas and the lunar mantle. An approach using secondary ion mass spectrometry, Lunar Planet. Sci., 1998, vol. 29, Abstract no. 1284.
Shearer, C.K., Hess, P.C., Wieczorek, M.A., et al., Thermal and magmatic evolution of the Moon, Rev. Mineral. Geochem., 2006, vol. 60, pp. 365–518.
Siegel, S.M. and Siegel, B.Z., Geochemical hazards. Mercury emission, Environ. Sci. Tech., 1975, vol. 9, no. 5, pp. 473–474.
Sunshine, J.M., Farnham, T.L., Feaga, L.M., et al., Temporal and spatial variability of lunar hydration as observed by the Deep Impact spacecraft, Science, 2009, vol. 326, no. 5952, p. 565.
Tartèse, R., Anand, M., Barnes, J.J., et al., Distinct petrogenesis of low- and high-Ti mare basalts revealed by OH content and H isotope composition of apatite, Lunar Planet. Sci., 2013, vol. 44, Abstract no. 2222.
Taylor, L., Helium-3 on the Moon: model assumptions and abundances, Engineering, Construction, and Operations in Space IV, Proc. Space’94, Albuquerque, ASCE Publ., 1994, pp. 678–686.
Taylor, L.A. and Kulcinski, G.L., Helium-3 on the Moon for fusion energy: the Persian Gulf of the 21st century, Solar Syst. Res., 1999, vol. 33, pp. 338–345.
Thiemens, M.H. and Clayton, R.N., Solar and cosmogenic nitrogen in the Apollo 17 deep drill core, Proc. 11th Conf. Lunar Planet. Sci., 1980, pp. 1435–1451.
Vinogradov, A.P. and Zadorozhnyi, I.K., Inertial gases in Mare Fecunditatis regolith, in Lunnyi grunt iz Morya Izobiliya (Lunar Soil from Mare Fecunditatis), Moscow: Nauka, 1974, pp. 379–386.
Von Gunten, H.R., Wegmöller, F., and Kröhenbühl, U., Low temperature volatilization on the Moon, Proc. 13th Conf. Lunar Planet Sci., Houston, 1982, pp. A279–A282.
Watson, K., Murray, B., and Brown, H., On the possible presence of ice on the Moon, J. Geophys. Res., 1961, vol. 66, no. 5, pp. 1598–1600.
Weber, A., Saal, A.E., Hauri, E.H., et al., The volatile content and D/H ratios of the lunar picritic glasses, Lunar Planet. Sci., 2011, vol. 42, Abstract no. 2571.
Wegmüller, F., Sörensen, J., Kröhenbühl, U., and Von Gunten, H.R., Lunar regolith investigated by heating techniques: surface deposits and volatilities of trace elements, Proc. 11th Conf. Lunar Planet. Sci., Houston, 1980, pp. 1763–1776.
Weitz, C.M., Rutherford, M.J., Head, J.W. III, and McKay, D.S., Ascent and eruption of a lunar high-titanium magma as inferred from the petrology of the 74001/2 drill core, Meteorit. Planet. Sci., 1999, vol. 34, no. 4, pp. 527–540.
Zadorozhnyi, I.K. and Ivanov, A.V., Inertial gases isotopic composition and content in regolith basalt samples obtained by Luna-24, in Lunnyi grunt iz morya Krizisov (Lunar Soil from Mare Crisium), Moscow: Nauka, 1980, pp. 287–299.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Original Russian Text © A.V. Ivanov, 2014, published in Astronomicheskii Vestnik, 2014, Vol. 48, No. 2, pp. 120–138.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ivanov, A.V. Volatiles in lunar regolith samples: A survey. Sol Syst Res 48, 113–129 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0038094614020038
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0038094614020038