Abstract
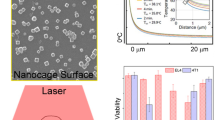
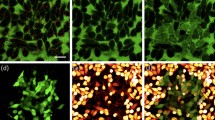
In this study, a microfluidic apparatus embedded with microstructures was designed and aligned with a laser and dark-field microscope for real-time, long-term observation of photothermal effects on cells. Gold nanorods (AuNRs, 10 ppm) were incubated with MG-63 human osteosarcoma cells for 3 h. Then, the cells were exposed to a continuous-wave laser at a wavelength of 830 nm for 10, 20, and 30 min at 5, 9,14, 24, and 32 W cm−2. Subsequent changes in morphology were observed. Under different conditions, cell membrane blebbing occurred at different times, indicating that actin filaments were destroyed in large quantities and apoptosis was induced. In suitable conditions, we first induced slight cell injury by causing cytoskeletal fractures with a high-energy laser; then, the cells were irradiated with a low-energy laser at 0.3 W cm−2.We found that among cells treated with the high-energy laser, cells treated additionally with a low-energy laser showed extended viability compared with cells that did not receive the additional treatment.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
C. M. Nelson and C. S. Chen, Cell-cell signaling by direct contact increases cell proliferation via a PI3K-dependent signal, FEBSLett., 2002, 514, 238–242.
L. A. Tiemeijer, J. P. Frimat, O. M. J. A. Stassen, C. V. C. Bouten and C. M. Sahlgren, Spatial patterning of the Notch ligand Dll4 controls endothelial sprouting in vitro, Sci. Rep., 2018, 8, 6392.
D. H. Kohn, M. Sarmadi, J. I. Helman and P. H. Krebsbach, Effects of pH on human bone marrow stromal cells in vitro: implications for tissue engineering of bone, J. Biomed. Mater. Res., 2002, 60, 292–299.
S. Razaq, R. J. Wilkins and J. P. G. Urban, The effect of extracellular pH on matrix turnover by cells of the bovine nucleus pulposus, Eur. Spine J., 2003, 12, 341–349.
S. Miao, H. Cui, M. Nowicki, S. J. Lee, J. Almeida, X. Zhou, W. Zhu, X. Yao, F. Masood, M. W. Plesniak, M. Mohiuddin and L. G. Zhang, Photolithographic-stereolithographic-tandem fabrication of 4D smart scaffolds for improved stem cell cardiomyogenic differentiation, Biofabrication, 2018, 10, 035007.
K. W. Kwon, J. C. Choi, K. Y. Suh and J. Doh, Multiscale fabrication of multiple proteins and topographical struc tures by combining capillary force lithography and microscope projection photolithography, Langmuir, 2011, 27, 3238–3243.
H. Kim, G. H. Yang, C. H. Choi, Y. S. Cho and G. Kim, Gelatin/PVA scaffolds fabricated using a 3D-printing process employed with a low-temperature plate for hard tissue regeneration: Fabrication and characterizations, Int. J. Biol. Macromol., 2018, 120, 119–127.
M. Seidenstuecker, L. Kerr, A. Bernstein, H. O. Mayr, N. P. Suedkamp, R. Gadow, P. Krieg, S. H. Latorre, R. Thomann, F. Syrowatka and S. Esslinger, 3D powder printed bioglass and ß-tricalcium phosphate bone scaffolds, Materials, 2017, 11, 13, DOI: 10.3390/ ma11010013.
M. H. Ghanian, Z. Farzaneh, J. Barzin, M. Zandi, M. Kazemi-Ashtiani, M. Alikhani, M. Ehsani and H. Baharvand, Nanotopographical control of human embryonic stem cell differentiation into definitive endoderm, J. Biomed. Mater. Res., Part A, 2015, 103, 3539–3553.
B. Luo, L. Tian, N. Chen, S. Ramakrishna, N. Thakor and I. H. Yang, Electrospun nanofibers facilitate better alignment, differentiation, and long-term culture in an in vitro model of the neuromuscular junction (NMJ), Biomater. Sci., 2018, 6, 3262–3272.
J. Foncy, A. Estève, A. Degache, C. Colin, X. Dollat, J. C. Cau, C. Vieu, E. Trévisiol and L. Malaquin, Dynamic inking of large-scale stamps for multiplexed microcontact printing and fabrication of cell microarrays, PLoS One, 2018, 13, e0202531.
Y. B. Lee, S. J. Kim, E. M. Kim, H. Byun, H. K. Chang, J. Park, Y. S. Choi and H. Shin, Microcontact printing of polydopamine on thermally expandable hydrogels for controlled cell adhesion and delivery of geometrically defined microtissues, Acta Biomater., 2017, 61, 75–87.
Y. H. Su, P. C. Chianga, L. J. Cheng, C. H. Lee, N. S. Swami and C. F. Chou, High aspect ratio nanoimprinted grooves of poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) control the length and direction of retraction fibers during fibroblast cell division, Biointerphases, 2015, 10, 1–8.
H. Hufnagel, A. Huebner, C. Gulch, K. Guse, C. Abell and F. Hollfelder, An integrated cell culture lab on a chip: modular microdevices for cultivation of mammalian cells and delivery into microfluidic microdroplets, Lab Chip, 2009, 9, 1576–1582.
S. M. Grist, L. Chrostowski and K. C. Cheung, Optical oxygen sensors for applications in microfluidic cell culture, Sensors, 2010, 10, 9286–9316.
S. Kobel, A. Valero, J. Latt, P. Renaud and M. Lutolf, Optimization of microfluidic single cell trapping for longterm on-chip culture, Lab Chip, 2010, 10, 857–863.
D. Di Carlo, L. Y. Wu and L. P. Lee, Dynamic single cell culture array, Lab Chip, 2006, 6, 1445–1449.
W. Chen, N. T. Huang, B. Oh, R. H. Lam, R. Fan, T. T. Cornell, T. P. Shanley, K. Kurabayashi and J. Fu, Surface-micromachined microfiltration membranes for efficient isolation and functional immunophenotyping of subpopulations of immune cells, Adv. Healthcare Mater., 2013, 2, 965–975.
J. Kim, D. Taylor, N. Agrawal, H. Wang, H. Kim, A. Han, K. Rege and A. Jayaraman, A programmable microfluidic cell array for combinatorial drug screening, Lab Chip, 2012, 12, 1813–1822.
C. H. Lin, Y. H. Hsiao, H. C. Chang, C. F. Yeh, C. K. He, E. M. Salm, C. Chen, I. M. Chiu and C. H. Hsu, A microfluidic dual-well device for high-throughput single-cell capture and culture, Lab Chip, 2015, 15, 2928–2938.
F. Shen, X. Li and P. C. Li, Study of flow behaviors on single-cell manipulation and shear stress reduction in microfluidic chips using computational fluid dynamics simulations, Biomicrofluidics, 2014, 8, 014109.
V. Biju, Chemical modifications and bioconjugate reactions of nanomaterials for sensing, imaging, drug delivery and therapy, Chem. Soc. Rev., 2014, 43, 744–764.
J. Shi, Z. Chen, L. Wang, B. Wang, L. Xu, L. Hou and Z. Zhang, A tumor-specific cleavable nanosystem of PEG-modified C60@Au hybrid aggregates for radio frequency-controlled release, hyperthermia, photodynamic therapy and X-ray imaging, Acta Biomater., 2015, 29, 282–297.
S. F. Lai, B. H. Ko, C. C. Chien, C. J. Chang, S. M. Yang, H. H. Chen, C. Petibois, D. Y. Hueng, S. M. Ka, A. Chen, G. Margaritondo and Y. Hwu, Gold nanoparticles as multimodality imaging agents for brain gliomas, J. Nanobiotechnol., 2015, 13, 85.
M. Xuan, J. Shao, L. Dai, J. Li and Q. He, Macrophage cell membrane camouflaged au nanoshells for in vivo prolonged circulation life and enhanced cancer photothermal therapy, ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2016, 8, 9610–9618.
P. Zhang, J. Wang, H. Huang, B. Yu, K. Qiu, J. Huang, S. Wang, L. Jiang, G. Gasser, L. Ji and H. Chao, Unexpected high photothemal conversion efficiency of gold nanospheres upon grafting with two-photon luminescent ruthe-nium(II) complexes: A way towards cancer therapy?, Biomaterials, 2015, 63, 102–114.
K. Jadhav, R. Hr, S. Deshpande, S. Jagwani, D. Dhamecha, S. Jalalpure, K. Subburayan and D. Baheti, Phytosynthesis of gold nanoparticles: Characterization, biocompatibility, and evaluation of its osteoinductive potential for application in implant dentistry, Mater. Sci. Eng., C, 2018, 93, 664–670.
C. Yi, D. Liu, C. C. Fong, J. Zhang and M. Yang, Gold nanoparticles promote osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells through p38 MAPK pathway, ACS Nano, 2010, 4, 6439–6448.
C. C. Medalha, A. L. Santos, O. Veronez Sde, K. R. Fernandes, A. M. Magri and A. C. Renno, Low level laser therapy accelerates bone healing in spinal cord injured rats, J. Photochem. Photobiol., B, 2016, 159, 179–185.
M. Xavier, D. R. David, R. A. de Souza, A. N. Arrieiro, H. Miranda, E. T. Santana, J. A. Silva Jr., M. A. Salgado, F. Aimbire and R. Albertini, Anti-inflammatory effects of low-level light emitting diode therapy on Achilles tendinitis in rats, Lasers Surg. Med., 2010, 42, 553–558.
R. Medina-Huertas, F. J. Manzano-Moreno, E. De Luna-Bertos, J. Ramos-Torrecillas, O. Garcia-Martinez and C. Ruiz, The effects of low-level diode laser irradiation on differentiation, antigenic profile, and phagocytic capacity of osteoblast-like cells (MG-63), Lasers Med. Sci., 2014, 29, 1479–1484.
L. R. Rau, W. Y. Huang, J. W. Liaw and S. W. Tsai, Photothermal effects of laser-activated surface plasmonic gold nanoparticles on the apoptosis and osteogenesis of osteoblast-like cells, Int. J. Nanomed., 2016, 11, 3461–3473.
E. Zeinizade, M. Tabei, A. Shakeri-Zadeh, H. Ghaznavi, N. Attaran, A. Komeili, B. Ghalandari, S. Maleki and S. K. Kamrava, Selective apoptosis induction in cancer cells using folate-conjugated gold nanoparticles and controlling the laser irradiation conditions, Artif. Cells, Nanomed., Biotechnol., 2018, 46, 1026–1038.
K. Yue, J. Nan, X. Zhang, J. Tang and X. Zhang, Photothermal effects of gold nanoparticles induced by light emitting diodes, Appl. Therm. Eng., 2016, 99, 1093–1100.
Y. Liu, M. Xu, Q. Chen, G. Guan, W. Hu, X. Zhao, M. Qiao, H. Hu, Y. Liang, H. Zhu and D. Chen, Gold nanorods/meso-porous silica-based nanocomposite as theranostic agents for targeting near-infrared imaging and photothermal therapy induced with laser, Int. J. Nanomed., 2015, 10, 4747–4761.
B. Nikoobakht and M. A. El-Sayed, Preparation and growth mechanism of gold nanorods (nrs) using seed-mediated growth method, Chem. Mater., 2003, 15, 1957–1962.
Q. Sun, X. Shi, J. Feng, Q. Zhang, Z. Ao, Y. Ji, X. Wu, D. Liu and D. Han, Cytotoxicity and cellular responses of gold nanorods to smooth muscle cells dependent on surface chemistry coupled action, Small, 2018, 14, e1803715.
G. N. Abdelrasoul, M. Scotto, R. Cingolani, A. Diaspro, A. Athanassiou and F. Pignatelli, Effect of precursor solution dark incubation on gold nanorods morphology, J. Cryst. Growth, 2012, 361, 159–165.
A. J. Zollinger, H. Xu, J. Figueiredo, J. Paredes, R. Seruca, D. Stamenovic and M. L. Smith, Dependence of tensional homeostasis on cell type and on cell-cell interactions, Cell. Mol. Bioeng., 2018, 11, 175–184.
M. Wesseling, T. R. Sakkers, S. C. A. de Jager, G. Pasterkamp and M. J. Goumans, The morphological and molecular mechanisms of epithelial/endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition and its involvement in atherosclerosis, Vasc. Pharmacol., 2018, 106, 1–8.
M. Natoli, B. D. Leoni, I. D'Agnano, M. D'Onofrio, R. Brandi, I. Arisi, F. Zucco and A. Felsani, Cell growing density affects the structural and functional properties of Caco-2 differentiated monolayer, J. Cell. Physiol., 2011, 226, 1531–1543.
S. W. Tsai, J. W. Liaw, Y. C. Kao, M. Y. Huang, C. Y. Lee, L. R. Rau, C. Y. Huang, K. C. Wei and T. C. Ye, Internalized gold nanoparticles do not affect the osteogenesis and apoptosis of mg63 osteoblast-like cells: a quantitative, in vitro study, PLoS One, 2013, 8, e76545.
L. R. Rau, S. W. Tsao, J. W. Liaw and S. W. Tsai, Selective targeting and restrictive damage for nonspecific cells by pulsed laser-activated hyaluronan-gold nanoparticles, Biomacromolecules, 2016, 17, 2514–2521.
C. S. Rejiya, J. Kumar, V. Raji, M. Vibin and A. Abraham, Laser immunotherapy with gold nanorods causes selective killing of tumour cells, Pharmacol. Res., 2012, 65, 261–269.
M. J. Akhtar, M. Ahamed, H. A. Alhadlaq and A. Alshamsan, Mechanism of ROS scavenging and antioxidant signalling by redox metallic and fullerene nanomaterials: Potential implications in ROS associated degenerative disorders, Biochim. Biophys. Acta, Gen. Subj., 2017, 1861, 802–813.
J. Balke, P. Volz, F. Neumann, R. Brodwolf, A. Wolf, H. Pischon, M. Radbruch, L. Mundhenk, A. D. Gruber, N. Ma and U. Alexiev, Visualizing oxidative cellular stress induced by nanoparticles in the subcytotoxic range using fluorescence lifetime imaging, Small, 2018, 14, e1800310.
Y. Son, Y. K. Cheong, N. H. Kim, H. T. Chung, D. G. Kang and H. O. Pae, Mitogen-activated protein kinases and reactive oxygen species: how can ros activate mapk pathways?, J. Signal Transduction, 2011, 2011, 792639.
L. Luo, Z. Sun, L. Zhang, X. Li, Y. Dong and T. C. Y. Liu, Effects of low-level laser therapy on ROS homeostasis and expression of IGF-1 and TGF-ß1 in skeletal muscle during the repair process, Lasers Med. Sci., 2013, 28, 725–734.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, YC., Lei, K.F., Liaw, JW. et al. The influence of laser intensity activated plasmonic gold nanoparticle-generated photothermal effects on cellular morphology and viability: a real-time, long-term tracking and monitoring system. Photochem Photobiol Sci 18, 1419–1429 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1039/c9pp00054b
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/c9pp00054b