Abstract
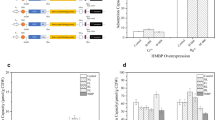
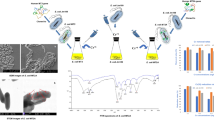
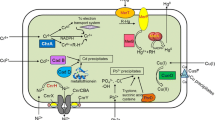
The present study introduced and evaluated modification of E. coli BL21 (DE3) to improve its biosorption capacity by the transfer of the Corynebacterium glutamicum metallothionein gene (C.gMT). The C.gMT sequence was extracted and cloned in pET28a vector and the ligation product was transferred into E. coli BL21 (DE3). It has been also submitted to the GenBank database (accession number KJ638906.1). The performance of the recombinant bacterium was evaluated at different metal ions concentrations, contact times, pH values, and co-ions. The results show that recombinant BL21 (DE3) was able to uptake Pb+2, and Zn+2 at greater percentages than could BL21 (DE3). The optimum pH for the removal of each heavy metal was different. As contact time increased, Pb+2 and Zn+2 biosorption by the recombinant bacterium increased, while the biosorption of Cd+2 remained at a nearly steady rate for contact times of more than 1 h. Increasing the concentrations of Pb+2 and Zn+2 in solution increased biosorption of these metals by the recombinant BL21 (DE3) over that of Cd+2. It could be hypothesized that Pb+2 and Zn+2 removal by C.gMT-engineered BL21 (DE3) occurred mainly via intracellular biosorption (absorption) and that Cd+2 was mainly taken up through cell surface biosorption (adsorption).
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altschul, S.F., Madden, T.L., Schäffer, A.A., Zhang, J., Zhang, Z., Miller, W., and Lipman, D.J., Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST, a new generation of protein database search programs, Nucleic Acids Res., 1997, vol. 25, pp. 3389–3402.
Amiard, J.C., Amiard-Triquet, C., Barka, S., Pellerin, J., and Rainbow, P.S., Metallothioneins in aquatic invertebrates: their role in metal detoxication and their use as biomarkers, Aquatic Toxicol., 2006, vol. 76, pp. 160–202.
Beach, L.R. and Palmiter, R.D., Amplification of the metallothionein-I gene in cadmium-resistant mouse cells, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A., 1981, vol. 78, pp. 2110–2114.
Blindauer, C.A., Metallothioneins with unusual residues: histidines as modulators of zinc affinity and reactivity, J. Inorg. Biochem., 2008, vol. 102, pp. 507–521.
Bradford, M.M., A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding, Anal. Biochem., 1976, vol. 72, pp. 248–254.
Barth, S., Huhn, M., Matthey, B. Klimka, A., Galinski, E.A., and Engert, A., Compatible-solute-supported periplasmic expression of functional recombinant proteins under stress conditions, Appl. Environ. Microbiol., 2000, vol. 66, no. 4, pp. 1572–1579.
Chang, W.C., Hsu, G.S., Chiang, S.M., and Su, M.C., Heavy metal removal from aqueous solution by wasted biomass from a combined AS-biofilm process, Bioresour. Technol., 2006, vol. 97, pp. 1503–1508.
Chubar, N., Carvalho, J.R., and Correia, M.J.N., Heavy metals biosorption on cork biomass: effect of the pre-treatment, Colloids Surf. A., 2004, vol. 238, pp. 51–58.
Choi, S.B. and Yun, Y.S., Lead biosorption by waste biomass of Corynebacterium glutamicum generated from lysine fermentation process, Biotech. Lett., 2004, vol. 26, pp. 331–336.
Cobbett, C. and Goldsbrough, P., Phytochelatins and Metallothioneins: Roles in heavy metal detoxification and homeostasis, Annu. Rev. Plant Biol., 2002, vol. 53, pp. 159–164.
Coyle, P., Philcox, J.C., Carey, L.C., and Rofe, A.M., Metallothionein: the multipurpose protein. Cell Mol. Life Sci., 2002, vol. 59, pp. 627–647.
Feng, Q., Lin, Q., Gong, F., Sugita, S., Shoya, M., Adsorption of lead and mercury by rice husk ash, J. Colloid Interf. Sci., 2004, vol. 278, pp. 1–8.
Ferraz, A.I. and Teixeira, J.A., The use of flocculating brewer’s yeast for Cr(III) and Pb(II) removal from residual wastewaters, Bioprocess Eng., 1999, vol. 21, pp. 431–437.
Fomina, M. and Gadd, G.M., Biosorption: current perspectives on concept, definition and application, Bioresour Technol., 2014, vol. 160, pp. 3–14.
García, R., Campos, J., Alfonso, J., Cruz, Ma., Calderón, E., Raynal, M.E., and Buitrón, G., Biosorption of Cd,Cr,Mn,and Pb from aqueous solutions by Bacillus sp. strains isolated from industrial waste activate sludge, TIP Rev. Esp. Cienc. Quím. Biol., 2016, vol. 19, pp. 5–14.
Gold, B., Deng, H., Bryk, R., Vargas, D., Eliezer, D., Roberts, J., Jiang, X., and Nathan, C., Identification of copperbinding metallothionein in pathogenic mycobacteria, Nat. Chem. Biol., 2008, vol. 4, pp. 609–616.
Goyal, N., Jain, S.C., and Banerjee, U.C., Comparative studies on the microbial adsorption of heavy metals, Adv. Environ Res., 2003, vol. 7, pp. 311–319.
Hana, R., Li, H., Li, Y., Zhang, J., Xiao, H., and Shi, J., Biosorption of copper and lead ions by waste beer yeast, J. Hazard. Mater. B., 2006, vol. 137, pp. 1569–1576.
Jafarian, V., Sariri, R., Hosseinkhani, S., Aghamaali, M.R., Sajedi, R.H., Taghdir, M., and Hassannia, S., A unique EF-hand motif in mnemiopsin photoprotein from Mnemiopsis leidyi: implication for its low calcium sensitivity, Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 2011, vol. 413, pp. 164–170.
Kao, W.C., Wu, J.Y., Chang, C.C., and Chang, J.S., Cadmium biosorption by polyvinyl alcohol immobilized recombinant Escherichia coli, J. Hazard, Mater., 2009, vol. 169, pp. 651–658.
Kao, W.C., Chiu, Y.P., Chang, C.C., and Chang, J.S., Localization effect on the metal biosorption capability of recombinant mammalian and fish metallothioneins in Escherichia coli, Biotechnol. Prog., 2006, vol. 22, pp. 1256–1264.
Kurniawan, T.A., Chan, G.Y.S., Lo, W.H., and Babel, S., Physico-chemical treatment techniques for wastewater laden with heavy metals, Chem. Eng. J., 2006, vol. 118, pp. 83–98.
Mapolelo, M. and Torto, N., Trace enrichment of metal ions in aquatic environments by Saccharomyces cerevisiae, Talanta, 2004, vol. 64, pp. 39–47.
McCloskey, D., Palsson, B., and Feist, A.M., Basic and applied uses of genome-scale metabolic network reconstructions of Escherichia coli, Mol. Syst. Biol., 2013, vol. 9, p. 661.
McFarland, J., Nephelometer: an instrument for estimating the number of bacteria in suspensions used for calculating the opsonic index and for vaccines, JAMA, 1907, vol. 14, pp. 1176–1178.
Olafson, R.W., Loya, S., and Sim, R.G., Physiological parameters of prokaryotic metallothionein induction, Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 1980, vol. 95, pp. 1495–1503.
Osman, D. and Cavet, J.S., Bacterial metal-sensing proteins exemplified by ArsR–SmtB family repressors, Nat. Prod. Reports., 2010, vol. 27, pp. 668–680.
Ozdemira, S., Kilinc, E., Poli, A., Nicolausc, B., and Guvena, K., Biosorption of Cd, Cu, Ni, Mn and Zn from aqueous solutions by thermophilic bacteria, Geobacillus toebii subsp. decanicus and Geobacillus thermoleovorans subsp. stromboliensis: equilibrium, kinetic and thermodynamic studies, J. Chem. Eng., 2009, vol. 152, pp. 195–206.
Özer, A. and Özer, D., Comparative study of the biosorption of Pb(II),Ni(II) and Cr(VI) ions onto S. cerevisiae: determination of biosorption heats, J. Hazard. Mater., 2003, vol. 100, pp. 219–229.
Pamukoglu, M.Y. and Kargi, F., Batch kinetics and isotherms for biosorption of copper(II) ions onto pre-treated powdered waste sludge (PWS), J. Hazard. Mater., 2006, vol. 138, pp. 479–484.
Paul, S., Bera, D., Chattopadhyay, P., and Ray, L., Biosorption of Pb(II) by Bacillus cereus M1 16 immobilized in calcium alginate gel, J. Hazard. Subst. Res., 2005, vol. 5, pp. 1–13.
Pavasant, P., Apiratikul, R., Sungkhum, V., Suthiparinyanont, P., Wattanachira, S., and Marhaba, T.F., Biosorption of Cu2+,Cd2+,Pb2+,and Zn2+ using dried marine green macroalga Caulerpa lentillifera, Bioresource Technol., 2006, vol. 97, pp. 2321–2329.
Ramírez, M., Díaz, C., Vargas, E., Riveros, H., Campos, J., and Cervantes, C., Mechanisms of bacterial resistance to chromium compounds, Biometals, 2008, vol. 21, pp. 321–332.
Rensing, C., Escherichia coli mechanisms of copper homeostasis in a changing environment, FEMS Microbiol. Rev., 2003, vol. 27, pp. 197–213.
Sawalha, M.F., Peralta-Videa, J.R., Romero-González, J., Duarte-Gardea, M., and Gardea-Torresdey, J.L., Thermodynamic and isotherm studies of the biosorption of Cu(II),Pb(II),and Zn(II) by leaves of saltbush (Atriplex canescens), J. Chem. Thermodyn., 2007, vol. 39, pp. 488–492.
Selatnia, A., Bakhti, M.Z., Madani, A., Kertous, L., and Mansouri, Y., Biosorption of Cd2+ from aqueous solution by a NaOH-treated bacterial dead Streptomyces rimosus biomass, Hydrometallurgy, 2004a, vol. 75, pp. 11–24.
Selatnia, A., Madani, A., Bakhti, M.Z., Kertous, L., Mansouri, Y., and Yous, R., Biosorption of Ni2+ from aqueous solution by a NaOH-treated bacterial dead Streptomyces rimosus biomass, Miner Eng., 2004b, vol. 17, pp. 903–911.
Shi, J., Lindsay, W.P., Huckle, J.W., Morby, A.P., and Robinson, N.J., Cyanobacterial metallothionein gene expressed in Escherichia coli,metal-binding properties of the expressed proteins, FEBS Lett., 1992, vol. 303, pp. 159–163.
Suh, J.H. and Kim, D.S., Comparison of different sorbents (inorganic and biological) for the removal of Pb2+ from aqueous solutions, Technol. Biotech., 2000, vol. 75, pp. 279–284.
Sutherland, D.E.K. and Stillman, M.J., The “magic numbers” of metallothionein, Metallomics, 2011, vol. 3, pp. 444–463.
Thirumoorthy, N., Manisenthil Kumar, K.T., Shyam Sundar, A., Panayappan, L., and Chatterjee, M., Metallothionein: an overview, World J. Gastroenter., 2007, vol. 13, pp. 993–996.
Velásquez, L. and Dussan, J., Biosorption and bioaccumulation of heavy metals on dead and living biomass of Bacillus sphaericus, J. Hazard. Mater., 2009, vol. 167, pp. 713–716.
Wang, J.L. and Chen, C., Biosorbents for heavy metals removal and their future, Biotech. Advances, 2009, vol. 27, pp. 195–226.
Yun, Y.S. and Volesky, B., Modeling of lithium interference in cadmium biosorption, Sci. Technol., 2003, vol. 37, pp. 3601–3608.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The article is published in the original.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jafarian, V., Ghaffari, F. A unique metallothionein-engineered in Escherichia coli for biosorption of lead, zinc, and cadmium; absorption or adsorption?. Microbiology 86, 73–81 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0026261717010064
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0026261717010064