Abstract—
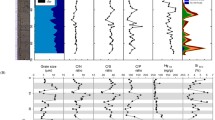
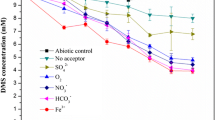
Psychroactive enrichment cultures reducing anthraquinone 2,6-disulfonate (AQDS) and soluble complexes of ferric iron at 5–20°C were isolated from the samples of Lake Baikal bottom sediments collected at the depths of 404 to 1396 m. Cultivation resulted in production of up to 6 mM Fe(II), which was over 50% of the initial Fe(III) concentration in the medium, and of 5.5 mM AH2QDS (~30% of the initial quinone concentration). The enrichment culture of iron-reducing bacteria St3 used Fe(III) citrate as the terminal electron acceptor, oxidizing formate from 6.5 to 2.0 g L–1 at 15°C. Phylogenetic analysis showed that the initial samples of the Lake Baikal bottom sediments and the enrichments obtained from these samples contained the taxa of classes Alpha- and Betaproteobacteria, which were closely related to bacteria capable of oxidizing aromatic compounds using inorganic electron acceptors, including ferric iron.


Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Anderson, R.T., Rooney-Varga, J., Gaw, C.V., and Lovley, D.R., Anaerobic benzene oxidation in the Fe(III)-reduction zone of petroleum-contaminated aquifers, Environ. Sci. Technol., 1998, vol. 32, pp. 1222–1229.
Bel’kova, N.L., Parfenova, V.V., Kostornova, T.Ya., Denisova, L.Ya, and Zaichikov, E.F., Microbial biodiversity in the water of Lake Baikal, Microbiology (Moscow), 2003, vol. 72, pp. 203‒212. Cervantes, F.J., van der Velde, S., Lettinda, G., and Field, J.A., Competition between methanogenesis and quinone respiration for ecologically important substrates in anaerobic consortia, FEMS Microbiol. Ecol., 2000, vol. 34, pp. 161–171.
Chernitsyna, S.M., Mamaeva, E.V., Lomakina, A.V., Pogodaeva, T.V., Galach’yants, Yu.P., Bukin, S.V., Pimenov, N.V., Khlystov, O.M., and Zemskaya, T.I., Phylogenetic diversity of microbial communities of the Posolsk Bank bottom sediments, Lake Baikal, Microbiology (Moscow), 2016, vol. 85, pp. 664‒671.
Dedysh, S.N., Berestovskaya, Y.Y., Vasylieva, L.V., Belova, S.E., Khmelenina, V.N., Suzina, N.E., Trotsenko, Y.A., Liesack, W., and Zavarzin, G.A., Methylocella tundrae sp. nov., a novel methanotrophic bacterium from acidic tundra peatlands, Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol., 2004, vol. 54, pp. 151–156.
Holmes, D., Nicoll, J., Bond, D., and Lovley, D., Potential role of a novel psychrotolerant member of the family Geobacteraceae, Geopsychrobacter electrodiphilus gen. nov., sp. nov., in electricity production by a marine sediment fuel cell, Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 2004, vol. 70, pp. 6023–6030.
Inoue, D., Hara, S., Kashihara, M., Murai, Y., Danzl, E., Sei, K., Tsunoi, S., Fujita, M., and Ike, M., Degradation of bis(4-hydroxyphenyl)methane (bisphenol F) by Sphingobium yanoikuyae strain FM-2 isolated from river water, Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 2008, vol. 74, pp. 352–358.
Kashefi, K., Holmes, D.E., Lovley, D.R., and Tor, J., Potential importance of dissimilatory Fe(III)-reducing microorganisms in hot sedimentary environments, in The Subseafloor Biosphere at Mid-Ocean Ridges, Geophysical Monograph Series, Washington, DC: American Geophysical Union Press, 2004, no. 144, pp. 199–211.
Kojima, H. and Fukui, M., Sulfuritalea hydrogenivorans gen. nov., sp. nov., a facultative autotroph isolated from a freshwater lake, Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol., 2011, vol. 61, pp. 1651–1655.
Lovley, D.R., Dissimilatory Fe(III) and Mn(IV) reduction, Microbiol. Rev., 1991, vol. 55, pp. 259‒287.
Netrusov, A.I., Egorova, M.A., and Zakharchuk, L.M., Praktikum po mikrobiologii (Practical Course in Microbiology), Moscow: Akademiya, 2005.
Nevin, K.P., Holmes, D.E., Woodard, T.L., Hinlein, E.S., Ostendorf, D.W., and Lovley, D.R., Geobacter bemidjiensis sp. nov. and Geobacter psychrophilus sp. nov., two novel Fe(III)-reducing subsurface isolates, Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol., 2005, vol. 55, pp. 1667–1674.
Ramana, C. and Sasikala, C., Albidoferax, a new genus of Comamonadaceae and reclassification of Rhodoferax ferrireducens (Finneran et al., 2003) as Albidoferax ferrireducens comb. nov., J. Gen. Appl. Microbiol., 2009, vol. 55, pp. 301‒304.
Saxena, A., Anand, S., Dua, A., Sangwan, N., Khan, F., and Lal, R., Novosphingobium lindaniclasticum sp. nov., a hexachlorocyclohexane (HCH)-degrading bacterium isolated from an HCH dumpsite, Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol., 2013, vol. 63, pp. 2160–2167.
Slobodkin, A.I. and Wiegel, J., Fe(III) as an electron acceptor for H2 oxidation in thermophilic anaerobic enrichment cultures from geothermal areas, Extremophiles, 1997, vol. 1, pp. 106‒109.
Sugio, T., Domatsu, C., Munakata, O., Tano, T., and Imai, K., Role of a ferric ion-reducing system in sulfur oxidation of Thiobacillus ferrooxidans, Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 1985, pp. 1401‒1406.
Tamura, K., Stecher, G., Peterson, D., Filipski, A., and Kumar, S., MEGA6: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis Version 6.0, Mol. Biol. Evol., 2013, vol. 30, pp. 2725–2729.
Ting L., Williams, T.J., Cowley, M.J., Lauro, F.M., Guilhaus, M., Raftery, M.J., and Cavicchioli, R., Cold adaptation in the marine bacterium, Sphingopyxis alaskensis, assessed using quantitative proteomics, Environ. Microbiol., 2010, vol. 12, pp. 2658–2676.
Todorova, S.G. and Costello, A.M., Design of Shewanella-specific 16S rRNA primers and application to analysis of Shewanella in a minerotrophic wetland, Environ. Microbiol., 2006, vol. 3, pp. 426–432.
Vargas, M., Kashefi, K., Blunt-Harris, E.L., and Lovley, D.R., Microbiological evidence for Fe(III) reduction on early Earth, Nature, 1998, vol. 395, pp. 65–67.
Viollier, E., Inglett, P.W., Hunter, K., Roychoudhury, A.N., and van Cappellen, P., The ferrozine method revisited: Fe(II)/Fe(III) determination in natural waters, Appl. Geochem., 2000, vol. 15, pp. 785–790.
Watanabe, T., Kojima, H., and Fukui, M., Sulfuriferula multivorans gen. nov., sp. nov., isolated from a freshwater lake, reclassification of ‘Thiobacillus plumbophilus’ as Sulfuriferula plumbophilus sp. nov., and description of Sulfuricellaceae fam. nov. and Sulfuricellales ord. nov., Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol., 2015, vol. 65, pp. 1504–1508.
Weelink, S.A.B., Van Doesburg, W., Saia, F.T., Rijpstra, W.I.C., Roling, W.F.M., Smidt, H., and Stams, A.J.M., A strictly anaerobic Betaproteobacterium Georgfuchsia toluolica gen. nov., sp. nov. degrades aromatic compounds with Fe(III), Mn(IV) or nitrate as an electron acceptor, FEMS Microbiol. Ecol., 2009, vol. 70, pp. 575–585.
Wolin, E.A., Wolin, M.J., and Wolfe R.S., Formation of methane by bacterial extracts, J. Biol. Chem., 1963, vol. 238, pp. 2882–2886.
Zakharova, Yu.R., Kurilkina, M.I., Likhoshvay, A.V., Shishlyannikov, S.M., Kalyuzhnaya, O.V., Petrova, D.P., and Likhoshway, E.V., Effect of bacteria from the bottom water layer of Lake Baikal on degradation of diatoms, Paleontol. J., 2013, vol. 47, no. 9, pp. 1030–1034.
Zavarzina, D.G., Kolganova, T.V., Boulygina, E.S., Kostrikina, N.A., Tourova, T.P., and Zavarzin, G.A., Geoalkalibacter ferrihydriticus gen. nov. sp. nov., the first alkaliphilic representative of the family Geobacteraceae, isolated from a soda lake, Microbiology (Moscow), 2006, vol. 75, pp. 664‒672.
Zemskaya, T.I., Sitnikova, T.Y., Kiyashko, S.I., Kalmychkov, G.V., Pogodaeva, T.V., Mekhanikova, I.V., Naumova, T.V., Shubenkova, O.V., Chernitsina, S.M., Kotsar, O.V., Chernyaev, E.S., and Khlystov, O.M., Faunal communities at sites of gas- and oil-bearing fluids in Lake Baikal, Geo-Mar. Lett., 2012, vol. 32, pp. 437–451.
Zemskaya, T.I., Pogodaeva, T.V., Shubenkova, O.V., Chernitsina, S.M., Dagurova, O.P., Buryukhaev, S.P., Namsaraev, B.B., Khlystov, O.M., Egorov, A.V., Krylov, A.A., and Kalmychkov, G.V., Geochemical and microbiological characteristics of sediments near the Malenky mud volcano (Lake Baikal, Russia), with evidence of Archaea intermediate between the marine anaerobic methanotrophs ANME-2 and ANME-3, Geo-Mar. Lett., 2010, vol. 30, pp. 411–425.
Zhang, C., Stapleton, R.D., Zhou, J., Palumbo, A.V., and Phelps T.J., Iron reduction by psychrotrophic enrichment cultures, FEMS Microbiol. Ecol., 1999, vol. 30, pp. 367–371.
Zhilina, T.N., Zavarzina, D.G., Osipov, G.A., Kostrikina, N.A., and Tourova, T.P., Natronincola ferrireducens sp. nov., and Natronincola peptidovorans sp. nov., a new anaerobic alkaliphilic peptolytic iron-reducing bacteria isolated from soda lakes, Microbiology (Moscow), 2009, vol. 78, pp. 445‒454.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
The authors are grateful to T.I. Zemskaya (Laboratory of Carbohydrate Microbiology, Limnological Institute, Siberian Branch, Russian Academy of Sciences) and to O.P. Dagurova (Institute of General and Experimental Biology, Siberian Branch, Russian Academy of Sciences) for providing Lake Baikal bottom sediments. The work was supported by the Russian Foundation for Basic Researh, projects nos. 12-04-31353 and 12-05-01085.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest. This article does not contain any studies involving animals or human participants performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Translated by P. Sigalevich
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zakharyuk, A.G., Ryzhmanova, Y.V., Avtukh, A.N. et al. Iron-Reducing Microbial Communities of the Lake Baikal Low-Temperature Bottom Sediments. Microbiology 88, 156–163 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0026261719020139
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0026261719020139