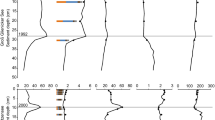
Abstract
Using data obtained in recent years, we considered the external mass balance and characteristics of internal iron and manganese cycles in Lake Baikal (biological uptake, remineralization, sedimentary and diffusive fluxes, accumulation in sediments, time of renewal, etc.). Some previous results and common concepts were critically reevaluated.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
K. K. Votintsev, Hydrochemistry of Lake Baikal (Akad. Nauk SSSR, Moscow, 1961) [in Russian].
M. N. Shimaraev, V. I. Verbolov, N. G. Granin, and P. P. Sherstyankin, Physical Limnology of Lake Baikal: A Review (BICER, Irkutsk-Okayama, 1994).
R. F. Weiss, E. C. Carmak, and V. M. Koropalov, “Deep-Water Renewal and Biological Production in Lake Baikal,” Nature 349, 665–669 (1991).
M. N. Shimaraev, V. M. Domysheva, and L. A. Gorbunova, “Oxygen Dynamics in Lake Baikal during Spring Mixing,” Dokl. Akad. Nauk 347, 814–817 (1996) [Dokl. Earth Sci. 347, 527–531 (1996)].
P. Martin, L. Granina, K. Martens, B. Goddeeris, “Oxygen Concentration Profiles in Sediments of Two Ancient Lakes: Lake Baikal (Siberia, Russia) and Lake Malawi (East Africa),” Hydrobiologia 367, 163–174 (1998).
P. D. Tortell, M. T. Maldonado, and N. M. Price, “The Role of Heterotrophic Bacteria in Iron-Limited Ocean Ecosystems,” Nature 383, 330–332 (1996).
A. P. Vinogradov, Chemical Elemental Composition of Marine Organisms (Nauka, Moscow, 2001) [in Russian].
V. A. Vetrov and A. I. Kuznetsova, Trace Elements in Environmental Objects of the Lake Baikal Region (SO RAN OIGGM, Novosibirsk, 1997) [in Russian].
L. Z. Granina, “The Chemical Budget of Lake Baikal: A Review,” Limnol. Oceanogr. 42, 373–378 (1997).
G. N. Baturin, Geochemistry of the Oceanic Fe-Mn Nodules (Nauka, Moscow, 1986) [in Russian].
L. Z. Granina, “Vertical Profiles of Iron and Manganese Contents in Mud Solutions,” Geokhimiya, No. 10, 1493–1500 (1991).
L. Granina, B. Müller, and B. Wehrli, “Origin and Dynamics of Fe-and Mn-Sedimentary Layers in Lake Baikal,” Chem. Geol. 205, 55–72 (2004).
E. M. Kolokol’tseva, Mesozoic and Cenozoic Lakes of Siberia (Nauka, Moscow, 1968) [in Russian].
E. Callender and L. Granina, “Geochemical Mass Balances of Major Elements in Lake Baikal,” Limnol. Oceanogr. 42, 148–155 (1997).
K. K. Votintsev, I. V. Glazunov, and A. P. Tolmacheva, Hydrochemistry of Rivers of the Lake Baikal Basin (Nauka, Moscow, 1965) [in Russian].
L. Z. Leibovich-Granina, “On the Problem of Iron and Manganese Circulation in Lake Baikal,” Vodn. Resur., No. 3, 67–73 (1987).
T. V. Khodzher, V. A. Obolkin, and V. L. Potemkin, “On the Problems of the Role of the Atmosphere in the Formation of the Chemical Composition of Baikal Water,” Optika Atmosf. Okeana 12, 493–496 (1999).
O. V. Levina, V. A. Bychinskii, O. A. Proidakova, et al., “Chemical Composition and Thermodynamic Properties of Diatom Valves with Applications to the Precipitation-Dissolution of Biogenic Silica in Lake Baikal,” Geol. Geofiz. 42, 319–329 (2001).
V. S. Savenko, “Elemental Chemical Composition of Oceanic Plankton,” Geokhimiya, No. 8, 1084–1089 (1988).
E. N. Tarasova, Organic Matter of Soutehrn Baikal Waters (Nauka, Novosibirsk, 1975) [in Russian].
M. Sturm, E. Vologina, A. W. Mackay, et al., “Results of Sediment Trap Deployments in the N-and S-Basin of Lake Baikal (Preliminary Results),” in Proceedings of BAIK-SED-2 International Workshop on Sedimentary Processes in Large Lakes, Gent, Belgium 2003 (Gent, 2003), p. 15.
L. Z. Granina, E. Callender, A. M. Grachev, and M. A. Grachev, “Inflow of Suspended Forms of Elements (Ti, Cr, Sr, Cu, Zn, Pb, and Br) with River Water into Lake Baikal and Their Contribution to Chemical Balance,” Dokl. Akad. Nauk 362, 691–695 (1998) [Dokl. Earth Sci. 362, 1123–1127 (1998)].
K. K. Votintsev, “Primary Production in Baikal and Its Significance for Biolimnic Processes in the Lake,” Izv. Akad. Nauk SSSR, Ser. Biol., No. 6, 892–900 (1971).
K. K. Votintsev, A. I. Meshcheryakova, and G. I. Popovskaya, Cycle of Organic Matter in Lake Baikal (Nauka, Novosibirsk, 1975) [in Russian].
I. B. Mizandrontsev and K. N. Mizandrontseva, “The Oxygen Cycle in Lake Baikal,” Vodn. Resur. 28, 552–558 (2001) [Water Resour. 28, 502–508 (2001)].
E. Callender and L. Granina, “Biogeochemical Phosphorus Mass Balance for Lake Baikal, Southeastern Siberia, Russia,” Mar. Geol. 139, 5–19 (1997).
B. Mueller, M. Maerki, M. Schmid, et al., “Internal Carbon and Nutrient Cycling in Lake Baikal: Sedimentation, Upwelling, and Early Diagenesis,” Glob. Planet. Change 46, 101–124 (2005).
L. A. Vykhristyuk, Organic Matter in the Bottom Sediments of Lake Baikal (Nauka, Novosibirsk, 1980) [in Russian].
D. B. Ryves, D. H. Jewson, M. Sturm, et al., “Quantitative and Qualitative Relationships between Planktonic Diatom Communities and Diatom Assemblages in Sedimenting Material and Surface Sediments in Lake Baikal, Siberia,” Limnol. Oceanogr. 48, 1643–1661 (2003).
T. G. Potyomkina and V. L. Potyomkin, in Lake Baikal (Elsevier, 2000), Vol. 2, pp. 229–235.
L. Z. Granina and L. Sigg, “New Data on the Composition of Suspended Material in Baikal and its Tributaries,” in Proceedings of 2nd Vereshchagin Baikal Conference, Irkutsk, Russia, 1995 (Irkutsk, 1995), p. 51.
L. Z. Granina, U. Tomza, R. Arimoto, et al., “A Study of the Chemical Budget of Lake Baikal Using Neutron Activation and Synchrotron Radiation,” Nucl. Instr. Methods Phys. Res. A448, 419–424 (2001).
R. A. Jahnke, “A Simple, Reliable, and Inexpensive Pore-Water Sampler,” Limnol. Oceanogr. 33, 483–487 (1988).
V. D. Pampoura, M. I. Kuzmin, A. N. Gvozdikov, et al., “Geochemistry of Recent Sedimentation in Lake Baikal,” Geol. Geofiz. 34(10–11), 52–68 (1993).
B. P. Agafonov, Exolithodynamics of the Baikal Rift Zone (Nauka, Novosibirsk, 1990) [in Russian].
E. N. Tarasova and A. I. Meshcheryakova, Recent Hydrochemical Regime of Lake Baikal (Nauka, Novosibirsk, 1992) [in Russian].
A. P. Khaustov, V. N. Fedorov, and I. S. Lomonosov, “Estimate of Material Migration in Geochemical Landscapes as Exemplified by the Baikal Region,” Dokl. Akad. Nauk SSSR 317, 444–449 (1991).
A. N. Afanas’ev, Water Resources and Water Balance of the Lake Baikal Basin (Nauka, Novosibirsk, 1976) [in Russian].
I. B. Mizandrontsev and M. K. Shimaraeva, in Geological and Hydrological Studies of Lakes in Middle Siberia (Nauka, Moscow, 1973), pp. 3–14 [in Russian].
V. G. Nikolaev, “Structure of the Sedimentary Complexes of Continental Rifts,” Geotektonika, No. 2, 116–124 (1986).
G. E. Hutchinson, A Treatise of Limnology, (Wiley, New York, 1957), Vol. 1.
L. Z. Leibovich-Granina, “Iron and Manganese in Baikal Water,” Vodn. Resur., No. 4, 118–127 (1985).
A. A. Matveev and A. M. Anikanov, “Chemical and Energy Cycle in Basins,” in Hydrochemistry and Quality of Water (Listvenichnoe na Baikale, 1977), p. 77.
I. B. Mizandrontsev, in Late Genozoic Evolution of Lakes in the USSR (Nauka, Novosibirsk, 1982), pp. 33–46 [in Russian].
L. Sigg, “Surface Chemical Aspects of the Distribution and Fate of Metal Ions in Lakes,” in Aquatic Surface Chemistry, Ed. by W. Stumm (Wiley-Interscience, New York, 1987), pp. 319–349 (1987).
Y. Shaked, Yi. Erel, and A. Sukenik, “Phytoplankton-Mediated Redox Cycle of Iron in the Epilimnion of Lake Kinneret,” Environ. Sci. Technol. 36, 460–467 (2002).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © L.Z. Granina, E. Callender, 2007, published in Geokhimiya, 2007, No. 9, pp. 999–1007.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Granina, L.Z., Callender, E. Elements of the iron and manganese cycles in Lake Baikal. Geochem. Int. 45, 918–925 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0016702907090054
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0016702907090054