Abstract
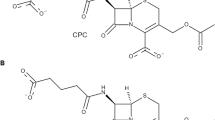
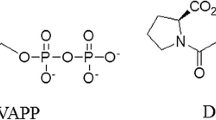
Molecular modeling has revealed intimate details of the mechanism of binding of natural substrate, penicillin G (PG), in the penicillin acylase active center and solved questions raised by analysis of available X-ray structures, mimicking Michaelis complex, which substantially differ in the binding pattern of the PG leaving group. Three MD trajectories were launched, starting from PDB complexes of the inactive mutant enzyme with PG (1FXV) and native penicillin acylase with sluggishly hydrolyzed substrate analog penicillin G sulfoxide (1GM9), or from the complex obtained by PG docking. All trajectories converged to a similar PG binding mode, which represented the near-to-attack conformation, consistent with chemical criteria of how reactive Michaelis complex should look. Simulated dynamic structure of the enzyme-substrate complex differed significantly from 1FXV, resembling rather 1GM9; however, additional contacts with residues bG385, bS386, and bN388 have been found, which were missing in X-ray structures. Combination of molecular docking and molecular dynamics also clarified the nature of extremely effective phenol binding in the hydrophobic pocket of penicillin acylase, which lacked proper explanation from crystallographic experiments. Alternative binding modes of phenol were probed, and corresponding trajectories converged to a single binding pattern characterized by a hydrogen bond between the phenol hydroxyl and the main chain oxygen of bS67, which was not evident from the crystal structure. Observation of the trajectory, in which phenol moved from its steady bound to pre-dissociation state, mapped the consequence of molecular events governing the conformational transitions in a coil region a143-a146 coupled to substrate binding and release of the reaction products. The current investigation provided information on dynamics of the conformational transitions accompanying substrate binding and significance of poorly structured and flexible regions in maintaining catalytic framework.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- MD:
-
molecular dynamics
- PA:
-
penicillin acylase
- PG:
-
penicillin G
- PGSO:
-
penicillin G sulfoxide
- RHF:
-
Restricted Hartree-Fock method
- RMSD:
-
root mean square deviation
- RMSF:
-
root mean square fluctuation
References
Rolinson, G. N., Batchelor, F. R., Butterworth, D., Cameron-Wood, J., Cole, M., Eustace, G. C., Hart, M. V., Richards, M., and Chain, E. B. (1960) Nature, 187, 236–237.
Margolin, A. L., Švedas, V. K., and Berezin, I. V. (1980) Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 616, 283–289.
Roa, A., Castillon, M. P., Goble, M. L., Virden, R., and Garcia, J. L. (1995) Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 206, 629–636.
Bruggink, A., Roos, E. C., and de Vroom, E. (1998) Org. Process Res. Dev., 2, 128–133.
Švedas, V. K., Savchenko, M. V., Beltser, A. I., and Guranda, D. F. (1996) Ann. N.-Y. Acad. Sci., 799, 659–669.
Guranda, D. T., van Langen, L. M., van Rantwijk, F., Sheldon, R. A., and Švedas, V. K. (2001) Tetrahedron: Asymmetry, 12, 1645–1650.
Chilov, G. G., and Švedas, V. K. (2002) Can. J. Chem., 80, 699–707.
Ferreira, J. S., Straathof, A. J. J., Franco, T. T., and van der Wielen, L. A. M. (2004) J. Mol. Catalysis B: Enzymatic, 27, 29–35.
Chilov, G. G., Moody, H. M., Boesten, W. H. J., and Švedas, V. K. (2003) Tetrahedron: Asymmetry, 14, 2613–2617.
Duggleby, H. J., Tolley, S. P., Hill, C. P., Dodson, E. J., Dodson, G., and Moody, P. C. (1995) Nature, 373, 264–268.
Brannigan, J. A., Dodson, G., Duggleby, H. J., Moody, P. C., Smith, J. L., Tomchick, D. R., and Murzin, A. G. (1995) Nature, 378, 416–419.
Done, S. H., Brannigan, J. A., Moody, P. C. E., and Hubbard, R. E. (1998) J. Mol. Biol., 284, 463–475.
Alkema, W. B. L., Hensgens, C. M. H., Kroezinga, E. H., de Vries, E., Floris, R., van der Laan, J.-M., Dijkstra, B. W., and Janssen, D. B. (2000) Protein Eng., 13, 857–863.
McVey, C. E., Walsh, M. A., Dodson, G. G., Wilson, K. S., and Brannigan, J. (2001) J. Mol. Biol., 313, 139–150.
Berendsen, H. J. C., van der Spoel, D., and van Drunen, R. (1995) Comp. Phys. Comm., 91, 43–56.
Lindahl, E., Hess, B., and van der Spoel, D. (2001) J. Mol. Mod., 7, 306–317.
Jorgensen, W. L., and Tirado-Rives, J. (1988) J. Am. Chem. Soc., 110, 1657–1666.
Jorgensen, W. L., Chandrasekhar, J. D., Madura, R., Impey, W., and Klein, M. L. (1983) J. Chem. Phys., 79, 926–935.
Feenstra, K. A., Hess, B., and Berendsen, H. J. C. (1999) J. Comp. Chem., 20, 786–798.
Hess, B., Bekker, H., Berendsen, H. J. C., and Fraaije, J. G. E. M. (1997) J. Comp. Chem., 18, 1463–1472.
Tironi, I. G., Sperb, R., Smith, P. E., and van Gunsteren, W. F. (1995) J. Chem. Phys., 102, 5451–5459.
Shmidt, M. W., Baldringe, K. K., Boatz, J. A., Elbert, S. T., Gordon, M. S., Jensen, J. H., Koseki, S., Matsunaga, N., Nguyen, K. A., Su, S. J., and Windus, T. L. (1993) J. Comp. Chem., 14, 1347–1363.
Granovsky, A. A., http://www.classic.chem.msu.su/gran/gamess/index.html
Bayly, C. L., Cieplak, P., Cornell, W. D., and Kollman, P. A. (1993) J. Phys. Chem., 97, 10269–10280.
Stroganov, O. V., Chilov, G. G., and Švedas, V. K. (2003) J. Mol. Structure (THEOCHEM), 631, 117–125.
Morris, G. M., Goodsell, D. S., Halliday, R. S., Huey, R., Hart, W., Belew, R. K., and Olson, A. J. (1998) J. Comp. Chem., 19, 1639–1662.
Chilov, G. G., Sidorova, A. V., and Švedas, V. K. (2007) Biochemistry (Moscow), 72, 495–500.
Chilov, G. G., Guranda, D. T., and Švedas, V. K. (2000) Biochemistry (Moscow), 65, 963–966.
Alkema, W. B. L., Prins, A. K., de Vries, E., and Janssen, D. B. (2002) Biochem. J., 365, 303–309.
Alkema, W. B. L., Dijkhuis, A.-J., de Vries, E., and Janssen, D. B. (2002) Eur. J. Biochem., 269, 2093–2100.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Published in Russian in Biokhimiya, 2008, Vol. 73, No. 1, pp. 69–79.
Originally published in Biochemistry (Moscow) On-Line Papers in Press, as Manuscript BM07-204, October 14, 2007.
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chilov, G.G., Stroganov, O.V. & Švedas, V.K. Molecular modeling studies of substrate binding by penicillin acylase. Biochemistry Moscow 73, 56–64 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0006297908010082
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0006297908010082